
BeppoSAX was an Italian–Dutch satellite for X-ray astronomy which played a crucial role in resolving the origin of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), the most energetic events known in the universe. It was the first X-ray mission capable of simultaneously observing targets over more than 3 orders-of-magnitude of energy, from 0.1 to 300 kiloelectronvolts (keV) with relatively large area, good energy resolution and imaging capabilities. BeppoSAX was a major programme of the Italian Space Agency (ASI) with the participation of the Netherlands Agency for Aerospace Programmes (NIVR). The prime contractor for the space segment was Alenia while Nuova Telespazio led the development of the ground segment. Most of the scientific instruments were developed by the Italian National Research Council (CNR) while the Wide Field Cameras were developed by the Netherlands Institute for Space Research (SRON) and the LECS was developed by the astrophysics division of the European Space Agency's ESTEC facility.

Chang'e 1 was an uncrewed Chinese lunar-orbiting spacecraft, part of the first phase of the Chinese Lunar Exploration Program. The spacecraft was named after the Chinese Moon goddess, Chang'e.

Lodewijk van den Berg was a Dutch-born American chemical engineer. He studied crystal growth and flew on a 1985 Space Shuttle Challenger mission as a payload specialist.
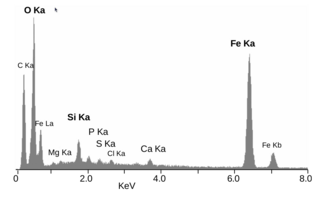
Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy, sometimes called energy dispersive X-ray analysis or energy dispersive X-ray microanalysis (EDXMA), is an analytical technique used for the elemental analysis or chemical characterization of a sample. It relies on an interaction of some source of X-ray excitation and a sample. Its characterization capabilities are due in large part to the fundamental principle that each element has a unique atomic structure allowing a unique set of peaks on its electromagnetic emission spectrum. The peak positions are predicted by the Moseley's law with accuracy much better than experimental resolution of a typical EDX instrument.
A semiconductor detector in ionizing radiation detection physics is a device that uses a semiconductor to measure the effect of incident charged particles or photons.

Suzaku was an X-ray astronomy satellite developed jointly by the Institute of Space and Aeronautical Science at JAXA and NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center to probe high-energy X-ray sources, such as supernova explosions, black holes and galactic clusters. It was launched on 10 July 2005 aboard the M-V launch vehicle on the M-V-6 mission. After its successful launch, the satellite was renamed Suzaku after the mythical Vermilion bird of the South.
Cadmium zinc telluride, (CdZnTe) or CZT, is a compound of cadmium, zinc and tellurium or, more strictly speaking, an alloy of cadmium telluride and zinc telluride. A direct bandgap semiconductor, it is used in a variety of applications, including semiconductor radiation detectors, photorefractive gratings, electro-optic modulators, solar cells, and terahertz generation and detection. The band gap varies from approximately 1.4 to 2.2 eV, depending on composition.

GSAT-2 was an experimental communication satellite built by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and launched on one of the first GSLVs. The satellite was positioned at 48 deg east longitude in the geo-stationary orbit.

An X-ray telescope (XRT) is a telescope that is designed to observe remote objects in the X-ray spectrum. X-rays are absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere, so instruments to detect X-rays must be taken to high altitude by balloons, sounding rockets, and satellites.

AstroSat is India's first dedicated multi-wavelength space telescope. It was launched on a PSLV-XL on 28 September 2015. With the success of this satellite, ISRO has proposed launching AstroSat-2 as a successor for AstroSat.

Kvant-1 (37KE) was the first module to be attached in 1987 to the Mir Core Module, which formed the core of the Soviet space station Mir. It remained attached to Mir until the entire space station was deorbited in 2001.

The Solar Anomalous and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer was a NASA solar and magnetospheric observatory and was the first spacecraft in the Small Explorer program. It was launched into low Earth orbit on 3 July 1992, from Vandenberg Air Force Base aboard a Scout G-1 launch vehicle. SAMPEX was an international collaboration between NASA and the Max Planck Institute for Extraterrestrial Physics of Germany. The Solar Anomalous and Magnetospheric Particle Explorer (SAMPEX) is the first of a series of spacecraft that was launched under the Small Explorer (SMEX) program for low-cost spacecraft.

The International Astrophysical Observatory "GRANAT", was a Soviet space observatory developed in collaboration with France, Denmark and Bulgaria. It was launched on 1 December 1989 aboard a Proton rocket and placed in a highly eccentric four-day orbit, of which three were devoted to observations. It operated for almost nine years.

Koronas-Foton, also known as CORONAS-Photon, was a Russian solar research satellite. It was the third satellite in the Russian CORONAS programme, and part of the international Living With a Star programme. It was launched on 30 January 2009, from Site 32/2 at the Plesetsk Cosmodrome, aboard the final flight of the Tsyklon-3 rocket. On 1 December 2009 all scientific instruments on the satellite were turned off due to the problems with power supply that were caused by a design flaw. On 18 April 2010 the creators of the satellite announced it was lost "with a good deal of certainty".

Aditya-L1 is a coronagraphy spacecraft for studying the solar atmosphere, designed and developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and various other Indian Space Research Institutes. It is orbiting at about 1.5 million km from Earth in a halo orbit around the Lagrange point 1 (L1) between the Earth and the Sun, where it will study the solar atmosphere, solar magnetic storms, and their impact on the environment around the Earth.
PERDaix is a novel, small and light weight magnetic spectrometer to measure the charge and mass dependent solar modulation periodically for deeper understanding of cosmic rays. For a better understanding of sources and acceleration of cosmic particles direct measurements of cosmic rays are necessary. Also for a better understanding of the solar modulation which is expected to follow the 22-year solar cycle, time dependent measurements are needed. PERDaix is a newly designed detector which is constructed by the Department of Physics 1b, RWTH Aachen University. Being proposed to the German Space Agency in November 2009 for a participation in the BEXUS Program after a first canceled flight attempt in October 2010 the actual flight took place as a post-BEXUS-campaign flight opportunity in November 2010.

The International X-ray Observatory (IXO) is a cancelled X-ray telescope that was to be launched in 2021 as a joint effort by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA). In May 2008, ESA and NASA established a coordination group involving all three agencies, with the intent of exploring a joint mission merging the ongoing XEUS and Constellation-X Observatory (Con-X) projects. This proposed the start of a joint study for IXO. NASA was forced to cancel the observatory due to budget constraints in fiscal year 2012. ESA however decided to reboot the mission on its own developing Advanced Telescope for High Energy Astrophysics as a part of Cosmic Vision program.

X-ray detectors are devices used to measure the flux, spatial distribution, spectrum, and/or other properties of X-rays.

The X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) is an Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)-manufactured space observatory to study polarisation of cosmic X-rays. It was launched on 1 January 2024 on a PSLV rocket, and it has an expected operational lifespan of at least five years.
The Disturbed and quiet time Ionosphere-thermosphere System at High Altitudes (DISHA) is a proposed twin satellite aeronomy mission by the Indian Space Research Organisation. It will study the effects of space weather events on the uppermost layers of Earth's atmosphere. The mission will consist of two small satellites namely DISHA-H and DISHA-L in high and low inclinations for simultaneous observation in polar and equatorial regions. DISHA satellites will have expected mission life of 5 years with at least 3 years of combined operations and are expecting readiness by 2024–25.















