
Carnatic music, known as Karnāṭaka saṃgīta or Karnāṭaka saṅgītam in the South Indian languages, is a system of music commonly associated with South India, including the modern Indian states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, and Sri Lanka. It is one of two main subgenres of Indian classical music that evolved from ancient Sanatana dharma sciences and traditions, particularly the Samaveda. The other subgenre being Hindustani music, which emerged as a distinct form because of Persian or Islamic influences from Northern India. The main emphasis in Carnatic music is on vocal music; most compositions are written to be sung, and even when played on instruments, they are meant to be performed in gāyaki (singing) style.
A raga or raag is a melodic framework for improvisation akin to a melodic mode in Indian classical music. The rāga is a unique and central feature of the classical Indian music tradition, and as a result has no direct translation to concepts in classical European music. Each rāga is an array of melodic structures with musical motifs, considered in the Indian tradition to have the ability to "colour the mind" and affect the emotions of the audience.

Indian classical music is the classical music of the Indian subcontinent. It has two major traditions: the North Indian classical music known as Hindustani and the South Indian expression known as Carnatic. These traditions were not distinct until about the 15th century. During the period of Mughal rule of the Indian subcontinent, the traditions separated and evolved into distinct forms. Hindustani music emphasizes improvisation and exploration of all aspects of a raga, while Carnatic performances tend to be short composition-based. However, the two systems continue to have more common features than differences.

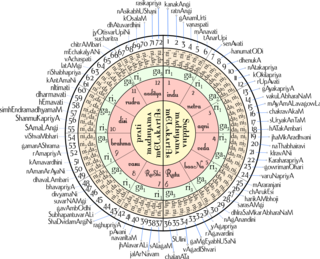
Mēḷakartā is a collection of fundamental musical scales (ragas) in Carnatic music. Mēḷakartā ragas are parent ragas from which other ragas may be generated. A melakarta raga is sometimes referred as mela, karta or sampurna as well, though the latter term is inaccurate, as a sampurna raga need not be a melakarta.
Hindustani classical music is the classical music of northern regions of the Indian subcontinent. It may also be called North Indian classical music or, in Hindustani, shastriya sangeet. Its origins date from the 12th century CE, when it diverged from Carnatic music, the classical tradition of southern regions of the Indian subcontinent.

Shruti or śruti[ɕrʊtɪ] is a Sanskrit word, found in the Vedic texts of Hinduism where it means lyrics and "what is heard" in general. It is also an important concept in Indian music, where it means the smallest interval of pitch that the human ear can detect and a singer or musical instrument can produce and do nyaas(stay) on it. The musical shruti concept is found in ancient and medieval Sanskrit texts such as the Natya Shastra, the Dattilam, the Brihaddeshi, and the Sangita Ratnakara. Chandogya Upanishad speaks of the division of the octave in 22 parts.

Ustad Amir Khan was one of the greatest and most influential Indian vocalists in the Hindustani classical tradition. He was the founder of the Indore gharana. Although his singing style was an amalgamation of Kirana and Bhendibazaar Gharanas.
A Thaat is a "Parent scale" in North Indian or Hindustani music. The concept of the thaat is not exactly equivalent to the western musical scale because the primary function of a thaat is not as a tool for music composition, but rather as a basis for classification of ragas. There is not necessarily strict compliance between a raga and its parent thaat; a raga said to 'belong' to a certain thaat need not allow all the notes of the thaat, and might allow other notes. Thaats are generally accepted to be heptatonic by definition.
Svara or swara is a Sanskrit word that connotes simultaneously a breath, a vowel, the sound of a musical note corresponding to its name, and the successive steps of the octave or saptaka. More comprehensively, it is the ancient Indian concept about the complete dimension of musical pitch. Most of the time a svara is identified as both musical note and tone, but a tone is a precise substitute for sur, related to tunefulness. Traditionally, Indians have just seven svaras/notes with short names, e.g. saa, re/ri, ga, ma, pa, dha, ni which Indian musicians collectively designate as saptak or saptaka. It is one of the reasons why svara is considered a symbolic expression for the number seven.

Janya is a term meaning "derive". In Carnatic music a janya raga is one derived from one of the 72 melakarta ragas. Janya ragas are classified into various types based on a variety of features.
Arohana, Arohanam or Aroha, in the context of Indian classical music, is the ascending scale of notes in a raga. The pitch increases as we go up from Shadja (Sa) to the Taar Shadja (Sa), possibly in a crooked (vakra) manner.
Darbari Kanada, or simply Raga Darbari,, is a raga in the Kanada family, which is thought to have originated in Carnatic music and brought into Hindustani classical music by Miyan Tansen, the legendary 16th-century composer in emperor Akbar's court. This tradition is reflected in the name itself; Darbar is the Persian derived word in Hindi meaning "court." As the most familiar raga in the Kanada family, it may sometimes also be called Shuddha Kanada or pure Kanada. It belongs to the Asavari thaat. This raag is called raaga Kaanada in Yakshagana Karnataka state dance
Puriya Dhanashree is a rāga in Hindustani classical music. It belongs to the Poorvi Thaat and has been derived from the Janak raga.
Bhoopali, also known as Bhoop, Bhopali, or Bhupali, is a Hindustani classical raga. Bhupālī, is a raag in Kalyan Thaat. It is a pentatonic scale. Most of the songs in this raga are based on Bhakti rasa. Since it uses 5 notes, belongs to the "Audav jaati" of ragas.
Raga Bihag is a Hindustani classical raga belonging to the Bilaval Thaat. It is a melodious Raaga for beginners as well as experts. Raga Bihag uses all seven music swars. In Bihag, both the Madhyams are used. The Shuddha Madhyam is the prominent one while Teevra Madhyama is only used with Panchama in Phrase PA MA' GA MA GA. In Avaroha, Rishabh and Dhaivat are not used as resting notes however they are used in Meend. In this Raag, Nishad is a prominent note and Aalaps or Taans are generally started from this note.
Sohini is a raga in Hindustani classical music in the Marwa thaat. Alternate transliterations include Sohani and Sohni. Like Bahar, it is a small raga, with not much space for elaboration. It emotes the feel of longing, of passive sensuousness.

Carnatic music is usually performed by a small ensemble of musicians, who sit on an elevated stage. This usually consists of at least; a principal performer, a melodic accompaniment, a rhythm accompaniment, and a drone.
Hameer is a nocturnal Hindustani classical raga nominally placed in Kalyan thaat. All the (shuddha swaras along with (teevra madhyam are used in it. Generally, its vaadi swar is dhaivat and the samavaadi swar is gandhar. However, some exponents consider the vaadi swar to be pancham as Hameer is mainly sung in the upper half of an octave and is nocturnal. Pancham is not taken in the aaroh but is taken in avroh. Its jati is "Shadav Sampurn". "Vadi Svar" is Dhaivat and Samvadi Swar is Gandhar.

Carnatic raga refers to ragas used in Carnatic music. A Carnatic raga has several components - primordial sound (nāda), tonal system (swara), pitch (śruti), scale, ornaments (gamaka) and important tones.
Shankara is a raga in Hindustani classical music.




