Related Research Articles
The separation of church and state is a philosophical and jurisprudential concept for defining political distance in the relationship between religious organizations and the state. Conceptually, the term refers to the creation of a secular state and to disestablishment, the changing of an existing, formal relationship between the church and the state. Although the concept is older, the exact phrase "separation of church and state" is derived from "wall of separation between church and state", a term coined by Thomas Jefferson. The concept was promoted by Enlightenment philosophers such as John Locke.

A state religion is a religion or creed officially endorsed by a sovereign state. A state with an official religion, while not a secular state, is not necessarily a theocracy. State religions are official or government-sanctioned establishments of a religion, but the state does not need to be under the control of the clergy, nor is the state-sanctioned religion necessarily under the control of the state.

Laïcité is the constitutional principle of secularism in France. Article 1 of the French Constitution is commonly interpreted as the separation of civil society and religious society. It discourages religious involvement in government affairs, especially in the determination of state policies as well as the recognition of a state religion. It also forbids government involvement in religious affairs, and especially prohibits government influence in the determination of religion, such that it includes a right to the free exercise of religion.
"Separation of church and state" is a metaphor paraphrased from Thomas Jefferson and used by others in discussions regarding the Establishment Clause and Free Exercise Clause of the First Amendment to the United States Constitution which reads: "Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof..."

State atheism or atheist state is the incorporation of hard atheism or non-theism into political regimes. It is considered the opposite of theocracy and may also refer to large-scale secularization attempts by governments. To some extent, it is a religion-state relationship that is usually ideologically linked to irreligion and the promotion of irreligion or atheism. State atheism may refer to a government's promotion of anti-clericalism, which opposes religious institutional power and influence in all aspects of public and political life, including the involvement of religion in the everyday life of the citizen. In some instances, religious symbols and public practices that were once held by religions were replaced with secularized versions of them. State atheism in these cases is considered as not being politically neutral toward religion, and therefore it is often considered non-secular.
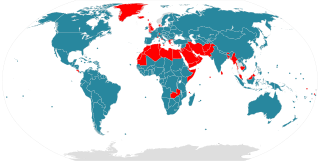
A secular state is an idea pertaining to secularity, whereby a state is or purports to be officially neutral in matters of religion, supporting neither religion nor irreligion. A secular state claims to treat all its citizens equally regardless of religion, and claims to avoid preferential treatment for a citizen based on their religious beliefs, affiliation or lack of either over those with other profiles.
Freedom of religion in the Philippines is guaranteed by the Constitution of the Philippines.
Freedom of religion in Sri Lanka is a protected right under Chapter II, Article 9 of the constitution of Sri Lanka. This applies to all religions, though Buddhism is given the foremost place under the 1978 Republican Constitution. Sri Lanka is regarded by its Supreme Court as being a secular state.
India since its independence in 1947 has been a secular state. The secular values were enshrined in the constitution of India. India's first prime minister Jawaharlal Nehru is credited with the formation of secular values in the modern history of the country.

The United States Commission on International Religious Freedom (USCIRF) is a U.S. federal government commission created by the International Religious Freedom Act (IRFA) of 1998. USCIRF Commissioners are appointed by the President and the leadership of both political parties in the Senate and the House of Representatives. USCIRF's principal responsibilities are to review the facts and circumstances of violations of religious freedom internationally and to make policy recommendations to the President, the Secretary of State, and the Congress.

Human rights in Tajikistan, a country in Central Asia, have become an issue of international concern. The access to basic human rights remains limited, with corruption in the government and the systematic abuse of the human rights of its citizens slowing down the progress of democratic and social reform in the country.
Nepal is a secular state under the Constitution of Nepal 2015, where "secular" means religious, cultural freedoms, including protection of religion and culture handed down from time immemorial.
Freedom of religion in Tajikistan is provided for in Tajikistan's constitution. The country is secular by law. However, respect for religious freedom has eroded during recent years, creating some areas of concern.
Secularism—that is, the separation of religion from civic affairs and the state—has been a controversial concept in Islamic political thought, owing in part to historical factors and in part to the ambiguity of the concept itself. In the Muslim world, the notion has acquired strong negative connotations due to its association with removal of Islamic influences from the legal and political spheres under foreign colonial domination, as well as attempts to restrict public religious expression by some secularist nation states. Thus, secularism has often been perceived as a foreign ideology imposed by invaders and perpetuated by post-colonial ruling elites, and is frequently understood to be equivalent to irreligion or anti-religion.

The Constitution of Tajikistan was adopted on 6 November 1994 and amended three times, on 26 September 1999, on 22 June 2003 and on 22 May 2016.

Islam is the predominant religion in Uzbekistan.

Secularism in Bangladesh is known as "neutrality of religion" under Bangladeshi law. In the Constitution of Bangladesh, secularism is mentioned in the preamble as one of the fundamental principles of Bangladeshi law. Article 8 enshrines secularism as one of the fundamental principles of state policy. Article 12 elaborates further on secularism and freedom of religion.
A process of secularization in Syria occurred under the French mandate in the 1920s. Syria has been governed by the Arab nationalist Baath Party since 1963. The Baath regime combined Arab Socialism with elements of secular ideology and an authoritarian political system which also incorporated aspects of Islamic law, with different court systems operating for religious minorities. Non-Muslims are forbidden from the role of head of state.
The status of religious freedom in Africa varies from country to country. States can differ based on whether or not they guarantee equal treatment under law for followers of different religions, whether they establish a state religion, the extent to which religious organizations operating within the country are policed, and the extent to which religious law is used as a basis for the country's legal code.
The status of religious freedom in Asia varies from country to country. States can differ based on whether or not they guarantee equal treatment under law for followers of different religions, whether they establish a state religion, the extent to which religious organizations operating within the country are policed, and the extent to which religious law is used as a basis for the country's legal code.
References
- 1 2 "2022 Report on International Religious Freedom: Tajikistan". US Department of State.
The constitution declares the country a secular state and that "religious associations shall be separate from the state and shall not interfere in state affairs."
- ↑ Catherine Putz (17 April 2015). "Tajikistan: No Hajj, No Hijab, and Shave Your Beard". The Diplomat.