Related Research Articles

Commentarii de Bello Gallico, also Bellum Gallicum, is Julius Caesar's firsthand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it Caesar describes the battles and intrigues that took place in the nine years he spent fighting the Celtic and Germanic peoples in Gaul that opposed Roman conquest.

The Nervii were one of the most powerful Belgic tribes of northern Gaul at the time of its conquest by Rome. Their territory corresponds to the central part of modern Belgium, including Brussels, and stretched southwards into French Hainault. During their first century BC Roman military campaign, Julius Caesar's contacts among the Remi stated that the Nervii were the most warlike of the Belgae. In times of war, they were known to trek long distances to take part in battles. Being one of the northerly Belgic tribes, with the Menapii to the west, and the Eburones to their east, they were considered by Caesar to be relatively uncorrupted by civilization. According to Tacitus they claimed Germanic descent. According to Strabo they were of Germanic origin.

The Arverni were a Gallic people dwelling in the modern Auvergne region during the Iron Age and the Roman period. They were one of the most powerful tribes of ancient Gaul, contesting primacy over the region with the neighbouring Aedui.

The Battle of Alesia or siege of Alesia was the climactic military engagement of the Gallic Wars, fought around the Gallic oppidum of Alesia in modern France, a major centre of the Mandubii tribe. It was fought by the Roman army of Julius Caesar against a confederation of Gallic tribes united under the leadership of Vercingetorix of the Arverni. It was the last major engagement between Gauls and Romans, and is considered one of Caesar's greatest military achievements and a classic example of siege warfare and investment; the Roman army built dual lines of fortifications—an inner wall to keep the besieged Gauls in, and an outer wall to keep the Gallic relief force out. The Battle of Alesia marked the end of Gallic independence in the modern day territory of France and Belgium.
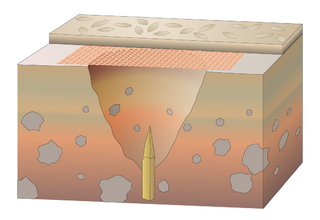
In medieval fortification, a trou de loup was a type of booby trap or defensive obstacle. Each trou de loup consisted of a conical pit about 2 m deep and 1.2 to 2 m wide at the top. At the bottom of the pit, a sharpened punji stick would be hammered in. In some cases, the pit was concealed by light cover of wicker and a layer of soil.

An aquilifer was a soldier signifer bearing the eagle standard of a Roman legion. The name derives from the type of standard, aquila, meaning "eagle", and ferre, the Latin word for bringing or carrying. Before that time, the wolf, boar, bull and horse were also used. The eagle standard was the most important possession of the legion, and its loss was a terrible disgrace.

The Bellovaci were a Belgic tribe dwelling in the modern Picardy region, near the present-day city of Beauvais, during the Iron Age and the Roman period. After they were defeated by Caesar in 57 BC, they gave lukewarm support to the Gallic revolt led by Vercingetorix in 52 BC. The Bellovaci nonetheless organized resistance against Rome in 51 BC.

Commius was a king of the Belgic nation of the Atrebates, initially in Gaul, then in Britain, in the 1st century BC.

The Pictones were a Gallic tribe dwelling south of the Loire river, in the modern departments of Vendée, Deux-Sèvres and Vienne, during the Iron Age and Roman period.

An evocatus was a soldier in the Ancient Roman army who had served out his time and obtained an honorable discharge but had voluntarily enlisted again at the invitation of the consul or other commander.

In the course of his Gallic Wars, Julius Caesar invaded Britain twice: in 55 and 54 BC. On the first occasion, Caesar took with him only two legions, and achieved little beyond a landing on the coast of Kent. The second invasion consisted of 800 ships, five legions and 2,000 cavalry. The force was so imposing that the Celtic Britons did not contest Caesar's landing, waiting instead until he began to move inland. Caesar eventually penetrated into Middlesex and crossed the Thames, forcing the British warlord Cassivellaunus to pay tribute to Rome and setting up Mandubracius of the Trinovantes as a client king. The Romans then returned to Gaul without conquering any territory.
De Bello Africo is a Latin work continuing Julius Caesar's accounts of his campaigns, De Bello Gallico and De Bello Civili, and its sequel by an unknown author De Bello Alexandrino. It details Caesar's campaigns against his Republican enemies in the province of Africa.

Titus Terrasidius was a Roman Knight of the Equestrian order and an officer of the cavalry in Julius Caesar's Legio VII Claudia. He and other officers of the legion were sent out to negotiate provisions for the winter of 56–55 BC; they were captured by Breton tribes who were then subjugated as Caesar describes in his Commentarii de Bello Gallico:
The occasion of that war was this: Publius Crassus, a young man, had taken up his winter-quarters with the seventh legion among the Andes, who border upon the Ocean. He, as there was a scarcity of corn in those parts, sent out some officers of cavalry [who would be equites], and several military tribunes [who would be of senatorial rank] among the neighbouring states, for the purpose of procuring corn and provision; in which number Titus Terrasidius was sent among the Esubii; Marcus Trebius Gallus among the Curiosolitae; Quintus Velanius, [and] Titus Silius, amongst the Veneti.
Mamurra was a Roman military officer who served under Julius Caesar.
Vercassivellaunus was a Gaulish commander of the Arverni who led a relief force to assist Vercingetorix, who was besieged and low on supplies, in the Battle of Alesia. Caesar refers to him as a cousin of Vercingetorix. He encamped with his generals to the west of the battle. According to Caesar, their names were Commius, Viridomarus and Eporedorix. Sedullos, chief of the Lemovices, joined Vercassivellaunus with 10,000 of his own men and was killed at the battle. According to Caesar's "Commentarii de Bello Gallico", Vercassivellaunus was taken prisoner. It is speculated that he was subsequently strangled to death with the other Gaulish prisoners of war as part of the Triumph in which Caesar celebrated his victory over the Gauls.

The Ambarri were a Gallic people dwelling in the modern Ain department during the Iron Age and the Roman period.
Aegus and Roscillus were two chiefs of the Allobroges, who had served Julius Caesar with great fidelity in the Gallic Wars, and were treated by him with great distinction. They accompanied him in his campaigns against Pompey, but having been reproved by Caesar on account of depriving the cavalry of its pay and appropriating the booty to themselves, they deserted to Pompey in Greece. Aegus was afterwards killed in an engagement between the cavalry of Caesar and Pompey.
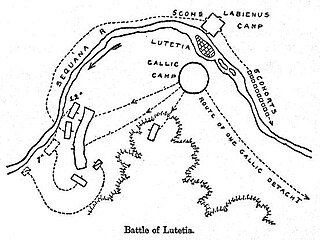
The Battle of Lutetia was a battle on the plain of Grenelle in what is now Paris between Roman forces under Titus Labienus and an anti-Roman Gallic coalition in 52 BC during the Gallic Wars. It was a Roman victory.
Caesar's Commentaries may refer to one of two works written by Julius Caesar:

Lucius Vorenus and Titus Pullo were two Roman centurions mentioned in the personal writings of Julius Caesar. Although it is sometimes stated they were members of the 11th Legion, Caesar never states the number of the legion concerned, giving only the words in ea legione. All that is known is that the legion in which they served under Caesar was one commanded at the time by Quintus Cicero.