Related Research Articles

Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC)'s PDP-10, later marketed as the DECsystem-10, is a mainframe computer family manufactured beginning in 1966 and discontinued in 1983. 1970s models and beyond were marketed under the DECsystem-10 name, especially as the TOPS-10 operating system became widely used.
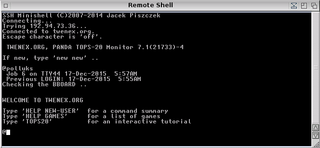
The TOPS-20 operating system by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) is a proprietary OS used on some of DEC's 36-bit mainframe computers. The Hardware Reference Manual was described as for "DECsystem-10/DECSYSTEM-20 Processor".
OS/8 is the primary operating system used on the Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP-8 minicomputer.
Uptime is a measure of system reliability, expressed as the percentage of time a machine, typically a computer, has been working and available. Uptime is the opposite of downtime.
Peripheral Interchange Program (PIP) was a utility to transfer files on and between devices on Digital Equipment Corporation's computers. It was first implemented on the PDP-6 architecture by Harrison "Dit" Morse early in the 1960s. It was subsequently implemented for DEC's operating systems for PDP-10, PDP-11, and PDP-8 architectures. In the 1970s and 1980s Digital Research implemented PIP on CP/M and MP/M.
TOPS-10 System is a discontinued operating system from Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) for the PDP-10 mainframe computer family. Launched in 1967, TOPS-10 evolved from the earlier "Monitor" software for the PDP-6 and PDP-10 computers; this was renamed to TOPS-10 in 1970.
DECWAR is a multiplayer computer game first written in 1978 at the University of Texas at Austin for the PDP-10. It was developed from a lesser-known two-player version, WAR, adding multi-terminal support for between one and ten players. WAR and DECWAR are essentially multiplayer versions of the classic Star Trek game, but with added strategic elements. The game was later used, by scrubbing copyright notices and replacing them, as MegaWars on CompuServe and Stellar Warrior on GEnie. Both versions ran for years.
In Unix operating systems, the term wheel refers to a user account with a wheel bit, a system setting that provides additional special system privileges that empower a user to execute restricted commands that ordinary user accounts cannot access.
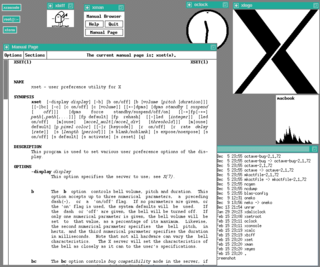
In computing, a shell is a computer program that exposes an operating system's services to a human user or other programs. In general, operating system shells use either a command-line interface (CLI) or graphical user interface (GUI), depending on a computer's role and particular operation. It is named a shell because it is the outermost layer around the operating system.
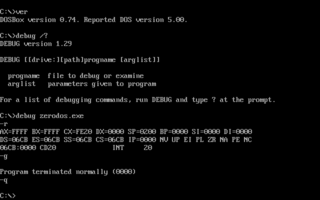
The line-oriented debugger DEBUG.EXE is an external command in operating systems such as DOS, OS/2 and Windows.
Control-C is a common computer command. It is generated by pressing the C key while holding down the Ctrl key on most computer keyboards.
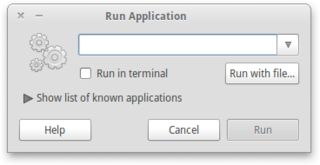
The Run command on an operating system such as Microsoft Windows and Unix-like systems is used to directly open an application or document whose path is known.

In computing, ren is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS, 4NT and Windows PowerShell. It is used to rename computer files and in some implementations also directories. It is analogous to the Unix mv command. However, unlike mv, ren cannot be used to move files, as a new directory for the destination file may not be used. Alternatively, move may be used if available. On versions of MS-DOS that do not support the move command, the user would simply copy the file to a new destination, and then delete the original file. A notable exception to this rule is DOSBox, in which ren may be used to move a file, since move is not supported.

In computing, type is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, 4DOS/4NT and Windows PowerShell used to display the contents of specified files on the computer terminal. The analogous Unix command is cat.

In computing, the print command provides single-user print spooling capability in a number of operating systems. It is roughly similar to that provided by the UNIX System V lp and BSD lpr print spooler systems.

In computing, help is a command in various command line shells such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe, Bash, qshell, 4DOS/4NT, Windows PowerShell, Singularity shell, Python, MATLAB and GNU Octave. It provides online information about available commands and the shell environment.

In computing, copy is a command in various operating systems. The command copies computer files from one directory to another.

Unix is a family of multitasking, multi-user computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others.

In computing, start is a command of the IBM OS/2, Microsoft Windows and ReactOS command-line interpreter cmd.exe to start programs or batch files or to open files or directories using the default program. start is not available as a standalone program. The underlying Win32 API is ShellExecute.
TENEX is an operating system developed in 1969 by BBN for the PDP-10, which later formed the basis for Digital Equipment Corporation's TOPS-20 operating system.
References
- ↑ TOPS-10 Operating System Commands Manual. Maynard, MA: Digital Equipment Corporation, 1988; part number AA-0916F-TB; pp. 2–305. Scan available at bitsavers.org (retrieved: 5-April-2015).