
Ealdred was Abbot of Tavistock, Bishop of Worcester, and Archbishop of York in early medieval England. He was related to a number of other ecclesiastics of the period. After becoming a monk at the monastery at Winchester, he was appointed Abbot of Tavistock Abbey in around 1027. In 1046 he was named to the Bishopric of Worcester. Ealdred, besides his episcopal duties, served Edward the Confessor, the King of England, as a diplomat and as a military leader. He worked to bring one of the king's relatives, Edward the Exile, back to England from Hungary to secure an heir for the childless king.

William I, usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 1087. A descendant of Rollo, he was Duke of Normandy from 1035 onward. By 1060, following a long struggle to establish his throne, his hold on Normandy was secure. In 1066, following the death of Edward the Confessor, William invaded England, leading an army of Normans to victory over the Anglo-Saxon forces of Harold Godwinson at the Battle of Hastings, and suppressed subsequent English revolts in what has become known as the Norman Conquest. The rest of his life was marked by struggles to consolidate his hold over England and his continental lands, and by difficulties with his eldest son, Robert Curthose.

William II was King of England from 26 September 1087 until his death in 1100, with powers over Normandy and influence in Scotland. He was less successful in extending control into Wales. The third son of William the Conqueror, he is commonly referred to as William Rufus, perhaps because of his ruddy appearance or, more likely, due to having red hair as a child that grew out in later life.

The Battle of Hastings was fought on 14 October 1066 between the Norman-French army of William, the Duke of Normandy, and an English army under the Anglo-Saxon King Harold Godwinson, beginning the Norman Conquest of England. It took place approximately 7 mi (11 km) northwest of Hastings, close to the present-day town of Battle, East Sussex, and was a decisive Norman victory.
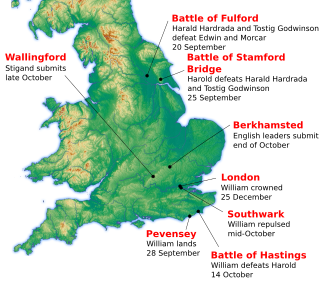
The Norman Conquest was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqueror.

Matilda of Flanders was Queen of England and Duchess of Normandy by marriage to William the Conqueror, and regent of Normandy during his absences from the duchy. She was the mother of ten children who survived to adulthood, including two kings, William II and Henry I.
Robert of Jumièges was the first Norman Archbishop of Canterbury. He had previously served as prior of the Abbey of St Ouen at Rouen in Normandy, before becoming abbot of Jumièges Abbey, near Rouen, in 1037. He was a good friend and adviser to the king of England, Edward the Confessor, who appointed him bishop of London in 1044, and then archbishop in 1051. Robert's time as archbishop lasted only about eighteen months. He had already come into conflict with the powerful Earl Godwin and, while archbishop, made attempts to recover lands lost to Godwin and his family. He also refused to consecrate Spearhafoc, Edward's choice to succeed Robert as Bishop of London. The rift between Robert and Godwin culminated in Robert's deposition and exile in 1052.

The Anglo-Normans were the medieval ruling class in England, composed mainly of a combination of francized ethnic Anglo-Saxons, Normans, Northern French, Flemings and Bretons, following the Norman conquest. A small number of Normans had earlier befriended future Anglo-Saxon king of England, Edward the Confessor, during his exile in his mother's homeland of Normandy in northern France. When he returned to England some of them went with him, and so there were Normans already settled in England prior to the conquest. Edward's successor, Harold Godwinson, was defeated by Duke William the Conqueror of Normandy at the Battle of Hastings, leading to William's accession to the English throne.

The Kingdom of England existed on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it unified from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
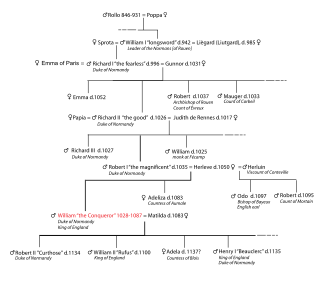
In the Middle Ages, the duke of Normandy was the ruler of the Duchy of Normandy in north-western France. The duchy arose out of a grant of land to the Viking leader Rollo by the French king Charles the Simple in 911. In 924 and again in 933, Normandy was expanded by royal grant. Rollo's male-line descendants continued to rule it until 1135. In 1202 the French king Philip II declared Normandy a forfeited fief and by 1204 his army had conquered it. It remained a French royal province thereafter, still called the Duchy of Normandy, but only occasionally granted to a duke of the royal house as an apanage.
Maud, Countess of Huntingdon, or Matilda, was Queen of Scotland as the wife of King David I. She was the great-niece of William the Conqueror and the granddaughter of Earl Siward.

From the 12th century onwards, a group of Normans invaded and then settled in Gaelic Ireland. These settlers later became known as Norman Irish or Hiberno-Normans. They originated mainly among Cambro-Norman families in Wales, and to a lesser extent, Anglo-Normans from England. During the High Middle Ages and Late Middle Ages the Hiberno-Normans constituted a feudal aristocracy and merchant oligarchy, known as the Lordship of Ireland. In Ireland, the Normans were also closely associated with the Gregorian Reform of the Catholic Church in Ireland. Over time the descendants of the 12th-century Norman settlers spread throughout Ireland and around the world, as part of the Irish diaspora; they ceased, in most cases, to identify as Norman, Cambro-Norman or Anglo-Norman.

The House of Clare was a prominent Anglo-Norman noble house that held at various times the earldoms of Pembroke, Hertford and Gloucester in England and Wales, as well as playing a prominent role in the Norman invasion of Ireland.

The Arden family is an English gentry family that can be traced back in the male line back to Anglo-Saxon landholders who managed to maintain status after the 1066 invasion of England by the Normans of France. The family takes its name from the Forest of Arden in Warwickshire.

In the history of England, the High Middle Ages spanned the period from the Norman Conquest in 1066 to the death of King John, considered by some historians to be the last Angevin king of England, in 1216. A disputed succession and victory at the Battle of Hastings led to the conquest of England by William of Normandy in 1066. This linked the Kingdom of England with Norman possessions in the Kingdom of France and brought a new aristocracy to the country that dominated landholding, government and the church. They brought with them the French language and maintained their rule through a system of castles and the introduction of a feudal system of landholding. By the time of William's death in 1087, England formed the largest part of an Anglo-Norman empire, ruled by nobles with landholdings across England, Normandy and Wales. William's sons disputed succession to his lands, with William II emerging as ruler of England and much of Normandy. On his death in 1100 his younger brother claimed the throne as Henry I and defeated his brother Robert to reunite England and Normandy. Henry was a ruthless yet effective king, but after the death of his only male heir William Adelin, he persuaded his barons to recognise his daughter Matilda as heir. When Henry died in 1135 her cousin Stephen of Blois had himself proclaimed king, leading to a civil war known as The Anarchy. Eventually Stephen recognised Matilda's son Henry as his heir and when Stephen died in 1154, he succeeded as Henry II.

The House of Blois is a lineage derived from the Frankish nobility, whose principal members were often named Theobald.
Fitz was a patronymic indicator used in Anglo-Norman England to help distinguish individuals by identifying their immediate predecessors. Meaning "son of", it would precede the father's forename, or less commonly a title held by the father. In rare cases it formed part of a matronymic to associate the bearer with a more prominent mother. Convention among modern historians is to represent the word as fitz, but in the original Norman French documentation it appears as fiz, filz, or similar forms, deriving from the Old French noun filz, fiz, meaning "son of", and ultimately from Latin filius (son). Its use during the period of English surname adoption led to its incorporation into patronymic surnames, and at later periods this form was adopted by English kings for the surnames given some of their recognized illegitimate children, and by Irish families when anglicizing their Gaelic patronymic surnames.

The Normans were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. The term is also used to denote emigrants from the duchy who conquered other territories such as England and Sicily. The Norse settlements in West Francia followed a series of raids on the French northern coast mainly from Denmark, although some also sailed from Norway and Sweden. These settlements were finally legitimized when Rollo, a Scandinavian Viking leader, agreed to swear fealty to King Charles III of West Francia following the siege of Chartres in 911. The intermingling in Normandy produced an ethnic and cultural "Norman" identity in the first half of the 10th century, an identity which continued to evolve over the centuries.

Brian of Brittany was a Breton nobleman who fought in the service of William I of England. A powerful magnate in south-western England, he was the first post-Conquest earl of Cornwall.















