Related Research Articles
The Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) is a cryptographic network protocol for operating network services securely over an unsecured network. Typical applications include remote command-line, login, and remote command execution, but any network service can be secured with SSH.
The Intelligent Network (IN) is the standard network architecture specified in the ITU-T Q.1200 series recommendations. It is intended for fixed as well as mobile telecom networks. It allows operators to differentiate themselves by providing value-added services in addition to the standard telecom services such as PSTN, ISDN on fixed networks, and GSM services on mobile phones or other mobile devices.
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) is the standard for the communication and management of medical imaging information and related data. DICOM is most commonly used for storing and transmitting medical images enabling the integration of medical imaging devices such as scanners, servers, workstations, printers, network hardware, and picture archiving and communication systems (PACS) from multiple manufacturers. It has been widely adopted by hospitals and is making inroads into smaller applications like dentists' and doctors' offices.
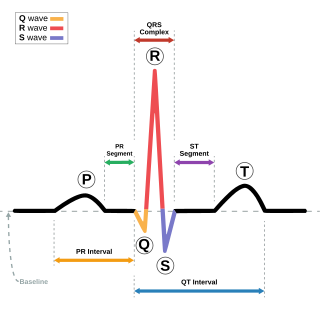
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram. It is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including cardiac rhythm disturbances, inadequate coronary artery blood flow, and electrolyte disturbances.
An application server is a server that hosts applications.

A subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module (SIM), widely known as a SIM card, is an integrated circuit running a card operating system (COS) that is intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices. It is also possible to store contact information on many SIM cards. SIM cards are always used on GSM phones; for CDMA phones, they are needed only for LTE-capable handsets. SIM cards can also be used in satellite phones, smart watches, computers, or cameras.

Secure Digital, officially abbreviated as SD, is a proprietary non-volatile memory card format developed by the SD Association (SDA) for use in portable devices.
In computing, the SSH File Transfer Protocol is a network protocol that provides file access, file transfer, and file management over any reliable data stream. It was designed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) as an extension of the Secure Shell protocol (SSH) version 2.0 to provide secure file transfer capabilities. The IETF Internet Draft states that, even though this protocol is described in the context of the SSH-2 protocol, it could be used in a number of different applications, such as secure file transfer over Transport Layer Security (TLS) and transfer of management information in VPN applications.
Secure copy protocol (SCP) is a means of securely transferring computer files between a local host and a remote host or between two remote hosts. It is based on the Secure Shell (SSH) protocol. "SCP" commonly refers to both the Secure Copy Protocol and the program itself. According to OpenSSH developers in April 2019, SCP is outdated, inflexible and not readily fixed; they recommend the use of more modern protocols like sftp and rsync for file transfer.
Far Manager is an orthodox file manager for Microsoft Windows and is a clone of Norton Commander. Far Manager uses the Win32 console and has a keyboard-oriented user interface.

WinSCP is a free and open-source SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), File Transfer Protocol (FTP), WebDAV, Amazon S3, and secure copy protocol (SCP) client for Microsoft Windows. Its main function is secure file transfer between a local and a remote computer. Beyond this, WinSCP offers basic file manager and file synchronization functionality. For secure transfers, it uses the Secure Shell Protocol (SSH) and supports the SCP protocol in addition to SFTP.
Software as a service is a software licensing and delivery model in which software is licensed on a subscription basis and is centrally hosted. It is sometimes referred to as "on-demand software", and was formerly referred to as "software plus services" by Microsoft. SaaS applications are also known as on-demand software and Web-based/Web-hosted software.
The ballistocardiograph (BCG) is a measure of ballistic forces generated by the heart. The downward movement of blood through the descending aorta produces an upward recoil, moving the body upward with each heartbeat. As different parts of the aorta expand and contract, the body continues to move downward and upward in a repeating pattern. Ballistocardiography is a technique for producing a graphical representation of repetitive motions of the human body arising from the sudden ejection of blood into the great vessels with each heart beat. It is a vital sign in the 1–20 Hz frequency range which is caused by the mechanical movement of the heart and can be recorded by noninvasive methods from the surface of the body. It was shown for the first time, after an extensive research work by Dr. Isaac Starr, that the effect of main heart malfunctions can be identified by observing and analyzing the BCG signal. Recent work also validates BCG could be monitored using camera in a non-contact manner.

In computing, SSHFS is a filesystem client to mount and interact with directories and files located on a remote server or workstation over a normal ssh connection. The client interacts with the remote file system via the SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), a network protocol providing file access, file transfer, and file management functionality over any reliable data stream that was designed as an extension of the Secure Shell protocol (SSH) version 2.0.
Shopping cart software is a piece of e-commerce software on a web server that allows visitors to have an Internet site to select items for eventual purchase.

A Wiggers diagram, named after its developer, Carl Wiggers, is a standard diagram that is used in teaching cardiac physiology. In the Wiggers diagram, the X-axis is used to plot time, while the Y-axis contains all of the following on a single grid:

Apache OFBiz is an open source enterprise resource planning (ERP) system. It provides a suite of enterprise applications that integrate and automate many of the business processes of an enterprise.

Vectorcardiography (VCG) is a method of recording the magnitude and direction of the electrical forces that are generated by the heart by means of a continuous series of vectors that form curving lines around a central point.

Automated ECG interpretation is the use of artificial intelligence and pattern recognition software and knowledge bases to carry out automatically the interpretation, test reporting, and computer-aided diagnosis of electrocardiogram tracings obtained usually from a patient.
CIPURSE is an open security standard for transit fare collection systems. It makes use of smart card technologies and additional security measures.
References
- ↑ Maglogiannis, Ilias G.; Karpouzis, Kostas; Wallace, Manolis. Image and Signal Processing for Networked E-health Applications. Morgan & Claypool Publishers. p. 41. ISBN 978-1-59829-036-3 . Retrieved 3 April 2021.