Related Research Articles

An astrolabe is an ancient astronomical instrument that was a handheld model of the universe. Its various functions also make it an elaborate inclinometer and an analog calculation device capable of working out several kinds of problems in astronomy. In its simplest form it is a metal disc with a pattern of wires, cutouts, and perforations that allows a user to calculate astronomical positions precisely. Historically used by astronomers, it is able to measure the altitude above the horizon of a celestial body, day or night; it can be used to identify stars or planets, to determine local latitude given local time, to survey, or to triangulate. It was used in classical antiquity, the Islamic Golden Age, the European Middle Ages and the Age of Discovery for all these purposes.
Herman of Carinthia, also called Hermanus Dalmata or Sclavus Dalmata, Secundus, by his own words born in the "heart of Istria", was a philosopher, astronomer, astrologer, mathematician and translator of Arabic works into Latin.

Gerard of Cremona was an Italian translator of scientific books from Arabic into Latin. He worked in Toledo, Kingdom of Castile and obtained the Arabic books in the libraries at Toledo. Some of the books had been originally written in Greek and, although well known in Byzantine Constantinople and Greece at the time, were unavailable in Greek or Latin in Western Europe. Gerard of Cremona is the most important translator among the Toledo School of Translators who invigorated Western medieval Europe in the twelfth century by transmitting the Arabs' and ancient Greeks' knowledge in astronomy, medicine and other sciences, by making the knowledge available in Latin. One of Gerard's most famous translations is of Ptolemy's Almagest from Arabic texts found in Toledo.
William of Moerbeke, O.P., was a prolific medieval translator of philosophical, medical, and scientific texts from Greek language into Latin, enabled by the period of Latin rule of the Byzantine Empire. His translations were influential in his day, when few competing translations were available, and are still respected by modern scholars.

Abū Isḥāq Ibrāhīm ibn Yaḥyā al-Naqqāsh al-Zarqālī al-Tujibi ; also known as Al-Zarkali or Ibn Zarqala (1029–1100), was an Arab maker of astronomical instruments and an astrologer from the western part of the Islamic world.

Abū al-ʿAbbās Aḥmad ibn Muḥammad ibn Kathīr al-Farghānī also known as Alfraganus in the West, was an astronomer in the Abbasid court in Baghdad, and one of the most famous astronomers in the 9th century. Al-Farghani composed several works on astronomy and astronomical equipment that were widely distributed in Arabic and Latin and were influential to many scientists. His best known work, Kitāb fī Jawāmiʿ ʿIlm al-Nujūmi, was an extensive summary of Ptolemy's Almagest containing revised and more accurate experimental data. Christopher Columbus used Al Farghani’s calculations for his voyages to America. In addition to making substantial contributions to astronomy, al-Farghani also worked as an engineer, supervising construction projects on rivers in Cairo, Egypt. The lunar crater Alfraganus is named after him.
Abraham bar Ḥiyya ha-Nasi, also known as Abraham Savasorda, Abraham Albargeloni, and Abraham Judaeus, was a Catalan Jewish mathematician, astronomer and philosopher who resided in Barcelona.
Dominicus Gundissalinus, also known as Domingo Gundisalvi or Gundisalvo, was a philosopher and translator of Arabic to Medieval Latin active in Toledo. Among his translations, Gundissalinus worked on Avicenna's Liber de philosophia prima and De anima, Ibn Gabirol's Fons vitae, and al-Ghazali's Summa theoricae philosophiae, in collaboration with the Jewish philosopher Abraham Ibn Daud and Johannes Hispanus. As a philosopher, Gundissalinus crucially contributed to the Latin assimilation of Arabic philosophy, being the first Latin thinker in receiving and developing doctrines, such as Avicenna's modal ontology or Ibn Gabirol's universal hylomorphism, that would soon be integrated into the thirteenth-century philosophical debate.
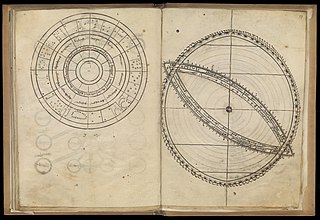
The Toledan Tables, or Tables of Toledo, were astronomical tables which were used to predict the movements of the Sun, Moon and planets relative to the fixed stars. They were a collection of mathematic tables that describe different aspects of the cosmos including prediction of calendar dates, times of cosmic events, and cosmic motion.

John of Seville was one of the main translators from Arabic into Castilian in partnership with Dominicus Gundissalinus during the early days of the Toledo School of Translators. John of Seville translated a litany of Arabic astrological works in addition to being credited with the production of several original works in Latin.

Māshāʾallāh ibn Atharī, known as Mashallah, was an 8th century Persian Jewish astrologer, astronomer, and mathematician. Originally from Khorasan, he lived in Basra during the reigns of the Abbasid caliphs al-Manṣūr and al-Ma’mūn, and was among those who introduced astrology and astronomy to Baghdad. The bibliographer ibn al-Nadim described Mashallah "as virtuous and in his time a leader in the science of jurisprudence, i.e. the science of judgments of the stars". Mashallah served as a court astrologer for the Abbasid caliphate and wrote works on astrology in Arabic. Some Latin translations survive.
Abū’l-‘Abbās al-Faḍl ibn Ḥātim al-Nairīzī was a Persian mathematician and astronomer from Nayriz, now in Fars Province, Iran.

Medieval Islamic astronomy comprises the astronomical developments made in the Islamic world, particularly during the Islamic Golden Age, and mostly written in the Arabic language. These developments mostly took place in the Middle East, Central Asia, Al-Andalus, and North Africa, and later in the Far East and India. It closely parallels the genesis of other Islamic sciences in its assimilation of foreign material and the amalgamation of the disparate elements of that material to create a science with Islamic characteristics. These included Greek, Sassanid, and Indian works in particular, which were translated and built upon.

Latin translations of the 12th century were spurred by a major search by European scholars for new learning unavailable in western Europe at the time; their search led them to areas of southern Europe, particularly in central Spain and Sicily, which recently had come under Christian rule following their reconquest in the late 11th century. These areas had been under Muslim rule for a considerable time, and still had substantial Arabic-speaking populations to support their search. The combination of this accumulated knowledge and the substantial numbers of Arabic-speaking scholars there made these areas intellectually attractive, as well as culturally and politically accessible to Latin scholars. A typical story is that of Gerard of Cremona, who is said to have made his way to Toledo, well after its reconquest by Christians in 1085, because he
arrived at a knowledge of each part of [philosophy] according to the study of the Latins, nevertheless, because of his love for the Almagest, which he did not find at all amongst the Latins, he made his way to Toledo, where seeing an abundance of books in Arabic on every subject, and pitying the poverty he had experienced among the Latins concerning these subjects, out of his desire to translate he thoroughly learnt the Arabic language....

The Toledo School of Translators is the group of scholars who worked together in the city of Toledo during the 12th and 13th centuries, to translate many of the Judeo-Islamic philosophies and scientific works from Classical Arabic into Latin.
Qusta ibn Luqa, also known as Costa ben Luca or Constabulus (820–912) was a Syrian Melkite Christian physician, philosopher, astronomer, mathematician and translator. He was born in Baalbek. Travelling to parts of the Byzantine Empire, he brought back Greek texts and translated them into Arabic.
Eric John Holmyard (1891–1959) was an English science teacher at Clifton College, and historian of science and technology.
Medieval Islamic geography and cartography refer to the study of geography and cartography in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age. Muslim scholars made advances to the map-making traditions of earlier cultures, particularly the Hellenistic geographers Ptolemy and Marinus of Tyre, combined with what explorers and merchants learned in their travels across the Old World (Afro-Eurasia). Islamic geography had three major fields: exploration and navigation, physical geography, and cartography and mathematical geography. Islamic geography reached its apex with Muhammad al-Idrisi in the 12th century.

The transmission of the Greek Classics to Latin Western Europe during the Middle Ages was a key factor in the development of intellectual life in Western Europe. Interest in Greek texts and their availability was scarce in the Latin West during the Early Middle Ages, but as traffic to the East increased, so did Western scholarship.

During the High Middle Ages, the Islamic world was at its cultural peak, supplying information and ideas to Europe, via Al-Andalus, Sicily and the Crusader kingdoms in the Levant. These included Latin translations of the Greek Classics and of Arabic texts in astronomy, mathematics, science, and medicine. Translation of Arabic philosophical texts into Latin "led to the transformation of almost all philosophical disciplines in the medieval Latin world", with a particularly strong influence of Muslim philosophers being felt in natural philosophy, psychology and metaphysics. Other contributions included technological and scientific innovations via the Silk Road, including Chinese inventions such as paper, compass and gunpowder.
References
- ↑ Arzobispo Raimundo de Toledo Escuela de Traductores [1130-1187]
- ↑ "MEDIEVAL SCIENCES: THE ISLAMIC FOUNDATION OF THE RENAISSANCE: Medievalhistory.net". Archived from the original on 2007-06-10. Retrieved 2007-10-30..
- ↑ looks at the network of translators.
- ↑ Richard Lorch, "The Treatise on the Astrolabe by Rudolph of Bruges", in: L. Nauta and A. Vanderjagt (eds.), Between Demonstration and Imagination: Essays in the History of Science and Philosophy Presented to John D. North (Leiden: Brill, 1999), pp. 55-100.
- ↑ History of Islamic Science - The time of abu-l-wafa