
University of Rovira i Virgili is located in the Catalan cities of Tarragona and Reus, Spain. Its name is in honour of Antoni Rovira i Virgili.

Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity realizing or redistributing value". Others have different definitions; a common element in the definitions is a focus on newness, improvement, and spread of ideas or technologies.

Science and technology in China have developed rapidly during the 1980s to 2010s, and major scientific and technological achievements have been made since the 1980s. From the 1980s to the 1990s, the Chinese government successively launched the "863 Plan" and the "Strategy for Rejuvenating the Country through Science and Education", which greatly promoted the development and progress of China's science and technology. The Chinese government has placed emphasis through funding, reform, and societal status on science and technology as a fundamental part of the socio-economic development of the country as well as for national prestige.
Technology transfer (TT), also called transfer of technology (TOT), is the process of transferring (disseminating) technology from the person or organization that owns or holds it to another person or organization, in an attempt to transform inventions and scientific outcomes into new products and services that benefit society. Technology transfer is closely related to knowledge transfer.

Shenyang Ligong University is a university in Shenyang, Liaoning, China under the provincial government. Its campus is in a new district of Hunnan New District.
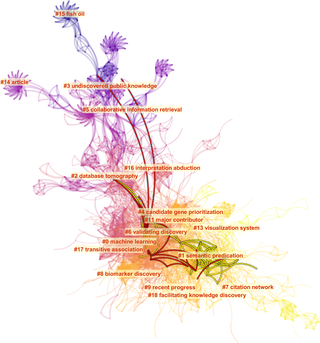
Bibliometrics is the use of statistical methods to analyse books, articles and other publications, especially in scientific contents. Bibliometric methods are frequently used in the field of library and information science. Bibliometrics is closely associated with scientometrics, the analysis of scientific metrics and indicators, to the point that both fields largely overlap.
Citation analysis is the examination of the frequency, patterns, and graphs of citations in documents. It uses the directed graph of citations — links from one document to another document — to reveal properties of the documents. A typical aim would be to identify the most important documents in a collection. A classic example is that of the citations between academic articles and books. For another example, judges of law support their judgements by referring back to judgements made in earlier cases. An additional example is provided by patents which contain prior art, citation of earlier patents relevant to the current claim.
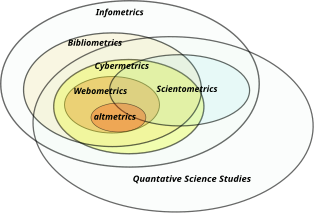
Informetrics is the study of quantitative aspects of information, it is an extension and evolution of traditional bibliometrics and scientometrics. Informetrics uses bibliometrics and scientometrics methods to study mainly the problems of literature information management and evaluation of science and technology. Informetrics is an independent discipline that uses quantitative methods from mathematics and statistics to study the process, phenomena, and law of informetrics. Informetrics has gained more attention as it is a common scientific method for academic evaluation, research hotspots in discipline, and trend analysis.
Technology forecasting attempts to predict the future characteristics of useful technological machines, procedures or techniques. Researchers create technology forecasts based on past experience and current technological developments. Like other forecasts, technology forecasting can be helpful for both public and private organizations to make smart decisions. By analyzing future opportunities and threats, the forecaster can improve decisions in order to achieve maximum benefits. Today, most countries are experiencing huge social and economic changes, which heavily rely on technology development. By analyzing these changes, government and economic institutions could make plans for future developments. However, not all of historical data can be used for technology forecasting, forecasters also need to adopt advanced technology and quantitative modeling from experts’ researches and conclusions.

The Ministry of Science and Technology is the central government ministry which coordinates science and technology activities in the country. The office is located in Xicheng District, Beijing. The ministry is responsible for formulating guidelines and related policies for science and technology in China development and promoting basic and special research on science and technology. The Ministry develop human resources, including introducing foreign intellectual planning and organising international scientific and technological cooperation and talent exchanges and strengthening China's innovation capabilities in the field of international scientific research.

An academic discipline or academic field is a subdivision of knowledge that is taught and researched at the college or university level. Disciplines are defined and recognized by the academic journals in which research is published, and the learned societies and academic departments or faculties within colleges and universities to which their practitioners belong. Academic disciplines are conventionally divided into the humanities, including language, art and cultural studies, and the scientific disciplines, such as physics, chemistry, and biology; the social sciences are sometimes considered a third category.

The Agora Center is a separate institute at the University of Jyväskylä in Central Finland. By its nature, the Agora Center is interdisciplinary and networked. Its purpose is to conduct, coordinate, and administrate top-level research and development that relates to the knowledge society and which places emphasis on the human perspective. The research and development is conducted in the form of fixed-period projects in cooperation with the University of Jyväskylä’s other faculties and separate institutes, businesses, the public sector and other relevant parties. The Agora Center also promotes researcher training through its various research projects. One of the core missions of the Agora Center is to effectively combine research and development with education. The project staff includes a high number of students and post-graduate students.
The following outlineof information science is provided as an overview of and topical guide to information science:
Reinhilde Veugelers is a Belgian economist and Professor of Managerial Economics, Strategy and Innovation at the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven from Belgium, known for her research on science and innovation. She is also a scholar at Bruegel in Brussels and at the Peterson Institute for International Economics in Washington D.C.
Alan Pilkington is a British engineer and researcher known for his work in technology management, operations management, Manufacturing strategy and enterprise engineering. He has been a professor at the Copenhagen Business School, Hult International Business School and S P Jain School of Global Management. He is currently Professor of Technology Management at Westminster Business School in London. He is past chair of the IEEE Technology Management Council for the UK and Republic of Ireland joint chapter on engineering management.
The GESIS – Leibniz Institute for the Social Sciences is the largest German infrastructure institute for the social sciences. It is headquartered in Mannheim, with a location in Cologne. With basic research-based services and consulting covering all levels of the scientific process, GESIS supports researchers in the social sciences. As of 2017, the president of GESIS is Christof Wolf.
Science and Technology in Nepal, sometimes shortened to S&T in Nepal, encompass the development and challenges of scientific research and technological innovation in Nepal, and how these developments, in turn, affect Nepali society, politics, and culture. Science and technology are small but emerging fields in Nepal. The Ministry of Education, Science and Technology is the apex government body tasked with the responsibility of overseeing the development of science and technology in the country.
Science and technology in Armenia describes trends and developments in science, technology and innovation policy and governance in Armenia.
Science and technology in Kazakhstan – government policies to develop science, technology and innovation in Kazakhstan.

The National Center for Science and Engineering Statistics (NCSES) is one of the thirteen principal statistical agencies of the United States and is tasked with providing objective data on the status of the science and engineering enterprise in the U.S. and other countries. NCSES sponsors or co-sponsors data collection on 15 surveys and produces two key publications: Science and Engineering Indicators, and Women, Minorities, and Persons with Disabilities in Science and Engineering. Though policy-neutral, the data and reports produced by NCSES are used by policymakers when making policy decisions regarding STEM education and research funding in the U.S.










