
The Roland D-50 is a synthesizer produced by Roland and released in April of 1987. Its features include digital sample-based subtractive synthesis, on-board effects, a joystick for data manipulation, and an analog synthesis-styled layout design. The external Roland PG-1000 (1987) programmer could also be attached to the D-50 for more complex manipulation of its sounds. It was also produced in a rack-mount variant design, the D-550, with almost 450 user-adjustable parameters.
A rompler is an electronic musical instrument that plays pre-fabricated sounds based on audio samples. The term rompler is a blend of the terms ROM and sampler. In contrast to samplers, romplers do not record audio. Both may have additional sound editing features, such as layering several waveforms and modulation with ADSR envelopes, filters and LFOs.

The Korg Triton is a music workstation synthesizer, featuring digital sampling and sequencing, released in 1999. It uses Korg's "HI Synthesis" system and was eventually available in several model variants with numerous upgrade options. The Triton became renowned as a benchmark of keyboard technology, and has been widely featured in music videos and live concerts. At the NAMM Show in 2007, Korg announced the Korg M3 as its successor.
The Yamaha TX81Z is a rack-mounted (keyboard-less) frequency modulation (FM) music synthesizer, released in 1987. It is also known as a keyboard-less Yamaha DX11. Unlike previous FM synthesizers of the era, the TX81Z was the first to offer a range of oscillator waveforms other than just sine waves, conferring the new timbres of some of its patches when compared to older, sine-only FM synths. The TX81Z has developed a famous reputation, largely based on some of its preset bass sounds. The Yamaha DX11 keyboard synth was released the following year, offering improved editing abilities.

The microKORG is a MIDI-capable digital synthesizer/vocoder from Korg featuring DSP-based analog modelling. The synthesizer is built in such a way that it is essentially a Korg MS-2000 with a programmable step arpeggiator, a less advanced vocoder, lack of motion sequencing, lack of an XLR microphone input, and in a smaller case with fewer real-time control knobs.
The Ensoniq Fizmo was Ensoniq's last attempt at creating the perfect synthesizer. Developed in 1998, the Fizmo uses a Digital Acoustic simulation Transwave with 4 MB of ROM, up to four voices per preset, each voice with two oscillators, independent LFOs and FX: 48 voices maximum, with three separate fx units built in for further sound sculpting. The Fizmo featured 61 keys, and responded to velocity, channel aftertouch, as well as allowing the sounds to be split by velocity and keyboard position (note). The name F-I-Z-M-O was mapped across five control knobs just above the keyboard keys, allowing real-time modulation of the waves for more user controlled evolving sounds than a usual synthesizer could provide, as well as also having 17 dedicated Sound and Effect editing knobs for further sound design and editing.

The discontinued Roland MC-909 Sampling Groovebox combines the features of a synthesizer, sequencer, and sampler, with extensive hands-on control of both the sound engine and the sequencing flow. It was intended primarily for live performance of pre-programmed patterns consisting of up to 16 tracks of MIDI data. It was released by Roland Corporation on October 8, 2002. This product was announced at the AES Fall Convention in 2002. It is the direct successor to the Roland MC-505 and is the predecessor to the Roland MC-808. Which eventually ended the "Groovebox by year 2010" line of products by Roland which began in the year 1996 with the Original Roland MC-303 groovebox. The Roland Groovebox began again resurgence in the year 2019 with a two new modern & redesign Roland MC-707 GROOVEBOX/Roland MC-101 GROOVEBOX. The Roland MC-909 was developed from the blueprint of Roland's own "Roland Fantom-S Workstation & Roland Fantom-X Workstation" and uses the same structure and operating system, with some differences regarding the Patterns section, not implemented in the Roland Fantom S/X6/X7/X8 Workstation.

The Korg Wavestation is a vector synthesis synthesizer first produced in the early 1990s and later re-released as a software synthesizer in 2004. Its primary innovation was Wave Sequencing, a method of multi-timbral sound generation in which different PCM waveform data are played successively, resulting in continuously evolving sounds. The Wavestation's "Advanced Vector Synthesis" sound architecture resembled early vector synths such as the Sequential Circuits Prophet VS.

The Roland JD-800 is a digital synthesizer that was manufactured between 1991 and 1996. It features many knobs and sliders for patch editing and performance control — features that some manufacturers, including Roland, had been omitting in the name of streamlining since the inception of the Yamaha DX7. The JD-800 thus became very popular with musicians who wished to take a hands-on approach to patch programming. The introduction in the manual states that Roland's intention with the JD-800 was to "return to the roots of synthesis".
The Yamaha SY85 is a digital music workstation introduced in 1992. Unlike other Yamaha synthesizers of the time the SY85 does not use FM synthesis. Instead, its sounds are based on samples, which can be layered and modified to create new sounds.
Linear arithmetic synthesis, or LAsynthesis, is a means of sound synthesis invented by the Roland Corporation when they released their D-50 synthesizer in 1987.

The Roland U-20 is a PCM-sample synthesizer, released by Roland in 1989. It was the keyboard version of the U-220 rack module, which was in turn a similar follow-up product to Roland's U-110 rack module of 1988.
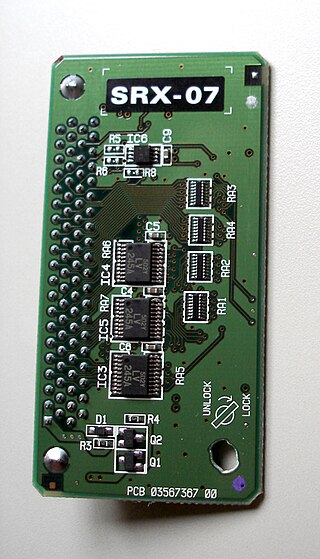
The SRX are a series of expansion boards produced by Roland Corporation. First introduced in 2000, they are small boards of electronic circuitry with 64MB ROMs containing patches (timbres) and rhythm sets. They are used to expand certain models of Roland synthesizers, music workstations, keyboards, and sound modules.
The Yamaha V50 is a hybrid music workstation introduced in 1989. It combines a sequencer, rhythm machine, an FM synthesis-based sound module and a MIDI keyboard.

The Roland XP-50 is a music workstation that combines the synthesizer engine of Roland's JV-1080 sound module with the sequencing capabilities of their MRC-Pro sequencer and a 61-note keyboard. First released in 1995, the XP-50 and the Roland XP-10 were the first two Roland XP-series products, later joined by the XP-80 and XP-30.

Yamaha SY77 is a 16 voice multitimbral music workstation first produced by Yamaha Corporation in 1989. The SY77 is a synthesizer whose architecture combines AFM synthesis, AWM2 for ROM-borne sample-based synthesis, and the combination of these two methods christened Realtime Convolution and Modulation Synthesis (RCM). The same technology was also packaged in a rack-mounted module released simultaneously, the TG77.
Casio's SDSynthesizers were a late-1980s line of analog synthesizers featuring a resonant filter. SD synthesis was traditional DCO-analog synthesis, with the main difference being that some of the SD waveforms' harmonic spectrums changed temporally, or dynamically in relation to the amplitude envelope.
The Alesis Quadrasynth is a 76-key, 64-note polyphonic PCM sample-based digital subtractive synthesizer first introduced in 1993. It was Alesis's first major foray into synthesizer production.

The Roland JV-2080 is a rack-mount expandable MIDI sound module and an updated version of the Roland JV-1080. Produced by the Roland Corporation, released in 1996 and built on a sample-based synthesis architecture, the JV-2080 provides a library of on-board sample material and a semi-modular synthesis engine.

The Roland JV-1080 is a sample-based synthesizer/sound module in the form of a 2U rack. The JV-1080's synthesizer engine was also used in Roland's XP-50 workstation (1995). Due to its library of high-quality sounds and multi-timbral capabilities, it became a mainstay with film composers.











