Related Research Articles

A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and may require a mordant to improve the fastness of the dye on the fiber.
Spinning is a twisting technique to form yarn from fibers. The fiber intended is drawn out, twisted, and wound onto a bobbin. A few popular fibers that are spun into yarn other than cotton, which is the most popular, are viscose, animal fibers such as wool, and synthetic polyester. Originally done by hand using a spindle whorl, starting in the 500s AD the spinning wheel became the predominant spinning tool across Asia and Europe. The spinning jenny and spinning mule, invented in the late 1700s, made mechanical spinning far more efficient than spinning by hand, and especially made cotton manufacturing one of the most important industries of the Industrial Revolution.

Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the only manufacturing method, and many other methods were later developed to form textile structures based on their intended use. Knitting and non-woven are other popular types of fabric manufacturing. In the contemporary world, textiles satisfy the material needs for versatile applications, from simple daily clothing to bulletproof jackets, spacesuits, and doctor's gowns.

Yarn is a long continuous length of interlocked fibres, used in sewing, crocheting, knitting, weaving, embroidery, ropemaking, and the production of textiles. Thread is a type of yarn intended for sewing by hand or machine. Modern manufactured sewing threads may be finished with wax or other lubricants to withstand the stresses involved in sewing. Embroidery threads are yarns specifically designed for needlework. Yarn can be made of a number of natural or synthetic materials, and comes in a variety of colors and thicknesses. Although yarn may be dyed different colours, most yarns are solid coloured with a uniform hue.

A mordant or dye fixative is a substance used to set dyes on fabrics. It does this by forming a coordination complex with the dye, which then attaches to the fabric. It may be used for dyeing fabrics or for intensifying stains in cell or tissue preparations. Although mordants are still used, especially by small batch dyers, they have been largely displaced in industry by directs.
Sulfur dyes are the most commonly used dyes manufactured for cotton in terms of volume. They are inexpensive, generally have good wash-fastness, and are easy to apply. Sulfur dyes are predominantly black, brown, and dark blue. Red sulfur dyes are unknown, although a pink or lighter scarlet color is available.

Dyeing is the application of dyes or pigments on textile materials such as fibers, yarns, and fabrics with the goal of achieving color with desired color fastness. Dyeing is normally done in a special solution containing dyes and particular chemical material. Dye molecules are fixed to the fiber by absorption, diffusion, or bonding with temperature and time being key controlling factors. The bond between the dye molecule and fiber may be strong or weak, depending on the dye used. Dyeing and printing are different applications; in printing, color is applied to a localized area with desired patterns. In dyeing, it is applied to the entire textile.

Acid-fastness is a physical property of certain bacterial and eukaryotic cells, as well as some sub-cellular structures, specifically their resistance to decolorization by acids during laboratory staining procedures. Once stained as part of a sample, these organisms can resist the acid and/or ethanol-based decolorization procedures common in many staining protocols, hence the name acid-fast.

An acid dye is a dye that is typically applied to a textile at low pH. They are mainly used to dye wool, not cotton fabrics. Some acid dyes are used as food colorants, and some can also be used to stain organelles in the medical field.

Textile manufacturing or textile engineering is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods such as clothing, household items, upholstery and various industrial products.

Tufting is a type of textile manufacturing in which a thread is inserted on a primary base. It is an ancient technique for making warm garments, especially mittens. After the knitting is done, short U-shaped loops of extra yarn are introduced through the fabric from the outside so that their ends point inwards.

Spinning is an ancient textile art in which plant, animal or synthetic fibres are drawn out and twisted together to form yarn. For thousands of years, fibre was spun by hand using simple tools, the spindle and distaff. After the introduction of the spinning wheel in the 13th century, the output of individual spinners increased dramatically. Mass production later arose in the 18th century with the beginnings of the Industrial Revolution. Hand-spinning remains a popular handicraft.

Open-end spinning is a technology for creating yarn without using a spindle. It was invented and developed in Czechoslovakia in Výzkumný ústav bavlnářský / Cotton Research Institute in Ústí nad Orlicí in 1963.
Heat setting is a term used in the textile industry to describe a thermal process usually taking place in either a steam atmosphere or a dry heat environment. The effect of the process gives fibers, yarns or fabric dimensional stability and, very often, other desirable attributes like higher volume, wrinkle resistance or temperature resistance. Very often, heat setting is also used to improve attributes for subsequent processes.
Ventile, is a registered trademark used to brand a special high-quality woven cotton fabric first developed by scientists at the Shirley Institute in Manchester, England. Originally created to overcome a shortage of flax used for fire hoses and water buckets, its properties were also useful for pilots' immersion suits, but expensive and leaky if exposed to sweat or oils.

In textile manufacturing, finishing refers to the processes that convert the woven or knitted cloth into a usable material and more specifically to any process performed after dyeing the yarn or fabric to improve the look, performance, or "hand" (feel) of the finish textile or clothing. The precise meaning depends on context.
Lightfastness is a property of a colourant such as dye or pigment that describes its resistance to fading when exposed to light. Dyes and pigments are used for example for dyeing of fabrics, plastics or other materials and manufacturing paints or printing inks.
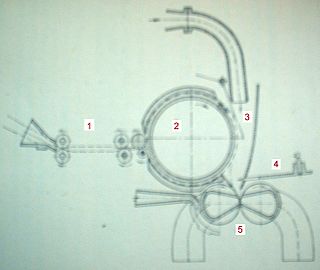
Friction spinning or DREF spinning is a textile technology that is suitable for spinning coarse counts of yarns and technical core-wrapped yarns. DREF yarns are bulky with low tensile strength, making them suitable for blankets and mop yarns. They can be spun from asbestos, carbon fibres and are capable of being made into filters for water systems. Yarns such as Rayon and Kevlar can be spun using this method. The technology was developed around 1975 by Dr. Ernst Fehrer.
Colour fastness is a term—used in the dyeing of textile materials—that characterizes a material's colour's resistance to fading or running. Colour fastness is the property of dyes and it is directly proportional to the binding force between photochromic dye and the fibre. The colour fastness may also be affected by processing techniques and choice of chemicals and auxiliaries.
Wet Processing Engineering is one of the major streams in Textile Engineering or Textile manufacturing which refers to the engineering of textile chemical processes and associated applied science. The other three streams in textile engineering are yarn engineering, fabric engineering, and apparel engineering. The processes of this stream are involved or carried out in an aqueous stage. Hence, it is called a wet process which usually covers pre-treatment, dyeing, printing, and finishing.
References
- ↑ Aspland, J. Richard (1997). Textile Dyeing and Coloration. AATCC. p. 17. ISBN 978-0-9613350-1-4.
