Related Research Articles

Girnar is an ancient hill in Junagadh, Gujarat, India.
Vikram Samvat, also known as the Vikrami calendar is a Hindu calendar historically used in the Indian subcontinent and still used in several states. It is a solar calendar, using twelve to thirteen lunar months each solar sidereal years. The year count of the Vikram Samvat calendar is usually 57 years ahead of the Gregorian calendar, except during January to April, when it is ahead by 56 years.

Chanderi, is a town of historical importance in Ashoknagar District of the state Madhya Pradesh in India. It is situated at a distance of 127 km from Shivpuri, 37 km from Lalitpur, 55 km from Ashok Nagar and about 46 km from Isagarh. It is surrounded by hills southwest of the Betwa River. Chanderi is surrounded by hills, lakes and forests and is spotted with several monuments of the Bundela Rajputs and Malwa sultans. It is famous for ancient Jain Temples. Its population in 2011 was 33,081.
Wadhwan, also spelled Vadhwan, is a city and a municipality in Surendranagar district in the Indian state of Gujarat. Located on the banks of the Bhogavo River, around 3 km from Surendranagar and 111 km from Ahmedabad, Wadhwan is a known location for its old world royal charm and serene space with a life and culture of its own. It was historically the capital of Wadhwan State.

Gumla district is one of the twenty-four districts of Jharkhand state, India, and Gumla town is the administrative headquarters of this district.

Shankheshwar is a town in the Patan district of Gujarat state of India. It is an important place of pilgrimage for the followers of Jainism.
Bamnera is a small village situated along the inner margin of the southwestern part of the Thar Desert in the foothills of Aravali mountain range with panoramic landscapes and a few sandy tracks. In more urban geographical terms, it is situated in the Sumerpur tehsil of Pali District in the state of Rajasthan, 12.5 km west of Sheoganj-Sirohi District from Beawar-Radhanpur NH 14.
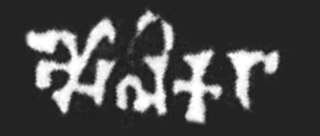
The Aulikara dynasty, was an ancient dynasty that ruled the Kingdom of Malwa between the 4th-century CE and 6th-century CE. They were based in the Malwa (Malava) region of central India near Mandsaur, with their power center near what is now western Madhya Pradesh, southeastern Rajasthan and northeastern Gujarat. Two royal houses belonging to this clan ruled over the present-day western Malwa region of Madhya Pradesh state from c. 350 CE to 550 CE, much of it as feudatories of the Gupta Empire.

There is a group of temples of Jainism on Mount Girnar near Junagadh in Junagadh district, Gujarat, India. These temples are sacred to both Digambara and the Śvetāmbara branches of Jainism.
The Nagvanshis of Chotanagpur, also known as the Khokhra chieftaincy, was an Indian dynasty which ruled the parts of Chota Nagpur plateau region during much of ancient, medieval and modern period. Phani Mukut Rai is considered the first king of dynasty claim to be son of Pundrika Naga, a mythical Naga. Lal Chintamani Sharan Nath Shahdeo (1931–2014) was last ruling king of the dynasty, until the estate was merged to the Republic of India.
The Nagpuria people, also Nagpuri or Sadan, are an Indo-Aryan speaking ethnolinguistic group who are the native speakers of the Nagpuri language and natives of the western Chota Nagpur Plateau region of Indian states of Jharkhand, Bihar, Chhattisgarh and Odisha.

Navratangarh (Doisagarh) was one of the capitals of the Nagvanshi dynasty, who ruled parts of what is now the state of Jharkhand, India. It is located in Sisai block of Gumla district. It is said that king Durjan Shah shifted his capital from Khukhragarh to Navratangarh. He constructed the fort between 1636 and 1639. The palace was a five-storeyed structure with its "water-gate" and garh-khai (moat) arrangement. It has a kiaclmy (court), a treasury house and a prison-cell with its underground dungeon. It was declared national heritage in 2009.

Raghunath Shah was a Nagvanshi king in the 17th century. He succeeded his father Ram Shah in 1663. His capital was at Navratangarh. He built several temples during his reign.

Ambika Temple, also known as Ambaji Temple, is a temple dedicated to goddess Ambikaon Girnar hill in Junagadh, Gujarat, India. The earliest mention of the temple is recorded in the 8th century. The present temple was built in the 15th century.
The Khayaravala dynasty, was a tribal kingdom that ruled parts of the present-day Indian states of Bihar and Jharkhand, during the 11th and 12th centuries. Their capital was located at Khayaragarh in Shahabad district. The dynasty ruled the Japila territory as feudatories of the Gahadavala dynasty of Varanasi. This is demonstrated by inscriptions which show land grants being made to the Khayaravalas.
Pratap Dhavala was Khayaravala king in 12th century. There are inscription of Pratapdhavala in Phulwaria, Tutrahi fall rock inscription of Vikram Samvat 1214, Tarachandi rock inscription of Vikram Samvat 1225.
Shri Pratapa was Khayaravala king in 13th century. There are inscription of Shri Pratapa in Rohtas of Vikram Samvat 1279. According to inscription he defeated a "Yavana" army; the "Yavana" here probably refers to a Muslim general. According to the inscription of Rohtas Fort, Shri Pratapa was descendant and successor of Pratapdhavala.
Ram Shah was Nagvanshi king in the 17th century. He succeed his brother Durjan Shah and ruled from 1640 to 1663 CE. Earlier their capital was at Khukhragarh, but later they shifted to Navratangarh. He was brother of king Durjan Shah.
Gajghat Rai was Nagvanshi king in 9th century. He succeeded Gajdant Rai.
Kapilnath Temple near Navratangarh, is a 17th-century temple dedicated to Shiva in Gumla district of Jharkhand. It was built by king Ram Shah in 1643 CE. Many people come to worship daily and in Shivratri festival.
References
- ↑ "Hapamuni". gumla.nic.in. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- ↑ Jharkhand Encyclopedia Hulgulanon Ki Partidhwaniyan-1 . Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- ↑ Ranjan, Manish (19 August 2002). Jharkhand Samanya Gyan. ISBN 9789351867982 . Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- ↑ "The Supreme Personality of Godhead at Hapamuni". Radha.name. 2 September 2019.
- ↑ "1100 years old Maa Mahamaya Temple is located in Gumla district, know what is the story behind its establishment". newsncr. 8 October 2021. Retrieved 17 August 2022.