
In Egyptian hieroglyphs, a cartouche is an oval with a line at one end tangent to the oval, indicating that the text enclosed is a royal name. The first examples of the cartouche are associated with pharaohs at the end of the Third Dynasty, but the feature did not come into common use until the beginning of the Fourth Dynasty under Pharaoh Sneferu. While the cartouche is usually vertical with a horizontal line, if it makes the name fit better it can be horizontal, with a vertical line at the end. The ancient Egyptian word for cartouche was shenu, and the cartouche was essentially an expanded shen ring. Demotic script reduced the cartouche to a pair of brackets and a vertical line.
Gardiner's Sign List is a list of common Egyptian hieroglyphs compiled by Sir Alan Gardiner. It is considered a standard reference in the study of ancient Egyptian hieroglyphs.
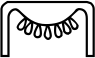
The Egyptian hieroglyph representing gold, phonetic value nb, is important due to its use in the Horus-of-Gold name, one of the Fivefold Titulary names of the Egyptian pharaoh.
The ancient Egyptian child hieroglyph is part of the Egyptian Gardiner's Sign List hieroglyphs for the beginning core subgroup of Man and his Occupations. It relates to the child, and childhood, and has a version for the Pharaoh, as a child.
The ancient Egyptian Egg hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. H8, is a portrayal of an oval-shaped egg, tilted at an angle, within the Gardiner signs for parts of birds.

The ancient Egyptian Adze on a Wood Block, or Axe in a Block of Wood hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. U20, is a portrayal of the adze. It is used mostly in the cartouches of pharaonic names especially, or other important names.

The ancient Egyptian Sky hieroglyph,, is Gardiner sign listed no. N1, within the Gardiner signs for sky, earth, and water.

The ancient Egyptian Townsite-city-region (hieroglyph) is Gardiner sign listed no. O49 for the intersection of a town's streets. In some Egyptian hieroglyphs books it is called a City Plan.
The ancient Egyptian Brazier hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. Q7 for the cooking brazier. It is shown from the Old Kingdom in the style of a vertical burning flame upon four feet, but the hieroglyph has the flame hiding the fourth foot. Another Gardiner unlisted form has the four feet, with no flame, and in a plan view.

The ancient Egyptian Sail hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. P5 for the sail of a ship. The hieroglyph shows a hoisted sail, curved because of wind filling it. It is used in Egyptian hieroglyphs as a determinative for words related to wind, air, breath, sailors,, floods-(of the Nile), etc. Also an ideogram in 'puff', 'wind', Egyptian (tsh)3w-(ṯau).

The use of the Spine with fluid hieroglyph is for words showing "length", as opposed to 'breadth',. Some example words for 'length' are: to be long, length, to extend, extended; and for to expand, to dilate, words like: joy, gladness, pleasure, delight.
The Ancient Egyptian Swallow hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. G36 for swallow birds. The Sparrow hieroglyph appears similar in size and shape, but it is used to represent small, or bad items.
The ancient Egyptian Grape arbor hieroglyph is Gardiner sign listed no. M43 in Gardiner's subcategory for trees and plants. The hieroglyph shows a horizontal vine with stylized bunches suspended below; each end is supported by the hieroglyph for a "prop", Gardiner no. O30,
The ancient Egyptian Face hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. D2 is a portrayal of the human face, frontal view.

The ancient Egyptian Night hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed nos. N3 is a portrayal of the sky with the 'was' scepter hanging from it; it is in the Gardiner subset for "sky, earth, and water".

The ancient Egyptian Leopard head hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. F9 is a portrayal of the head of a leopard; it is in the Gardiner subset for "parts of mammals".

In the Egyptian language, the single stair hieroglyph is used as a determinative.

The ancient Egyptian Water-jugs-in-stand hieroglyph, is Gardiner sign listed no. W17, W18, within the Gardiner signs for vessels of stone and earthenware.

The Three-Fox-Skins (hieroglyph) is Gardiner's sign listed no. F31, in the series of parts of animals. It consists of 3-fox skins tied at one end, and hanging, creating flowing skins.

The Land, irrigated hieroglyph represents "district, nome". It is a determinative in the name of provinces and regions in the noun ḥsp, for "garden", "vegetable garden", and "orchard".












