The Internet Protocol (IP) is the network layer communications protocol in the Internet protocol suite for relaying datagrams across network boundaries. Its routing function enables internetworking, and essentially establishes the Internet.

Plan 9 from Bell Labs is a distributed operating system which originated from the Computing Science Research Center (CSRC) at Bell Labs in the mid-1980s and built on UNIX concepts first developed there in the late 1960s. Since 2000, Plan 9 has been free and open-source. The final official release was in early 2015.
In distributed computing, a Remote Procedure Call (RPC) is when a computer program causes a procedure (subroutine) to execute in a different address space, which is written as if it were a normal (local) procedure call, without the programmer explicitly writing the details for the remote interaction. That is, the programmer writes essentially the same code whether the subroutine is local to the executing program, or remote. This is a form of client–server interaction, typically implemented via a request–response message passing system. In the object-oriented programming paradigm, RPCs are represented by remote method invocation (RMI). The RPC model implies a level of location transparency, namely that calling procedures are largely the same whether they are local or remote, but usually, they are not identical, so local calls can be distinguished from remote calls. Remote calls are usually orders of magnitude slower and less reliable than local calls, so distinguishing them is important.
giFT Internet File Transfer (giFT) is a computer software daemon that allows several file sharing protocols to be used with a simple client having a graphical user interface (GUI). The client dynamically loads plugins implementing the protocols, as they are required.
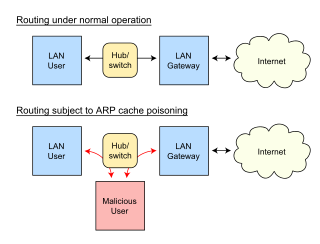
In computer networking, ARP spoofing, ARP cache poisoning, or ARP poison routing, is a technique by which an attacker sends (spoofed) Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) messages onto a local area network. Generally, the aim is to associate the attacker's MAC address with the IP address of another host, such as the default gateway, causing any traffic meant for that IP address to be sent to the attacker instead.

A wireless mesh network (WMN) is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. It can also be a form of wireless ad hoc network.
Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) is a communications protocol providing security to datagram-based applications by allowing them to communicate in a way designed to prevent eavesdropping, tampering, or message forgery. The DTLS protocol is based on the stream-oriented Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol and is intended to provide similar security guarantees. The DTLS protocol datagram preserves the semantics of the underlying transport—the application does not suffer from the delays associated with stream protocols, but because it uses UDP or SCTP, the application has to deal with packet reordering, loss of datagram and data larger than the size of a datagram network packet. Because DTLS uses UDP or SCTP rather than TCP, it avoids the "TCP meltdown problem", when being used to create a VPN tunnel.

The Hyper Text Coffee Pot Control Protocol (HTCPCP) is a facetious communication protocol for controlling, monitoring, and diagnosing coffee pots. It is specified in RFC 2324, published on 1 April 1998 as an April Fools' Day RFC, as part of an April Fools prank. An extension, HTCPCP-TEA, was published as RFC 7168 on 1 April 2014 to support brewing teas, also as an April Fools' Day RFC.

RepRap is a project to develop low-cost 3D printers that can print most of their own components. As open designs, all of the designs produced by the project are released under a free software license, the GNU General Public License.

A computer network is a set of computers sharing resources located on or provided by network nodes. Computers use common communication protocols over digital interconnections to communicate with each other. These interconnections are made up of telecommunication network technologies based on physically wired, optical, and wireless radio-frequency methods that may be arranged in a variety of network topologies.

Lego Mindstorms NXT is a programmable robotics kit released by Lego on August 2, 2006. It replaced the Robotics Invention System, the first-generation Lego Mindstorms kit. The base kit ships in two versions: the retail version and the education base set. It comes with the NXT-G programming software or the optional LabVIEW for Lego Mindstorms. A variety of unofficial languages exist, such as NXC, NBC, leJOS NXJ, and RobotC. A second-generation set, Lego Mindstorms NXT 2.0, was released on August 1, 2009, with a color sensor and other upgrades. The third-generation EV3 was released in September 2013.

Jitsi is a collection of free and open-source multiplatform voice (VoIP), video conferencing and instant messaging applications for the Web platform, Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS and Android. The Jitsi project began with the Jitsi Desktop. With the growth of WebRTC, the project team focus shifted to the Jitsi Videobridge for allowing web-based multi-party video calling. Later the team added Jitsi Meet, a full video conferencing application that includes web, Android, and iOS clients. Jitsi also operates meet.jit.si, a version of Jitsi Meet hosted by Jitsi for free community use. Other projects include: Jigasi, lib-jitsi-meet, Jidesha, and Jitsi.
Thrift is an interface definition language and binary communication protocol used for defining and creating services for programming languages. It was developed by Facebook. Since 2020, it is an open source project in the Apache Software Foundation.
Protocol Buffers (Protobuf) is a free and open-source cross-platform data format used to serialize structured data. It is useful in developing programs that communicate with each other over a network or for storing data. The method involves an interface description language that describes the structure of some data and a program that generates source code from that description for generating or parsing a stream of bytes that represents the structured data.
The Wave Federation Protocol is an open protocol, extension of the Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol (XMPP) that is used in Apache Wave. It is designed for near real-time communication between the computer supported cooperative work wave servers.
Fused filament fabrication (FFF), also known as fused deposition modeling, or filament freeform fabrication, is a 3D printing process that uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic material. Filament is fed from a large spool through a moving, heated printer extruder head, and is deposited on the growing work. The print head is moved under computer control to define the printed shape. Usually the head moves in two dimensions to deposit one horizontal plane, or layer, at a time; the work or the print head is then moved vertically by a small amount to begin a new layer. The speed of the extruder head may also be controlled to stop and start deposition and form an interrupted plane without stringing or dribbling between sections. "Fused filament fabrication" was coined by the members of the RepRap project to give an acronym (FFF) that would be legally unconstrained in its use.

Matrix is an open standard and communication protocol for real-time communication. It aims to make real-time communication work seamlessly between different service providers, in the way that standard Simple Mail Transfer Protocol email currently does for store-and-forward email service, by allowing users with accounts at one communications service provider to communicate with users of a different service provider via online chat, voice over IP, and videotelephony. It therefore serves a similar purpose to protocols like XMPP, but is not based on any existing communication protocol.
WebUSB is a JavaScript application programming interface (API) specification for securely providing access to USB devices from web applications.
Marlin is open source firmware originally designed for RepRap project FDM 3D printers using the Arduino platform.









