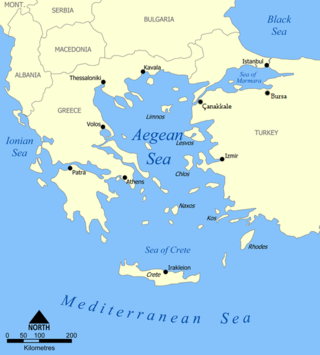
The Aegean Sea is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea between Europe and Asia. It is located between the Balkans and Anatolia, and covers an area of some 215,000 km2 (83,000 sq mi). In the north, the Aegean is connected to the Marmara Sea, which in turn connects to the Black Sea, by the straits of the Dardanelles and the Bosphorus, respectively. The Aegean Islands are located within the sea and some bound it on its southern periphery, including Crete and Rhodes. The sea reaches a maximum depth of 2,639 m (8,658 ft) to the west of Karpathos. The Thracian Sea and the Sea of Crete are main subdivisions of the Aegean Sea.

Obsidian is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock.

Santorini, officially Thira and Classical Greek Thera, is an island in the southern Aegean Sea, about 200 km (120 mi) southeast from the Greek mainland. It is the largest island of a small circular archipelago, which bears the same name and is the remnant of a caldera. It forms the southernmost member of the Cyclades group of islands, with an area of approximately 73 km2 (28 sq mi) and a 2011 census population of 15,550. The municipality of Santorini includes the inhabited islands of Santorini and Therasia, as well as the uninhabited islands of Nea Kameni, Palaia Kameni, Aspronisi and Christiana. The total land area is 90.623 km2 (34.990 sq mi). Santorini is part of the Thira regional unit.

A beach is a landform alongside a body of water which consists of loose particles. The particles composing a beach are typically made from rock, such as sand, gravel, shingle, pebbles, etc., or biological sources, such as mollusc shells or coralline algae. Sediments settle in different densities and structures, depending on the local wave action and weather, creating different textures, colors and gradients or layers of material.

Milos or Melos is a volcanic Greek island in the Aegean Sea, just north of the Sea of Crete. Milos is the southwesternmost island in the Cyclades group.
Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as their creating process, shape, elevation, slope, orientation, rock exposure, and soil type.

A pebble is a clast of rock with a particle size of 4–64 mm (0.16–2.52 in) based on the Udden-Wentworth scale of sedimentology. Pebbles are generally considered larger than granules and smaller than cobbles. A rock made predominantly of pebbles is termed a conglomerate. Pebble tools are among the earliest known man-made artifacts, dating from the Palaeolithic period of human history.

A ridge is a long, narrow, elevated geomorphologic landform, structural feature, or a combination of both separated from the surrounding terrain by steep sides. The sides of a ridge slope away from a narrow top, the crest or ridgecrest, with the terrain dropping down on either side. The crest, if narrow, is also called a ridgeline. Limitations on the dimensions of a ridge are lacking. Its height above the surrounding terrain can vary from less than a meter to hundreds of meters. A ridge can be either depositional, erosional, tectonic, or a combination of these in origin and can consist of either bedrock, loose sediment, lava, or ice depending on its origin. A ridge can occur as either an isolated, independent feature or part of a larger geomorphological and/or structural feature. Frequently, a ridge can be further subdivided into smaller geomorphic or structural elements.

Tinos is a Greek island situated in the Aegean Sea. It is located in the Cyclades archipelago. The closest islands are Andros, Delos, and Mykonos. It has a land area of 194.464 square kilometres (75.083 sq mi) and a 2011 census population of 8,636 inhabitants.

The Slate Islands are a small archipelago in Lake Superior, Ontario, Canada, about 12 kilometres (7.5 mi) south of the town of Terrace Bay. The island group, consisting of 15 islands in total, was created by a meteorite impact which formed a crater about 32 km (20 mi) wide. In 1985, the Ontario government established the Slate Islands as a natural environment provincial park. The islands are notable for having Ontario's largest herd of boreal woodland caribou.

Coastal geography is the study of the constantly changing region between the ocean and the land, incorporating both the physical geography and the human geography of the coast. It includes understanding coastal weathering processes, particularly wave action, sediment movement and weather, and the ways in which humans interact with the coast.

Kimolos is a Greek island in the Aegean Sea. It lies on the southwest of the island group of Cyclades, near the bigger island of Milos. Kimolos is the administrative center of the municipality of Kimolos, which also includes the uninhabited islands of Polyaigos, Agios Efstathios and Agios Georgios. The island has a land area of 36 square kilometres (13.900 sq mi), while the municipality's land area is 53.251 square kilometres (20.560 sq mi), and it reported a population of 910 inhabitants in the 2011 census.

Sigri is a small fishing village near the western tip of Lesbos Island. Its name derives through Greek σίγουρος from the Venetian word siguro, meaning "safe", based on the fact that it has a safe harbour. Sigri has a Turkish castle, built in 1746 during the Ottoman occupation, which looks over the bay and the long island of Nissiopi, which stretches across the mouth of the bay and acts as a buffer to the prevailing winds. The port of Sigri is able to accommodate large vessels, even cruise ship-size ferry boats coming from the mainline. Almost all shipping to Lesbos, however, comes into the east of the island.

Elizabeth Island lies just south of French Island in Western Port, Victoria, south-eastern Australia, and just north of Phillip Island. It is over 65 acres in area and is an unincorporated area of Victoria, one of the few privately owned, freehold islands in Victoria. Once used for farming, it has been converted into a holiday retreat, with the establishment of a pier and housing facilities. Access is via boat, barge or helicopter.

Salt Point State Park is a state park in Sonoma County, California, United States. The park covers 6,000 acres (2,428 ha) on the coast of Northern California, with 20 miles (32 km) of hiking trails and over 6 miles (9.7 km) of a rough rocky coastline including Salt Point which protrudes into the Pacific Ocean. The park also features the first underwater preserves in California. The constant impact of the waves forms the rocks into many different shapes. These rocks continue underwater providing a wide variety of habitats for marine organisms. The activities at Salt Point include hiking, camping, fishing, scuba diving and many others. The weather is often cool with fog and cold winds, even during the summer.

Achilles Point is a rocky point on the headland at the eastern end of the small sandy beach named Ladies Bay, Auckland, New Zealand. The name 'Te Pane o Horoiwi' can also sometimes refer to the whole headland between St Heliers and Tamaki River estuary. Achilles Point is named after a ship called HMNZS Achilles (70) which defeated the German pocket battleship Admiral Graf Spee in 1939. The headland, from the point round to the Tamaki heads, was previously known as Te Pane o Horoiwi, named after Horoiwi who arrived in New Zealand on the Tainui canoe (waka).

Santorini caldera is a large, mostly submerged caldera, located in the southern Aegean Sea, 120 kilometers north of Crete in Greece. Visible above water is the circular Santorini island group, consisting of Santorini, the main island, Therasia and Aspronisi at the periphery, and the Kameni islands at the center. It has been designated a Decade Volcano.

Firiplaka or Firiplaka Beach is a beach situated at the southern side in Milos Island, Greece between the other beaches of Provatas (West) and Tsigrado (East). It is one of the most popular beach on the island. The beach is extensive with majestic towering volcanic cliffs, snow-grey fine sand and white pebbles and shallow turquoise waters. There are umbrellas and sunbeds and a bar hut. There is also a huge rock with a cave under it in the water near the shore and it was sculptured out from a volcanic a long time ago. The access to the beach is possible by your own vehicle, taxi, bus or even boat which goes around the island from the port of Adamas. The largest part of the road is asphalt, however the last part of it, is a gravel paved driveway.

Point Lookout Foreshore is a heritage-listed headland at East Coast Road, Point Lookout, City of Redland, Queensland, Australia. It is also known as Mooloomba. It was added to the Queensland Heritage Register on 27 August 2004.
The geology of Greece is highly structurally complex due to its position at the junction between the European and African tectonic plates.






























