Filippo di ser Brunellesco di Lippo Lapi, commonly known as Filippo Brunelleschi and also nicknamed Pippo by Leon Battista Alberti, was an Italian architect, designer, goldsmith and sculptor. He is considered to be a founding father of Renaissance architecture. He is recognized as the first modern engineer, planner, and sole construction supervisor. In 1421, Brunelleschi became the first person to receive a patent in the Western world. He is most famous for designing the dome of the Florence Cathedral, and for the mathematical technique of linear perspective in art which governed pictorial depictions of space until the late 19th century and influenced the rise of modern science. His accomplishments also include other architectural works, sculpture, mathematics, engineering, and ship design. Most surviving works can be found in Florence.

The Pazzi were a noble Florentine family. Their main trade during the fifteenth century was banking. In the aftermath of the Pazzi conspiracy in 1478, members of the family were banished from Florence and their property was confiscated; the family name and coat-of-arms were permanently suppressed by order of the Signoria.

Florence Cathedral, formally the Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Flower, is the cathedral of Florence, Italy. It was begun in 1296 in the Gothic style to a design of Arnolfo di Cambio and was structurally completed by 1436, with the dome engineered by Filippo Brunelleschi. The exterior of the basilica is faced with polychrome marble panels in various shades of green and pink, bordered by white, and has an elaborate 19th-century Gothic Revival façade by Emilio De Fabris.

Lorenzo Monaco was an Italian painter and miniaturist of the late Gothic to early Renaissance age. He was born Piero di Giovanni. Little is known about his youth, apart from the fact that he was apprenticed in Florence. He has been considered the last important exponent of the Giotto style, before the Renaissance revolution that came with Fra Angelico and Masaccio.

The Basilica della Santissima Annunziata is a Renaissance-style, Catholic minor basilica in Florence, region of Tuscany, Italy. This is considered the mother church of the Servite Order. It is located at the northeastern side of the Piazza Santissima Annunziata near the city center.

Michelozzo di Bartolomeo Michelozzi was an Italian architect and sculptor. Considered one of the great pioneers of architecture during the Renaissance, Michelozzo was a favored Medici architect who was extensively employed by Cosimo de' Medici. He was a pupil of Lorenzo Ghiberti in his early years, and later collaborated with Donatello.

The Basilica of St. Mary of the Angels and of the Martyrs is a basilica and titular church in Rome, Italy, built inside the ruined frigidarium of the Roman Baths of Diocletian in the Piazza della Repubblica.

The Basilica di Santo Spirito is a church in Florence, Italy. Usually referred to simply as Santo Spirito, it is located in the Oltrarno quarter, facing the square with the same name. The interior of the building – internal length 97 meters – is one of the preeminent examples of Renaissance architecture.

The Ospedale degli Innocenti 'Hospital of the Innocents', also known in old Tuscan dialect as the Spedale degli Innocenti, is a historic building in Florence, Italy. It was designed by Filippo Brunelleschi, who received the commission in 1419 from the Arte della Seta. It was originally a children's orphanage. It is regarded as a notable example of early Italian Renaissance architecture. The hospital, which features a nine bay loggia facing the Piazza SS. Annunziata, was built and managed by the "Arte della Seta" or Silk Guild of Florence. That guild was one of the wealthiest in the city and, like most guilds, took upon itself philanthropic duties. Today the building houses a small museum of Renaissance art with works by Luca della Robbia, Sandro Botticelli, and Piero di Cosimo, as well as an Adoration of the Magi by Domenico Ghirlandaio.
The decade of the 1410s in art involved some significant events.
St. Mary of the Angels may refer to:

The Coronation of the Virgin is a 1414 tempera on panel polyptych by the Italian late Gothic artist Lorenzo Monaco, centred on the subject of the Coronation of the Virgin. Once in the Camaldolese monastery of Santa Maria degli Angeli, it is now housed in the Uffizi Gallery in Florence. It is dated February 1413 which, in the Florentine calendar, corresponded to 1414.

Santa Maria degli Angeli is a church in Murano, an island in the Venetian Lagoon, northern Italy.

Mariotto di Nardo di Cione was a Florentine painter in the Florentine Gothic style. He worked at the Duomo of Florence, the church of Santa Maria Maggiore, and the Orsanmichele. He created both frescoes and panel paintings, and was also active as a manuscript illuminator.
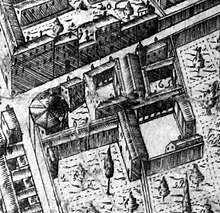
The Monastery of St. Mary of the Angels was a monastery of the Camaldolese Order in Florence, Italy.

The Palazzo Giugni, also called the Palazzo Firenzuola, is a late-Renaissance or Mannerist architecture palace designed by Bartolomeo Ammanati, and located on Via degli Alfani #48 in the quartiere San Giovanni of Florence, region of Tuscany, Italy. It is located down the street from the Brunelleschi's church of Santa Maria degli Angeli.

The Santa Croce Crucifix is a polychrome wood sculpture by Donatello, perhaps from c.1406-1408, or 1409-10. If the former is the correct dating, then Donatello was a young artist working in Lorenzo Ghiberti's workshop and beginning to get his own commissions. It is now in the Cappella Bardi di Vernio, just off the left transept of Santa Croce in Florence, Italy.