
A wind farm or wind park, also called a wind power station or wind power plant, is a group of wind turbines in the same location used to produce electricity. Wind farms vary in size from a small number of turbines to several hundred wind turbines covering an extensive area. Wind farms can be either onshore or offshore.

The production of renewable energy in Scotland is a topic that came to the fore in technical, economic, and political terms during the opening years of the 21st century. The natural resource base for renewable energy is high by European, and even global standards, with the most important potential sources being wind, wave, and tide. Renewables generate almost all of Scotland's electricity, mostly from the country's wind power.

Siemens Gamesa Renewable Energy S.A., formerly Gamesa Corporación Tecnológica S.A. and Grupo Auxiliar Metalúrgico S.A., is a Spanish-German wind engineering company based in Zamudio, Biscay, Spain. In Spain, the company has two other main sites one in Madrid and the other one in Sarriguren (Navarre). The Services Commercial Office is located in the Parque de la Innovación de Navarra in Sarriguren. It manufactures wind turbines and provides onshore and offshore wind services. It is the world's second largest wind turbine manufacturer.
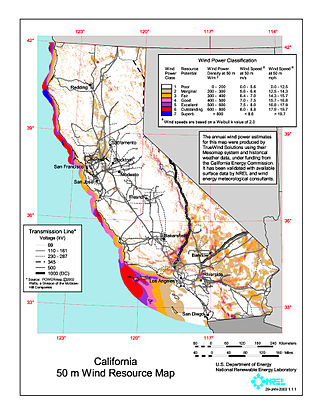
Wind power in California had initiative and early development during Governor Jerry Brown's first two terms in the late 1970s and early 1980s. The state's wind power capacity has grown by nearly 350% since 2001, when it was less than 1,700 MW. In 2016, wind energy supplied about 6.9% of California's total electricity needs, or enough to power more than 1.3 million households. Most of California's wind generation is found in the Tehachapi area of Kern County, California, with some large projects in Solano, Contra Costa and Riverside counties as well. California is among the states with the largest amount of installed wind power capacity. In recent years, California has lagged behind other states when it comes to the installation of wind power. It was ranked 4th overall for wind power electrical generation at the end of 2016 behind Texas, Iowa, and Oklahoma. As of 2019, California had 5,973 megawatts (MW) of wind power generating capacity installed.

The European Marine Energy Centre (EMEC) Ltd is a UKAS accredited test and research center focusing on wave and tidal power development based in the Orkney Islands, UK. The centre provides developers with the opportunity to test full-scale grid-connected prototype devices in unrivalled wave and tidal conditions.

In 2021 France reached a total of 18,676 megawatts (MW) installed wind power capacity placing France at that time as the world's seventh largest wind power nation by installed capacity, behind the United Kingdom and Brazil and ahead of Canada and Italy. According to the IEA the yearly wind production was 20.2 TWh in 2015, representing almost 23% of the 88.4 TWh from renewable sources in France during that year. Wind provided 4.3% of the country's electricity demand in 2015.

A floating wind turbine is an offshore wind turbine mounted on a floating structure that allows the turbine to generate electricity in water depths where fixed-foundation turbines are not feasible. Floating wind farms have the potential to significantly increase the sea area available for offshore wind farms, especially in countries with limited shallow waters, such as Japan, France and US West coast. Locating wind farms further offshore can also reduce visual pollution, provide better accommodation for fishing and shipping lanes, and reach stronger and more consistent winds.

Wind power in Italy, at the end of 2015, consisted of more than 1,847 wind turbines with a total installed capacity of 8,958 megawatts. Wind power contributed 5.4% of Italy electricity generation in 2015 (14,589 GWh). Italy is ranked as the world's tenth producer of wind power as of the end of 2016. Prospects for Italian wind energy beyond 2020 were positive, with several projects planned to go live before 2030.

BARD Offshore 1 is a 400 megawatt (MW) North Sea offshore wind farm with 80 BARD 5.0 turbines. Since the owner could not buy such 5MW offshore wind turbines in sufficient numbers in 2006, Dr. Bekker set up its own production of turbines. This should serve as the legacy for his children. The systems were developed by aerodyn Energiesysteme GmbH. A plant for rotor blades and nacelle assembly was built in Emden and a plant for the offshore foundations in Cuxhaven. Two turbine prototypes were set up at the Rysumer Nacken in 2007, and another prototype in Hooksiel in 2008. Construction was finished in July 2013 and the wind farm was officially inaugurated in August 2013. The wind farm is located 100 kilometres (60 mi) northwest of the isle Borkum in 40-metre (130 ft) deep water.

Offshore wind power or offshore wind energy is the generation of electricity through wind farms in bodies of water, usually at sea. There are higher wind speeds offshore than on land, so offshore farms generate more electricity per amount of capacity installed. Offshore wind farms are also less controversial than those on land, as they have less impact on people and the landscape.
GE Wind Energy is a branch of GE Renewable Energy, a subsidiary of General Electric. The company manufactures and sells wind turbines to the international market. In 2018, GE was the fourth largest wind turbine manufacturer in the world.

A tidal stream generator, often referred to as a tidal energy converter (TEC), is a machine that extracts energy from moving masses of water, in particular tides, although the term is often used in reference to machines designed to extract energy from run of river or tidal estuarine sites. Certain types of these machines function very much like underwater wind turbines, and are thus often referred to as tidal turbines. They were first conceived in the 1970s during the oil crisis.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to wind energy:

The Vestas V164 is a three-bladed offshore wind turbine, produced by Vestas, with a nameplate capacity of up to 10 megawatts, a world record. Vestas revealed the V164's design in 2011 with the first prototype unit operated at Østerild in northern Denmark in January 2014. The first industrial units were installed in 2016 at Burbo Bank, off the west coast of the United Kingdom. By 2021, Vestas had produced 500 of the series.
Dogger Bank Wind Farm is a group of offshore wind farms under construction 125 to 290 kilometres off the east coast of Yorkshire, England in the North Sea. It was developed by the Forewind consortium, with three phases envisioned - first phase, second phase and third phase. In 2015 the third phase was abandoned, while the first and second phases were granted consent. It is expected that the Dogger Bank development will consist of four offshore wind farms, each with a capacity of up to 1.2 GW, creating a combined capacity of 4.8 GW.
Wind power is a form of renewable energy in South Korea with the goal of reducing greenhouse gas (GHG) and particulate matter (PM) emissions caused by coal based power. After two oil crises dating back to the 1970s, the South Korean government needed to transition to renewable energy, which encouraged their first renewable energy law in 1987.

The VolturnUS is a floating concrete structure that supports a wind turbine, designed by University of Maine Advanced Structures and Composites Center and deployed by DeepCwind Consortium in 2013. The VolturnUS can support wind turbines in water depths of 150 ft (46 m) or more. The DeepCwind Consortium and its partners deployed a 1:8 scale VolturnUS in 2013. Efforts are now underway by Maine Aqua Ventus 1, GP, LLC, to deploy to full-scale VolturnUS structures off the coast of Monhegan Island, Maine, in the UMaine Deepwater Offshore Wind Test Site. This demonstration project, known as New England Aqua Ventus I, is planned to deploy two 6 MW wind turbines by 2020.
Hywind Scotland is the world's first commercial wind farm using floating wind turbines, situated 29 kilometres (18 mi) off Peterhead, Scotland. The farm has five 6 MW Siemens direct-drive turbines on Hywind floating monopiles, with a total capacity of 30 MW. It is operated by Hywind (Scotland) Limited, a joint venture of Equinor (75%) and Masdar (25%).
Seawind Ocean Technology B.V., a Netherlands based company, is a manufacturer (OEM) of integrated floating wind turbine and green hydrogen systems. Seawind is developing two-bladed floating wind turbines suitable for installation in all seas, including hurricane regions and ultra-deep waters. Founded on original research and development work by NASA, Hamilton Standard, Enel, and Aeritalia; Seawind's offshore wind power turbines with integrated foundations have been patented, proven at 1.5 MW, and achieved Type D DNV certification in December 2019. The company is now planning the launch of its Seawind 6 demonstrator to be followed by the pre-series Seawind 12, a project earmarked for installation as early as 2024-25 that seeks to obtain DNV's highest certification level.













