
In immunology, autoimmunity is the system of immune responses of an organism against its own healthy cells, tissues and other normal body constituents. Any disease resulting from this type of immune response is termed an "autoimmune disease". Prominent examples include celiac disease, post-infectious IBS, diabetes mellitus type 1, Henoch–Schönlein purpura (HSP) sarcoidosis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), Sjögren syndrome, eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis, Hashimoto's thyroiditis, Graves' disease, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, Addison's disease, rheumatoid arthritis (RA), ankylosing spondylitis, polymyositis (PM), dermatomyositis (DM), and multiple sclerosis (MS). Autoimmune diseases are very often treated with steroids.
Rheumatology is a branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis and management of disorders whose common feature is inflammation in the bones, muscles, joints, and internal organs. Rheumatology covers more than 100 different complex diseases, collectively known as rheumatic diseases, which includes many forms of arthritis as well as lupus and Sjögren's syndrome. Doctors who have undergone formal training in rheumatology are called rheumatologists.

Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leukemia, lung cancer, lymphoma, gestational trophoblastic disease, and osteosarcoma. Types of autoimmune diseases it is used for include psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, and Crohn's disease. It can be given by mouth or by injection.
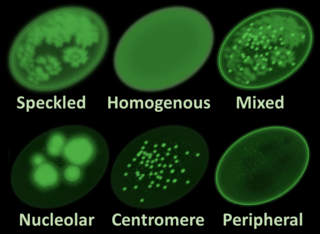
Antinuclear antibodies are autoantibodies that bind to contents of the cell nucleus. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies to foreign proteins (antigens) but not to human proteins (autoantigens). In some cases, antibodies to human antigens are produced.
A connective tissue disease (collagenosis) is any disease that has the connective tissues of the body as a target of pathology. Connective tissue is any type of biological tissue with an extensive extracellular matrix that supports, binds together, and protects organs. These tissues form a framework, or matrix, for the body, and are composed of two major structural protein molecules: collagen and elastin. There are many different types of collagen protein in each of the body's tissues. Elastin has the capability of stretching and returning to its original length—like a spring or rubber band. Elastin is the major component of ligaments and skin. In patients with connective tissue disease, it is common for collagen and elastin to become injured by inflammation (ICT). Many connective tissue diseases feature abnormal immune system activity with inflammation in tissues as a result of an immune system that is directed against one's own body tissues (autoimmunity).
Mixed connective tissue disease, commonly abbreviated as MCTD, is an autoimmune disease characterized by the presence of elevated blood levels of a specific autoantibody, now called anti-U1 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) together with a mix of symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), scleroderma, and polymyositis. The idea behind the "mixed" disease is that this specific autoantibody is also present in other autoimmune diseases such as systemic lupus erythematosus, polymyositis, scleroderma, etc. MCTD was characterized as an individual disease in 1972 by Sharp et al., and the term was introduced by Leroy in 1980.
Palindromic rheumatism (PR) is a syndrome characterised by recurrent, self-resolving inflammatory attacks in and around the joints, and consists of arthritis or periarticular soft tissue inflammation. The course is often acute onset, with sudden and rapidly developing attacks or flares. There is pain, redness, swelling, and disability of one or multiple joints. The interval between recurrent palindromic attacks and the length of an attack is extremely variable from few hours to days. Attacks may become more frequent with time but there is no joint damage after attacks. It is thought to be an autoimmune disease, possibly an abortive form of rheumatoid arthritis.

Belimumab, sold under the brand name Benlysta, is a human monoclonal antibody that inhibits B-cell activating factor (BAFF), also known as B-lymphocyte stimulator (BLyS). It is approved in the United States and Canada, and the European Union to treat systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis.

HLA-DR4 (DR4) is an HLA-DR serotype that recognizes the DRB1*04 gene products. The DR4 serogroup is large and has a number of moderate frequency alleles spread over large regions of the world.

Anti-cardiolipin antibodies (ACA) are antibodies often directed against cardiolipin and found in several diseases, including syphilis, antiphospholipid syndrome, livedoid vasculitis, vertebrobasilar insufficiency, Behçet's syndrome, idiopathic spontaneous abortion, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). They are a form of anti-mitochondrial antibody. In SLE, anti-DNA antibodies and anti-cardiolipin antibodies may be present individually or together; the two types of antibodies act independently. This is in contrast to rheumatoid arthritis with systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) because anti-cardiolipin antibodies are present in both conditions, and therefore may tie the two conditions together.

An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated that there are more than 80 recognized autoimmune diseases, with recent scientific evidence suggesting the existence of potentially more than 100 distinct conditions. Nearly any body part can be involved.
Michael D. Lockshin is an American professor and medical researcher. He is known for his work as a researcher of autoimmune diseases, with focus on antiphospholipid syndrome and lupus. He is Professor Emeritus of Medicine and the Director Emeritus of the Barbara Volcker Center for Women and Rheumatic Disease at Hospital for Special Surgery. He retired from HSS on January 31st, 2023.
Subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus is a clinically distinct subset of cases of lupus erythematosus that is most often present in white women aged 15 to 40, consisting of skin lesions that are scaly and evolve as poly-cyclic annular lesions or plaques similar to those of plaque psoriasis.

Lupus, technically known as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms.
Undifferentiated connective tissue disease (UCTD) is a disease in which the body mistakenly attacks its own tissues. It is diagnosed when there is evidence of an existing autoimmune condition which does not meet the criteria for any specific autoimmune disease, such as systemic lupus erythematosus or scleroderma. Latent lupus and incomplete lupus are alternative terms that have been used to describe this condition.

Anti-SSA autoantibodies are a type of anti-nuclear autoantibodies that are associated with many autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), SS/SLE overlap syndrome, subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus (SCLE), neonatal lupus and primary biliary cirrhosis. They are often present in Sjögren's syndrome (SS). Additionally, Anti-Ro/SSA can be found in other autoimmune diseases such as systemic sclerosis (SSc), polymyositis/dermatomyositis (PM/DM), rheumatoid arthritis (RA), and mixed connective tissue disease (MCTD), and are also associated with heart arrhythmia.
Blisibimod is a selective antagonist of B-cell activating factor, being developed by Anthera Pharmaceuticals as a treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus. It is currently under active investigation in clinical trials.
Daniel Jeffrey Wallace is an American rheumatologist, clinical professor, author, and fellow. Wallace has published 500 peer reviewed publications, 9 textbooks, and 28 book chapters on topics such as lupus, Sjögren syndrome, osteoarthritis, and fibromyalgia. He has the largest cohort of lupus patients in the United States (2000). A full professor of medicine, he is associate director of the Rheumatology Fellowship Program at Cedars-Sinai. His seminal contributions to research include being an author of the first paper to demonstrate vitamin D dysfunction and the importance of interleukin 6 in lupus, conducting the first large studies of apheresis in rheumatoid arthritis and lupus, and insights into the mechanisms of action of antimalarials. Wallace's research accomplishments also include conducting many clinical rheumatic disease trials, examining the role of microvascular angina and accelerated atherogenesis in lupus, and work on anti-telomere antibodies which have garnered him 6 papers in The New England Journal of Medicine. Wallace's monograph, The Lupus Book, has sold over 100,000 copies since 1995.
Ianalumab is a monoclonal antibody that is being investigated for autoimmune hepatitis, multiple sclerosis, pemphigus vulgaris, rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren syndrome, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
George C. Tsokos is an American immunologist who is a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and is the chief at Division of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center; Boston, MA







