
Wessex was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from 519 until England was unified by Æthelstan in 927.

Cricklade is a town and civil parish on the River Thames in north Wiltshire, England, midway between Swindon and Cirencester. It is the first downstream town on the Thames. The parish population at the 2011 census was 4,227.

Cookham is a historic Thames-side village and civil parish on the north-eastern edge of Berkshire, England, 2.9 miles (5 km) north-north-east of Maidenhead and opposite the village of Bourne End. Cookham forms the southernmost and most rural part of High Wycombe urban area. With adjoining Cookham Rise and Cookham Dean, it had a combined population of 5,779 at the 2011 Census. In 2011 The Daily Telegraph deemed Cookham Britain's second richest village.

Cookham Lock is a lock with weirs situated on the River Thames near Cookham, Berkshire, about a half-mile downstream of Cookham Bridge. The lock is set in a lock cut which is one of four streams here and it is surrounded by woods. On one side is Sashes Island and on the other is Mill Island connected to Formosa Island, the largest on the non-tidal Thames.

The Thames Path is a National Trail following the River Thames from its source near Kemble in Gloucestershire to the Thames Barrier at Charlton, south east London. It is about 184 miles (296 km) long. A path was first proposed in 1948 but it only opened in 1996.

A burh or burg was an Old English fortification or fortified settlement. In the 9th century, raids and invasions by Vikings prompted Alfred the Great to develop a network of burhs and roads to use against such attackers. Some were new constructions; others were situated at the site of Iron Age hillforts or Roman forts and employed materials from the original fortifications. As at Lundenburh, many were also situated on rivers: this facilitated internal lines of supply while aiming to restrict access to the interior of the kingdom for attackers in shallow-draught vessels such as longships.

Boulter's Lock is a lock and weir on the River Thames in England north-east of Maidenhead town centre, Berkshire. The present 1912-built lock replaces those at this point of the river to the immediate east dating from the late 16th century and that of 1772 built by the Thames Navigation Commission. The lock is on the western side of the north-south flowing reach between the A4094 Maidenhead to Cookham road and Ray Mill Island. The name is variably used for the immediate surrounding area.
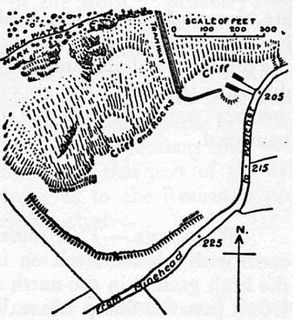
Daw's Castle is a sea cliff hill fort just west of Watchet, a harbour town in Somerset, England. It is a Scheduled Ancient Monument.

Cookham Bridge is a road bridge in Cookham, Berkshire, carrying the A4094 road across the River Thames in England. It is on the reach above Cookham Lock and links Cookham on the Berkshire bank with Bourne End in Buckinghamshire.

The Burghal Hidage is an Anglo-Saxon document providing a list of over thirty fortified places (burhs), the majority being in the ancient Kingdom of Wessex, and the taxes assigned for their maintenance. The document, so named by Frederic William Maitland in 1897, survives in two versions of medieval and early modern date. Version A, Cotton Otho B.xi was badly damaged in a fire at Ashburnham House in 1731 but the body of the text survives in a transcript made by the antiquary Laurence Nowell in 1562. Version B survives as a composite part of seven further manuscripts, usually given the title De numero hydarum Anglie in Britannia. There are several discrepancies in the lists recorded in the two versions of the document: Version A includes references to Burpham, Wareham and Bridport but omits Shaftesbury and Barnstaple which are listed in Version B. Version B also names Worcester and Warwick in an appended list.

Portus Adurni was a Roman fort in the Roman province of Britannia situated at the north end of Portsmouth Harbour. It was part of the Saxon Shore, and is the best-preserved Roman fort north of the Alps. Around an eighth of the fort has been excavated.

The Maidenhead Waterways are a system of canals in Maidenhead, England. Formerly disused, plans to restore and upgrade them were announced in 2011. The works would initially make the waterways navigable by small craft, and over time by larger craft, as limitations to navigation are gradually removed.

Formosa Island is an island in the River Thames in England at Cookham Lock near Cookham, Berkshire, with two smaller adjacent islands.

Gibraltar Islands are a pair of islands in the River Thames in England above Bourne End Railway Bridge on the reach above Cookham Lock, near Cookham Dean, Berkshire.

Hedsor Water is a stretch of the River Thames near Cookham, Berkshire which runs to the north of Sashes Island. Hedsor Water was once the main navigation of the Thames but was by-passed by the construction of Cookham Lock in 1830. Navigation is only possible for the first 100 metres (330 ft) from the downstream end, where a few temporary moorings are available, except for smaller boats.

Odney is a common and island (Eyot) in the Thames, part of the civil parish of Cookham, in the English county of Berkshire. The island may have been sacred to the main Saxon god, Woden, as "Wodenes-Eye".
The Battle of Bedcanford in 571 was a battle between the West Saxons and British that was a key part of the Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain.
Camlet Way was a Roman road in England which ran roughly east–west between Colchester (Camalodunum) in Essex and Silchester in Hampshire via St Albans (Verulamium). Camlet Way crossed the River Thames by bridge at Hedsor Wharf to Sashes Island near Cookham in Berkshire.

Eorpeburnan is the first place identified in the Burghal Hidage, a document created in the late 9th or early 10th century, that provides a list of thirty one fortified places in Wessex. It details the location of fortifications designed to defend the West Saxon kingdom from the Vikings but also the relative size of burghal defences and their garrisons. Eorpeburnan is designated as having a hidage of 324, its precise location is lost in history, but scholars have suggested some possible sites.
The Battle of Buttington was fought in 893 between a Viking army and an alliance of Anglo-Saxons and Welsh.
















