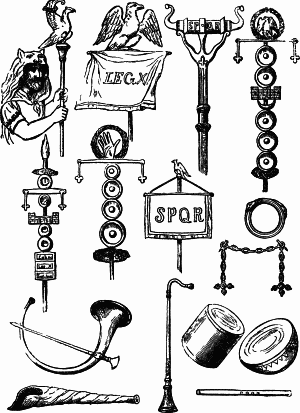A hammer is a tool, most often a hand tool, consisting of a weighted "head" fixed to a long handle that is swung to deliver an impact to a small area of an object. This can be, for example, to drive nails into wood, to shape metal, or to crush rock. Hammers are used for a wide range of driving, shaping, breaking and non-destructive striking applications. Traditional disciplines include carpentry, blacksmithing, warfare, and percussive musicianship.

Muay Thai, sometimes referred to as Thai boxing, is a combat sport that uses stand-up striking along with various clinching techniques. This discipline is known as the "Art of eight limbs", as it is characterised by the combined use of fists, elbows, knees and shins. Muay Thai became widespread internationally in the late 20th to 21st century, when Westernised practitioners from Thailand began competing in kickboxing and mixed-rules matches as well as matches under Muay Thai rules around the world. The professional league is governed by The Professional Boxing Association of Thailand (P.A.T), sanctioned by The Sports Authority of Thailand (S.A.T.).

A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry or projectiles such as arrows, by means of active blocks, as well as to provide passive protection by closing one or more lines of engagement during combat.

The tonfa, also spelled as tongfa or tuifa, also known as T-baton is a melee weapon with its origins in the armed component of Okinawan martial arts. It consists of a stick with a perpendicular handle attached a third of the way down the length of the stick, and is about 15–20 inches (380–510 mm) long. It was traditionally made from red or white oak, and wielded in pairs. The tonfa is believed to have originated in either China, Okinawa or Southeast Asia, where it is used in the respective fighting styles.
A mint is an industrial facility which manufactures coins that can be used as currency.

A grommet is a ring or edge strip inserted into a hole through thin material, typically a sheet of textile fabric, sheet metal or composite of carbon fiber, wood or honeycomb. Grommets are generally flared or collared on each side to keep them in place, and are often made of metal, plastic, or rubber. They may be used to prevent tearing or abrasion of the pierced material or protection from abrasion of the insulation on the wire, cable, line being routed through the penetration, and to cover sharp edges of the piercing, or all of the above.

Repoussé or repoussage is a metalworking technique in which a malleable metal is shaped by hammering from the reverse side to create a design in low relief. Chasing or embossing is a similar technique in which the piece is hammered on the front side, sinking the metal. The two techniques are often used in conjunction.

In martial arts, blocking is the act of stopping or deflecting an opponent's attack for the purpose of preventing injurious contact with the body. A block usually consists of placing a limb across the line of the attack.

A buckler is a small shield, up to 45 cm in diameter, gripped in the fist with a central handle behind the boss. While being used in Europe since antiquity, it became more common as a companion weapon in hand-to-hand combat during the Medieval and Renaissance periods. Its size made it poor protection against missile weapons but useful in deflecting the blow of an opponent's weapons, binding his arms, hindering his movements, or punching him.
A die is a specialized machine tool used in manufacturing industries to cut and/or form material to a desired shape or profile. Stamping dies are used with a press, as opposed to drawing dies and casting dies which are not. Like molds, dies are generally customized to the item they are used to create.

The scutum was a type of shield used among Italic peoples in antiquity, most notably by the army of ancient Rome starting about the fourth century BC.
A kite shield is a large, almond-shaped shield rounded at the top and curving down to a point or rounded point at the bottom. The term "kite shield" is a reference to the shield's unique shape, and is derived from its supposed similarity to a flying kite, although "leaf-shaped shield" and "almond shield" have also been used in recent literature. Since the most prominent examples of this shield have appeared on the Bayeux Tapestry, the kite shield has become closely associated with Norman warfare.

Footwork is a martial arts and combat sports term for the general usage of the legs and feet in stand-up fighting. Footwork involves keeping balance, closing or furthering the distance, controlling spatial positioning, and/or creating additional momentum for strikes.

A masonry heater is a device for warming an interior space through radiant heating, by capturing the heat from periodic burning of fuel, and then radiating the heat at a fairly constant temperature for a long period. Masonry heaters covered in tile are called cocklestoves. The technology has existed in different forms, from back into the Neoglacial and Neolithic periods. Archaeological digs have revealed excavations of ancient inhabitants utilizing hot smoke from fires in their subterranean dwellings, to radiate into the living spaces. These early forms have evolved into modern systems.
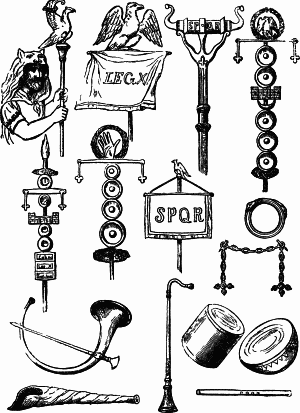
Roman military personal equipment was produced in large numbers to established patterns, and used in an established manner. These standard patterns and uses were called the res militaris or disciplina. Its regular practice during the Roman Republic and Roman Empire led to military excellence and victory. The equipment gave the Romans a very distinct advantage over their barbarian enemies, especially so in the case of armour. This does not mean that every Roman soldier had better equipment than the richer men among his opponents. According to Edward Luttwak, Roman equipment was not of a better quality than that used by the majority of Rome's adversaries. Other historians and writers have stated that the Roman army's need for large quantities of "mass produced" equipment after the Marian Reforms and subsequent civil wars led to a decline in the quality of Roman equipment compared to the earlier Republican era:
The production of these kinds of helmets of Italic tradition decreased in quality because of the demands of equipping huge armies, especially during civil wars...The bad quality of these helmets is recorded by the sources describing how sometimes they were covered by wicker protections, like those of Pompeius' soldiers during the siege of Dyrrachium in 48 BC, which were seriously damaged by the missiles of Caesar's slingers and archers.
It would appear that armour quality suffered at times when mass production methods were being used to meet the increased demand ..." and "...the reduced size curiasses would also have been quicker and cheaper to produce, which may have been a deciding factor at times of financial crisis, or where large bodies of men were required to be mobilized at short notice, possibly reflected in the poor-quality, mass produced iron helmets of Imperial Italic type C, as found, for example, in the River Po at Cremona, associated with the Civil Wars of AD 69 AD; Russell Robinson, 1975, 67
Up until then, the quality of helmets had been fairly consistent and the bowls well decorated and finished. However, after the Marian Reforms, with their resultant influx of the poorest citizens into the army, there must inevitably have been a massive demand for cheaper equipment, a situation which can only have been exacerbated by the Civil Wars...

A press brake is a machine used for bending sheet metal and metal plate, most commonly sheet metal. It forms predetermined bends by clamping the workpiece between a matching top tool and bottom die.

The Caetrati were a type of light infantry in ancient Iberia who often fought as skirmishers. They were armed with a caetra shield, swords, and javelins.

Caetra was the shield used by Iberian, Celtiberian, Gallaecian and Lusitanian warriors. The shield was circular shaped with a diameter between 30 cm to 90 cm. It was tied to the warrior's body with ropes or leather strips that passed over the shoulder and that gave great mobility to fight both on foot and on horseback. The shapes and decorations of the shields had variations in their metal, wood or leather protection. Warriors that carried this shield were usually light infantry called caetratus.

The Danum shield was a Roman shield found in the Danum Roman fort at Doncaster in 1971. It was discovered amid the remains of a bonfire and may have been intentionally disposed of during the partial abandonment of the fort. The shield was rectangular in shape and measured approximately 0.65 metres (2.1 ft) by 1.25 metres (4.1 ft). It is considered to have been part of the equipment of a Roman auxilium (non-citizen) soldier. An assessment in the 1970s considered it to have had an unusual vertical hand grip, suggesting a possible use by cavalry. However a recent work suggests the handgrip may have been horizontal and the shield used by an infantryman. The shield was covered in leather and was probably painted, though its original colour is not known. The outer face was decorated with bronze sheeting, possibly incised with a Celtic pattern.