Related Research Articles

Rigging comprises the system of ropes, cables and chains, which support a sailing ship or sail boat's masts—standing rigging, including shrouds and stays—and which adjust the position of the vessel's sails and spars to which they are attached—the running rigging, including halyards, braces, sheets and vangs.

A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships carry square sails on each mast—the brig and full-rigged ship, said to be "ship-rigged" when there are three or more masts. Others carry only fore-and-aft sails on each mast, for instance some schooners. Still others employ a combination of square and fore-and-aft sails, including the barque, barquentine, and brigantine.

A jibe (US) or gybe (Britain) is a sailing maneuver whereby a sailing vessel reaching downwind turns its stern through the wind, which then exerts its force from the opposite side of the vessel. Because the mainsail boom can swing across the cockpit quickly, jibes are potentially dangerous to person and rigging compared to tacking. Therefore accidental jibes are to be avoided while the proper technique must be applied so as to control the maneuver. For square-rigged ships, this maneuver is called wearing ship.

Running rigging is the rigging of a sailing vessel that is used for raising, lowering, shaping and controlling the sails on a sailing vessel—as opposed to the standing rigging, which supports the mast and bowsprit. Running rigging varies between vessels that are rigged fore and aft and those that are square-rigged.

A yard is a spar on a mast from which sails are set. It may be constructed of timber or steel or from more modern materials such as aluminium or carbon fibre. Although some types of fore and aft rigs have yards, the term is usually used to describe the horizontal spars used on square rigged sails. In addition, for some decades after square sails were generally dispensed with, some yards were retained for deploying wireless (radio) aerials and signal flags.
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water. Some remain current, while many date from the 17th to 19th centuries. The word nautical derives from the Latin nauticus, from Greek nautikos, from nautēs: "sailor", from naus: "ship".

A Bermuda rig, Bermudian rig, or Marconi rig is a configuration of mast and rigging for a type of sailboat and is the typical configuration for most modern sailboats. This configuration was developed in Bermuda in the 1600s; the term Marconi, a reference to the inventor of the radio, Guglielmo Marconi, became associated with this configuration in the early 1900s because the wires that stabilize the mast of a Bermuda rig reminded observers of the wires on early radio masts.

A full-rigged ship or fully rigged ship is a sailing vessel with a sail plan of three or more masts, all of them square-rigged. Such a vessel is said to have a ship rig or be ship-rigged, with each mast stepped in three segments: lower, top, and topgallant.
Rigging may refer to:

A derrick is a lifting device composed at minimum of one guyed mast, as in a gin pole, which may be articulated over a load by adjusting its guys. Most derricks have at least two components, either a guyed mast or self-supporting tower, and a boom hinged at its base to provide articulation, as in a stiffleg derrick. The most basic type of derrick is controlled by three or four lines connected to the top of the mast, which allow it both to move laterally and cant up and down. To lift a load, a separate line runs up and over the mast with a hook on its free end, as with a crane.
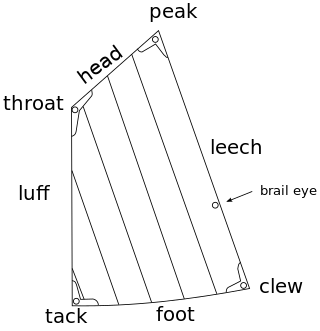
The spritsail is a four-sided, fore-and-aft sail that is supported at its highest points by the mast and a diagonally running spar known as the sprit. The foot of the sail can be stretched by a boom or held loose-footed just by its sheets. A spritsail has four corners: the throat, peak, clew, and tack. The Spritsail can also be used to describe a rig that uses a spritsail.

A fly system, or theatrical rigging system, is a system of ropes, blocks (pulleys), counterweights and related devices within a theater that enables a stage crew to fly (hoist) quickly, quietly and safely components such as curtains, lights, scenery, stage effects and, sometimes, people. Systems are typically designed to fly components between clear view of the audience and out of view, into the large opening, known as the fly loft, above the stage.

A brace on a square-rigged ship is a rope (line) used to rotate a yard around the mast, to allow the ship to sail at different angles to the wind. Braces are always used in pairs, one at each end of a yard (yardarm), termed port brace and starboard brace of a given yard or sail.

A rigger or slinger is a skilled tradesperson who specializes in the assistance of manual mechanical advantage device comprising pulley, block and tackle or motorised such as a crane or derrick or chain hoists or capstan winch.

The junk rig, also known as the Chinese lugsail, Chinese balanced lug sail, or sampan rig, is a type of sail rig in which rigid members, called battens, span the full width of the sail and extend the sail forward of the mast.
A theatrical technician, also known as a theatrical tech, theatre technician, or theatre tech is a person who operates technical equipment and systems in the performing arts and entertainment industry. In contrast to performers, this broad category contains all "unseen" theatrical personnel who practice stagecraft and are responsible for the logistic and production-related aspects of a performance including designers, operators, and supervisors.
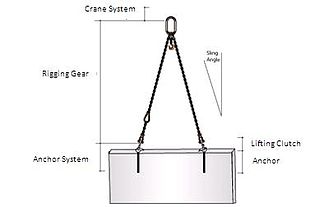
Rigging is both a noun, the equipment, and verb, the action of designing and installing the equipment, in the preparation to move objects. A team of riggers design and install the lifting or rolling equipment needed to raise, roll, slide or lift objects such as with a crane, hoist or block and tackle.

Dismasting, also spelled demasting, occurs to a sailing ship when one or more of the masts responsible for hoisting the sails that propel the vessel breaks. Dismasting usually occurs as the result of high winds during a storm acting upon masts, sails, rigging, and spars. Over compression of the mast owing to tightening the rigger too much and g-forces as a consequence of wave action and the boat swinging back and forth can also be result in a dismasting. Dismasting does not necessarily impair the vessel's ability to stay afloat, but rather its ability to move under sail power. Frequently, the hull of the vessel remains intact, upright and seaworthy.

A bolt rope, is the rope that is sewn at the edges of the sail to reinforce them, or to fix the sail into a groove in the boom or in the mast.
This glossary of nautical terms is an alphabetical listing of terms and expressions connected with ships, shipping, seamanship and navigation on water. Some remain current, while many date from the 17th to 19th centuries. The word nautical derives from the Latin nauticus, from Greek nautikos, from nautēs: "sailor", from naus: "ship".
References
- ↑ cgarena.com, Interview with Jeremie Passerin - Rigging Supervisor at Blur Studio
- ↑ animationmentor.com Why a Great Rigger is an Animator’s Best Friend, By: Ozgur Aydogdu
- ↑ Uva's Rigging Guide for Studio and Location, By Michael Uva, Sabrina Uva
- ↑ nmfilm.com, Glossary of Industry Job Positions
- ↑ hollywoodstuntcoordinator.com, Wire riggers