
1818 (MDCCCXVIII) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar, the 1818th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 818th year of the 2nd millennium, the 18th year of the 19th century, and the 9th year of the 1810s decade. As of the start of 1818, the Gregorian calendar was 12 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1923.

Jackson County is a county located in the U.S. state of Florida, on its northwestern border with Alabama. As of the 2020 census, the population was 47,319. Its county seat is Marianna.

St. Johns County is a county in the northeastern part of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 United States Census, its population was 273,425. The county seat and largest incorporated city is St. Augustine. St. Johns County is part of the Jacksonville metropolitan area.

The Seminole Wars were a series of three military conflicts between the United States and the Seminoles that took place in Florida between about 1816 and 1858. The Seminoles are a Native American nation which coalesced in northern Florida during the early 1700s, when the territory was still a Spanish colonial possession. Tensions grew between the Seminoles and settlers in the newly independent United States in the early 1800s, mainly because enslaved people regularly fled from Georgia into Spanish Florida, prompting slaveowners to conduct slave raids across the border. A series of cross-border skirmishes escalated into the First Seminole War in 1817, when General Andrew Jackson led an incursion into the territory over Spanish objections. Jackson's forces destroyed several Seminole and Black Seminole towns and briefly occupied Pensacola before withdrawing in 1818. The U.S. and Spain soon negotiated the transfer of the territory with the Adams-Onis Treaty of 1819.

West Florida was a region on the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico that underwent several boundary and sovereignty changes during its history. As its name suggests, it was formed out of the western part of former Spanish Florida, along with lands taken from French Louisiana; Pensacola became West Florida's capital. The colony included about two thirds of what is now the Florida Panhandle, as well as parts of the modern U.S. states of Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama.

East Florida was a colony of Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of Spanish Florida from 1783 to 1821. Great Britain gained control of the long-established Spanish colony of La Florida in 1763 as part of the treaty ending the French and Indian War. Deciding that the territory was too large to administer as a single unit, Britain divided Florida into two colonies separated by the Apalachicola River: East Florida with its capital in St. Augustine and West Florida with its capital in Pensacola. East Florida was much larger and comprised the bulk of the former Spanish territory of Florida and most of the current state of Florida. It had also been the most populated region of Spanish Florida, but before control was transferred to Britain, most residents – including virtually everyone in St. Augustine – left the territory, with most migrating to Cuba.
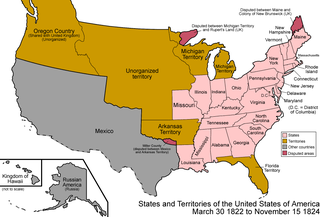
The Territory of Florida was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 30, 1822, until March 3, 1845, when it was admitted to the Union as the state of Florida. Originally the major portion of the Spanish territory of La Florida, and later the provinces of East and West Florida, it was ceded to the United States as part of the 1819 Adams–Onís Treaty. It was governed by the Florida Territorial Council.

John Williams was an American lawyer, soldier, and statesman, operating primarily out of Knoxville, Tennessee, in the first part of the 19th century. He represented Tennessee in the United States Senate from 1815 to 1823, when he lost reelection to Andrew Jackson. Williams also served as colonel of the 39th U.S. Infantry Regiment during the Creek Wars, and played a key role in Jackson's victory at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend in 1814.

William Orlando Butler was a U.S. political figure and U.S. Army major general from Kentucky. He served as a Democratic congressman from Kentucky from 1839 to 1843, and was the Democratic vice-presidential nominee under Lewis Cass in 1848.

William Pope Duval was the first civilian governor of the Florida Territory, succeeding Andrew Jackson, who had been a military governor. In his twelve-year governorship, from 1822 to 1834, he divided Florida into four territories, established the local court system, and chose Tallahassee as the territory's capital because of its central location. Duval County, where Jacksonville is located, Duval Street in Key West, and Duval Street in Tallahassee are named for him.

Alexander Outlaw Anderson was an American slave owner and attorney who represented Tennessee in the United States Senate, and later served in the California State Senate, and on the California Supreme Court.

The Plaza Ferdinand VII is an outdoor garden and park in the Historic Pensacola Village area of downtown Pensacola, Florida. It is located on Palafox Street between Government and Zaragoza Streets. It was named after Ferdinand VII of Spain, the King of Spain between 1813 and 1833. A National Historic Landmark, it is the site of the formal transfer of Florida to United States jurisdiction in 1821.

John McKee was an American politician active in the Southeastern United States. He served as agent to the Cherokees and Choctaws, and was the first Representative of Alabama's 2nd District from 1823 to 1829. He was also commissioned by President James Madison in 1811 to help wrest East and West Florida from Spanish control.
Events from the year 1818 in the United States.
José María Coppinger was a Spanish soldier who served in the infantry of the Royal Spanish Army (Ejército de Tierra) and governed East Florida (1816–1821) and several areas in Cuba including Pinar Del Río, Bayamo, the Cuatro Villas and Trinidad at various times between 1801 and 1834. He was also a member of the Royal and Military Order of Saint Ferdinand and San Hermenegildo.

This is a timeline of the U.S. state of Florida.

George J. F. Clarke was one of the most prominent and active men of East Florida during the Second Spanish Period. As a friend and trusted advisor of the Spanish governors of the province from 1811 to 1821, he was appointed to several public offices under the colonial regime, including that of surveyor general.
The Legislative Council of the Territory of Florida, often referred to as the Florida Territorial Council or Florida Territorial Legislative Council, was the legislative body governing the American territory of Florida before statehood. The territory of Florida was acquired by the U.S. in 1821 under the Adams–Onís Treaty. Replacing the form of martial law that had existed in the territory since Florida was acquired, the U.S. Congress in 1822 established a territorial government consisting of a governor, secretary, thirteen-member Legislative Council, and judiciary, all of whom were appointed by the U.S. president.
Enrique White was an Irish-born Spanish soldier who served as Governor of West Florida and of East Florida.














