Related Research Articles

Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have varied therapeutic uses. It is possible to create a mAb that binds specifically to almost any extracellular target, such as cell surface proteins and cytokines. They can be used to render their target ineffective, to induce a specific cell signal, to cause the immune system to attack specific cells, or to bring a drug to a specific cell type.
Catumaxomab is a rat-mouse hybrid monoclonal antibody which is used to treat malignant ascites, a condition occurring in people with metastasizing cancer. It binds to antigens CD3 and EpCAM. It was developed by Fresenius Biotech and Trion Pharma (Germany).
Tanox was a biopharmaceutical company based in Houston, Texas. The company was founded by two biomedical research scientists, Nancy T. Chang and Tse Wen Chang in March 1986 with $250,000, which was a large part of their family savings at that time. Both Changs grew up and received college education in chemistry in National Tsing Hua University in Taiwan and obtained Ph.D. degrees from Harvard University. For postdoctoral training, Tse Wen shifted to immunology and did research with Herman N. Eisen at the Center for Cancer Research, M.I.T. The two Changs successively became research managers and worked with a range of monoclonal antibody projects in Centocor, Inc. based in Malvern, Pennsylvania, from 1981 to 1985. The Changs were recruited by Baylor College of Medicine toward the end of 1985 and offered faculty positions in the Division of Molecular Virology. Soon after their arrival, they were encouraged by a high-ranking Baylor official and local business leaders to start a biotech venture in Houston. This was in a period of time when the economy of Houston was in slump as the result of the collapse of the oil industry.
A bispecific monoclonal antibody is an artificial protein that can simultaneously bind to two different types of antigen or two different epitopes on the same antigen. Naturally occurring antibodies typically only target one antigen. BsAbs can be manufactured in several structural formats. BsAbs can be designed to recruit and activate immune cells, to interfere with receptor signaling and inactivate signaling ligands, and to force association of protein complexes. BsAbs have been explored for cancer immunotherapy, drug delivery, and Alzheimer's disease.
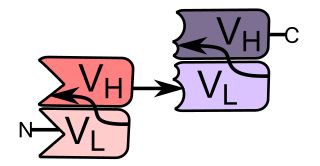
Bi-specific T-cell engagers (BiTEs) are a class of artificial bispecific monoclonal antibodies that are investigated for use as anti-cancer drugs. They direct a host's immune system, more specifically the T cells' cytotoxic activity, against cancer cells. BiTE is a registered trademark of Micromet AG.
Tanezumab is a monoclonal antibody against nerve growth factor as a treatment for pain via a novel mechanisms different from conventional pain-killer drugs. Tanezumab was discovered and developed by Rinat Neuroscience and was acquired by Pfizer in 2006.
MorphoSys AG is a German biopharmaceutical company founded in 1992. The company is headquartered near Munich, Germany, and has a wholly owned subsidiary, MorphoSys US Inc., in Boston, Massachusetts, in the US. The company has various antibody, protein and peptide technologies that it uses to discover and develop both proprietary and partnered drug candidates. The company has more than 100 drugs in its wider pipeline that are being investigated for a variety of diseases. While many of these are being developed in partnership with pharma and biotech companies, MorphoSys also has a proprietary pipeline with a focus on cancer and autoimmune diseases.
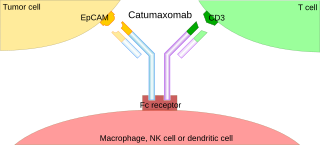
A trifunctional antibody is a monoclonal antibody with binding sites for two different antigens, typically CD3 and a tumor antigen, making it a type of bispecific monoclonal antibody. In addition, its intact Fc-part can bind to an Fc receptor on accessory cells like conventional monospecific antibodies. The net effect is that this type of drug links T cells and monocytes/macrophages, natural killer cells, dendritic cells or other Fc receptor expressing cells to the tumor cells, leading to their destruction.
Crenezumab is a fully humanized monoclonal antibody against human 1-40 and 1-42 beta amyloid, which is being investigated as a treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Crenezumab is highly homologous to solanezumab, another monoclonal antibody targeting amyloid-β peptides. In June 2022, the US National Institutes of Health announced that the drug failed as a medication for early-onset Alzheimer's disease following the results of a decade-long clinical trial.
Alirocumab, sold under the brand name Praluent, is a medication used as a second-line treatment for high cholesterol for adults whose cholesterol is not controlled by diet and statin treatment. It is a human monoclonal antibody that belongs to a novel class of anti-cholesterol drugs, known as PCSK9 inhibitors, and it was the first such agent to receive FDA approval. The FDA approval was contingent on the completion of further clinical trials to better determine efficacy and safety.
Lampalizumab (INN) is an antigen-binding fragment of a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to complement factor D; it was developed as a potential treatment of geographic atrophy secondary to age-related macular degeneration.
Seagen Inc. is an American biotechnology company focused on developing and commercializing innovative, empowered monoclonal antibody-based therapies for the treatment of cancer. The company, headquartered in Bothell, Washington, is the industry leader in antibody-drug conjugates or ADCs, a technology designed to harness the targeting ability of monoclonal antibodies to deliver cell-killing agents directly to cancer cells. Antibody-drug conjugates are intended to spare non-targeted cells and thus reduce many of the toxic effects of traditional chemotherapy, while potentially enhancing antitumor activity.
Novimmune is a privately held Swiss pharmaceutical development company focusing on monoclonal antibody therapies for treatment of immune-related diseases. The company was founded in 1998.
Fremanezumab, sold under the brand name Ajovy, is a medication used to prevent migraines in adults. It is given by injection under the skin.

Arnon Rosenthal is an Israeli-American neuroscientist, inventor, and biotechnology entrepreneur.

Faricimab, sold under the brand name Vabysmo, is a monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of neovascular age-related macular degeneration (nAMD) and diabetic macular edema (DME). Faricimab is the first bispecific monoclonal antibody to target both vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and angiopoietin 2 (Ang-2). By targeting these pathways, faricimab stabilizes blood vessels in the retina. It is given by intravitreal injection by an ophthalmologist.
AbCellera Biologics Inc. is a Vancouver, British Columbia-based biotechnology firm that researches and develops human antibodies. The company is best known for its leading role in the Pandemic Prevention Platform, a project of DARPA's Biological Technologies Office. AbCellera utilizes a proprietary technology platform, which they claim can develop "medical countermeasures within 60 days." Its platform for single-cell screening was initially developed at the University of British Columbia.
Mosunetuzumab, sold under the brand name Lunsumio, is a monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of follicular lymphoma. It bispecifically binds CD20 and CD3 to engage T-cells. It was developed by Genentech.
Teclistamab, sold under the brand name Tecvayli, is a human bispecific monoclonal antibody used for the treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma. It is a bispecific antibody that targets the CD3 receptor expressed on the surface of T-cells and B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), which is expressed on the surface of malignant multiple myeloma B-lineage cells.
Elranatamab, sold under the brand name Elrexfio, is a medication used for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Elranatamab is a bispecific B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA)-directed CD3 T-cell engager. Elranatamab is administered subcutaneously.
References
- ↑ Vastag, Brian. "Monoclonals expand into neural disorders". Nature.
- ↑ Lane, Nancy E.; et al. (2010). "Tanezumab for the Treatment of Pain from Osteoarthritis of the Knee". New England Journal of Medicine. 363 (16). The New England Journal of Medicine: 1521–1531. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0901510. PMC 6896791 . PMID 20942668. S2CID 16950684.
- ↑ "Ponezumab". ALZForum.
- ↑ "Teva Completes Acquisition of Labrys: Opens Door to a Strong and Novel Migraine Prevention and Treatment Franchise within its CNS Portfolio". Business Wire/Nasdaq.
- ↑ Carroll, John. "In biotech trifecta, startup lassos $31M, a CEO and a lead drug from Pfizer". FierceBiotech.
- ↑ Leuty, Ron. "Migraine drug developer Labrys targeted by Teva in $825 million deal". San Francisco Business Times.
- ↑ Berkrot, Bill; Beasley, Deena. "Experimental Pfizer cholesterol drug promising in study". Reuters.
- ↑ "An Investigational Therapy for Geographic Atrophy in Age-Related Macular Degeneration".
- ↑ Gumbiner, Barry; Esteves, Brooke; Dell, Vanessa; Joh, Tenshang; Garzone, Pamela D.; Forgie, Alison; Udata, Chandrasekhar (2018). "Single and multiple ascending-dose study of glucagon-receptor antagonist RN909 in type 2 diabetes". Endocrine. 62 (2): 371–380. doi:10.1007/s12020-018-1597-1. PMID 30203123. S2CID 52184370.
- ↑ "REGN4018, a novel MUC16xCD3 bispecific T-cell engager for the treatment of ovarian cancer".
- ↑ "FIH study of an OX40 agonist mAb PF-04518600 in adult patients with select advanced solid tumors".
- ↑ "Arnon Rosenthal Ph.D. - Executive Profile". Bloomberg Businessweek. Archived from the original on October 26, 2014.
- ↑ Leuty, Ron. "Alector snags funding in founder's latest attack on Alzheimer's". San Francisco Business Times.
- ↑ "Patrick G. Lynn - Executive Profile". Bloomberg Businessweek. Archived from the original on October 26, 2014.
- ↑ "Genentech and Rinat Neuroscience Announce Co-Development and Joint Commercialization Agreement for Anti-NGF Antibody for Acute and Chronic Pain". Genentech.
- ↑ Pollack, Andrew. "Pfizer to Buy Rinat, a Biotechnology Drug Maker". New York Times.
- ↑ "Pfizer to Expand Neuroscience Research with Acquisition of Biotech Company Rinat Neuroscience disorders". Pfizer. Archived from the original on 2015-09-24.
- ↑ "Rinat". Pfizer. Archived from the original on 2014-09-01.