
The Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, often shortened to Rio Grande, D&RG or D&RGW, formerly the Denver & Rio Grande Railroad, was an American Class I railroad company. The railroad started as a 3 ft narrow-gauge line running south from Denver, Colorado, in 1870. It served mainly as a transcontinental bridge line between Denver and Salt Lake City, Utah. The Rio Grande was also a major origin of coal and mineral traffic.

The Southern Pacific was an American Class I railroad network that existed from 1865 to 1996 and operated largely in the Western United States. The system was operated by various companies under the names Southern Pacific Railroad, Southern Pacific Company and Southern Pacific Transportation Company.

The Association of American Railroads (AAR) is an industry trade group representing primarily the major freight railroads of North America. Amtrak and some regional commuter railroads are also members. Smaller freight railroads are typically represented by the American Short Line and Regional Railroad Association (ASLRRA), although some smaller railroads and railroad holding companies are also members of the AAR. The AAR also has two associate programs, and most associates are suppliers to the railroad industry.
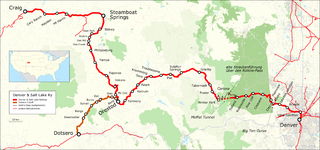
The Denver and Salt Lake Railway (D&SL) was a U.S. railroad company located in Colorado. It was incorporated in 1902 as the Denver, Northwestern and Pacific (DN&P) Railway with the goal of connecting Denver, Colorado with Salt Lake City, Utah. It underwent numerous reorganizations throughout its financially troubled history and, by the time it was acquired in 1931 by the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad, it had advanced only as far west as Craig, Colorado. After its acquisition, it was connected to the D&RGW main to give the D&RGW a more direct route to Denver via the eastern half of the DS&L. The portions of the D&SL still in use today comprise the Moffat Tunnel Subdivision of Union Pacific Railroad's Central Corridor, and Amtrak’s California Zephyr uses a portion of the former D&SL between Denver and Bond.

Union Pacific Corporation is a publicly traded railroad holding company. It is incorporated in Utah in 1969 and is headquartered in Omaha, Nebraska. Its only operating subsidiary is Union Pacific Railroad. Along with BNSF Railway, owned by Berkshire Hathaway, the companies have a near-duopoly on freight railroad transportation west of the Mississippi River.

The Chicago and North Western was a Class I railroad in the Midwestern United States. It was also known as the "North Western". The railroad operated more than 5,000 miles (8,000 km) of track at the turn of the 20th century, and over 12,000 miles (19,000 km) of track in seven states before retrenchment in the late 1970s. Until 1972, when the employees purchased the company, it was named the Chicago and North Western Railway.

The Western Pacific Railroad was a Class I railroad in the United States. It was formed in 1903 as an attempt to break the near-monopoly the Southern Pacific Railroad had on rail service into northern California. WP's Feather River Route directly competed with SP's portion of the Overland Route for rail traffic between Salt Lake City/Ogden, Utah, and Oakland, California, for nearly 80 years. The Western Pacific was one of the original operators of the California Zephyr passenger line.

The Colorado Pacific Rio Grande Railroad is a class III railroad operating in south-central Colorado. It runs on 154 miles (248 km) of former Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad tracks on three lines radiating from Alamosa and interchanges with the Union Pacific Railroad in Walsenburg. Much of the railroad is located in the San Luis Valley. In 2022, it was purchased by Stefan Soloviev.

Thistle is a ghost town in Spanish Fork Canyon in southeastern Utah County, Utah, United States. During the era of steam locomotives, the town's primary industry was servicing trains for the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad. The fortunes of the town were closely linked with those of the railroad until the changeover to diesel locomotives, when the town started to decline.

The Utah Division of the former Denver & Rio Grande Western Railroad (D&RGW) is a rail line that connects Grand Junction, Colorado and Salt Lake City, Utah in the Western United States. It is now incorporated into the Union Pacific Railroad (UP) system as part of the Central Corridor. The modern Union Pacific has split the line into two subdivisions for operational purposes, the Green River Subdivision between Grand Junction and Helper, Utah and the Provo Subdivision from Helper to Salt Lake City. Daily passenger service is provided by Amtrak's California Zephyr; the BNSF Railway and Utah Railway have trackage rights over the line.
The Kennecott Utah Copper rail line was an electric railroad in Salt Lake County, Utah. It was managed by the Kennecott Utah Copper Corporation and connected the Bingham Canyon Mine with its smelter at Garfield. The rail line has been replaced by a system of conveyors and a 17-mile-long (27 km) slurry pipeline. Current rail operations by Kennecott Utah Copper LLC only occur in the area of the smelter, on a remnant of what was a vast rail network.
The following is a brief history of the North American rail system, mainly through major changes to Class I railroads, the largest class by operating revenue.

Iowa Pacific Holdings was a holding company that owned railroad properties across North America and the United Kingdom, as well as providing services such as railcar repairs, leasing, management and consulting services to other operators. The company was founded in 2001 with headquarters in Chicago, Illinois.
Gale B. Aydelott, better known as "Gus Aydelott," was an American railroad president. He headed the Denver and Rio Grande Western Railroad for nearly three decades.
The history of the Southern Pacific ("SP") stretched from 1865 to 1998.










