In computing, Common Gateway Interface (CGI) is an interface specification for web servers to execute programs like console applications running on a server that generates web pages dynamically. Such programs are known as CGI scripts or simply as CGIs. The specifics of how the script is executed by the server are determined by the server. In the common case, a CGI script executes at the time a request is made and generates HTML.

The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) is an application protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include hyperlinks to other resources that the user can easily access, for example by a mouse click or by tapping the screen in a web browser.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) is an extension of the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP). It is used for secure communication over a computer network, and is widely used on the Internet. In HTTPS, the communication protocol is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) or, formerly, its predecessor, Secure Sockets Layer (SSL). The protocol is therefore also often referred to as HTTP over TLS, or HTTP over SSL.

The Lamiales are an order in the asterid group of dicotyledonous flowering plants. It includes about 23,810 species, 1,059 genera, and is divided into about 24 families. Well-known or economically important members of this order include lavender, lilac, olive, jasmine, the ash tree, teak, snapdragon, sesame, psyllium, garden sage, and a number of table herbs such as mint, basil, and rosemary.

The World Wide Web (WWW), commonly known as the Web, is an information system where documents and other web resources are identified by Uniform Resource Locators, which may be interlinked by hypertext, and are accessible over the Internet. The resources of the WWW are transferred via the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) and may be accessed by users by a software application called a web browser and are published by a software application called a web server.
The HTTP 404, 404 Not Found, 404, Page Not Found, or Server Not Found error message is a Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) standard response code, in computer network communications, to indicate that the browser was able to communicate with a given server, but the server could not find what was requested. The error may also be used when a server does not wish to disclose whether it has the requested information or not.

In computer networking, a proxy server is a server application or appliance that acts as an intermediary for requests from clients seeking resources from servers that provide those resources. A proxy server thus functions on behalf of the client when requesting service, potentially masking the true origin of the request to the resource server.

The Celastraceae, are a family of 96 genera and 1,350 species of herbs, vines, shrubs and small trees, belonging to the order Celastrales. The great majority of the genera are tropical, with only Celastrus, Euonymus and Maytenus widespread in temperate climates, and Parnassia (bog-stars) found in alpine and arctic climates.
Representational state transfer (REST) is a software architectural style that defines a set of constraints to be used for creating Web services. Web services that conform to the REST architectural style, called RESTful Web services, provide interoperability between computer systems on the Internet. RESTful Web services allow the requesting systems to access and manipulate textual representations of Web resources by using a uniform and predefined set of stateless operations. Other kinds of Web services, such as SOAP Web services, expose their own arbitrary sets of operations.
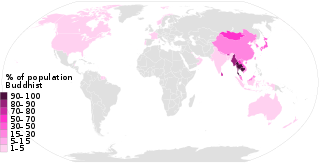
Buddhism is a religion practiced by an estimated 488 million in the world, 495 million, or 535 million people as of the 2010s, representing 7% to 8% of the world's total population.
An HTTP cookie is a small piece of data sent from a website and stored on the user's computer by the user's web browser while the user is browsing. Cookies were designed to be a reliable mechanism for websites to remember stateful information or to record the user's browsing activity. They can also be used to remember arbitrary pieces of information that the user previously entered into form fields such as names, addresses, passwords, and credit-card numbers.
The X-Forwarded-For (XFF) HTTP header field is a common method for identifying the originating IP address of a client connecting to a web server through an HTTP proxy or load balancer.
The N (Northern) postcode area, also known as the London N postcode area, is the part of the London post town covering part of North London, England.

Robsonodendron maritimum is a small, shrubby, evergreen tree that is indigenous to the coastal regions of South Africa.

archive.today is an archive site which stores snapshots of web pages. It retrieves one page at a time similar to WebCite, smaller than 50MB each, but with support for JavaScript-heavy sites such as Google Maps and Twitter.
A Uniform Resource Locator (URL), colloquially termed a web address, is a reference to a web resource that specifies its location on a computer network and a mechanism for retrieving it. A URL is a specific type of Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), although many people use the two terms interchangeably. Thus http://www.example.com is a URL, while www.example.com is not.</ref> URLs occur most commonly to reference web pages (http), but are also used for file transfer (ftp), email (mailto), database access (JDBC), and many other applications.









