
Lompoc is a city in Santa Barbara County, California. Located on the Central Coast, Lompoc has a population of 43,834 as of July 2021.

The Farallon Steamship Disaster was the wreck of a wooden Alaska Steamship Company passenger liner, SS Farallon, that hit Black Reef in Cook Inlet in the Territory of Alaska on 5 January 1910. All on board evacuated to a nearby island, where most had to survive for a month in a mid-winter climate before they were rescued. Six other survivors survived an attempt to row across Shelikof Strait in search of rescue for the stranded men.

Wapama, also known as Tongass, was a vessel last located in Richmond, California. She was the last surviving example of some 225 wooden steam schooners that served the lumber trade and other coastal services along the Pacific Coast of the United States. She was managed by the National Park Service at San Francisco Maritime National Historical Park until dismantled in August 2013.

The Nathan F. Cobb was a three-masted schooner named after the shipbuilder and founder of Cobb's Salvaging Company whose many rescues of stranded ships help lead to the formation of the United States Life-Saving Service. Despite its namesake's history of shipwreck rescues, the Nathan F. Cobb capsized in heavy seas on 1 December 1896 en route from Brunswick, Georgia to New York with a cargo of timber and cross ties. The cook and a shipmate drowned when they were swept overboard in violent seas. The crew righted the vessel by removing the three masts and they drifted for four days until they became grounded on a sandbar off Ormond Beach, Florida. Rescue attempts led to the drowning of volunteer Fred Waterhouse, whose body was never recovered, but no other crew members were lost. A plaque commemorates Fred Waterhouse's rescue efforts. The Cobb Cottage, a structure built using materials salvaged from the ship, is part of Ormond Beach's Historic Trail.
Sibyls were oracular women believed to possess prophetic powers in ancient Greece.

SS Myron was a wooden steamship built in 1888. She spent her 31-year career as lumber hooker, towing schooner barges on the Great Lakes. She sank in 1919, in a Lake Superior November gale. All of her 17 crew members were killed but her captain survived. He was found drifting on wreckage near Ile Parisienne. Her tow, the Miztec, survived. Myron defied the adage that Lake Superior "seldom gives up her dead" when all 17 crewmembers were found frozen to death wearing their life jackets. Local residents chopped eight of Myron's sailors from the ice on the shore of Whitefish Bay and buried them at the Mission Hill Cemetery in Bay Mills Township, Michigan.
The Advance was a composite schooner built in 1874 at Auckland, New Zealand, that was wrecked when she drifted onto rocks at Henrys Head, Botany Bay, New South Wales, Australia, on 12 June 1902, whilst carrying ballast between Wollongong and Newcastle, New South Wales.

Matthew Turner was an American sea captain, shipbuilder and designer. He constructed 228 vessels, of which 154 were built in the Matthew Turner shipyard in Benicia. He built more sailing vessels than any other single shipbuilder in America, and can be considered "the 'grandaddy' of big time wooden shipbuilding on the Pacific Coast."
Many ships have wrecked in and around San Francisco Bay. For centuries San Francisco Bay, with its strong currents, rocky reefs, and low fog conditions has experienced more than a hundred shipwrecks. Ever since San Francisco Bay was discovered during the land expedition of Gaspar de Portolà in 1769, it has been one of the most popular harbors.

Surf is an unincorporated area of Santa Barbara County, California, located along the Pacific coast within a publicly accessible area of Vandenberg Space Force Base west of the city of Lompoc. The site originally was established as a railroad town, with its growth peaking after Vandenberg was established in 1941. Since 2000 the site has just consisted of Surf Beach and the unstaffed Lompoc–Surf Amtrak Station. California State Route 246 used to run to Surf, but in 1984 the highway was truncated at Lompoc and the road from Lompoc to Surf is designated West Ocean Avenue.

The steam schooner San Pedro (1899-1920) was the first vessel constructed by John Lindstrom's shipbuilding yard at Aberdeen, Washington in 1899. She was one of many steam schooners constructed by the yard that year, and weighed 456 tons. On October 3, 1905, the San Pedro accompanied the tugboat Pomo when the latter was towing the lumber schooner Santa Barbara, damaged by grounding, to Hunter's Point, California.
J.W. Clise was a four master schooner built in 1904 in United States and sailed for both Norwegian and American companies.
The North Pacific Steamship Company was a shipping company operating along the west coast of the United States and to South America during the late 19th century and early 20th century.

SS Roanoke (1882–1916) was a passenger and cargo ship built by John Roach & Sons in Chester, Pennsylvania. The Roanoke was built for the Old Dominion Steamship Company's service from New York to Norfolk Virginia. In 1898 the ship was sold to the North American Transportation and Trading Company to take miners, supplies and gold between Seattle and ports in Alaska. Later the Roanoke was sold to the Oregon-based North Pacific Steamship Company. In 1907, the Roanoke helped to rescue the survivors of her former running mate Columbia. On May 9, 1916, the Roanoke sank in heavy seas off the California coast near San Luis Obispo with the loss of 47 lives. There were only three survivors.
The Hive Shipwreck is a heritage-listed shipwreck site of the Hive, a former convict transportation ship located approximately 40 metres (130 ft) off Bherwerre Beach, Jervis Bay Territory, Australia. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 1 April 2010.

Mohawk was a steam passenger ship built in 1908 by William Cramp & Sons of Philadelphia for Clyde Steamship Company with intention of operating between New England and southern ports of the United States. In early January 1925 the ship caught fire off New Jersey coast and eventually was abandoned and scuttled by the crew without a loss of life.

The SS Francis Hinton was a wooden-hulled steam barge that sank in a gale off the coast of Manitowoc, Wisconsin, on Lake Michigan in 1909 while heavily laden with a cargo of lumber. On December 16, 1996, the wreck of the Francis Hinton was listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
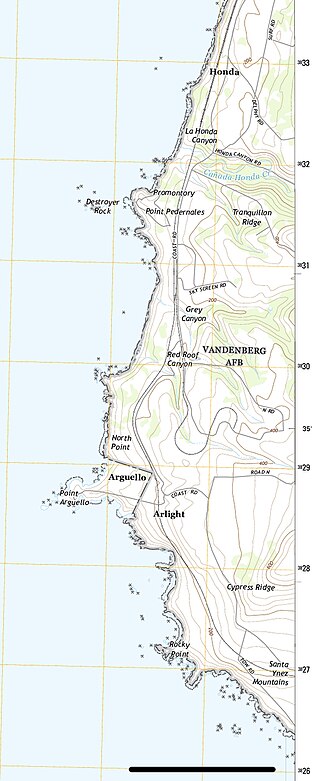
Honda was a remote and sparsely populated rural district in the vicinity of Cañada Honda Creek in Santa Barbara County, California, United States. The area produced sweet peas and beans, and supported dairy farms. A newspaper account of 1947 stated, "The Jesus Maria rancho, Packard rancho, Bear Creek ranch, Honda section, and a large area in the lower [Lompoc] valley once yielded great crops of cattle and produce and furnished a livelihood for many families." The area is now part of Vandenberg Space Force Base.

Craig Shipbuilding was a shipbuilding company in Long Beach, California. To support the World War I demand for ships Craig Shipbuilding shipyard switched over to military construction and built: US Navy Submarines and Cargo Ships. Craig Shipbuilding was started in 1906 by John F. Craig. John F. Craig had worked in Toledo, Ohio with his father, John Craig (1838-1934), and Blythe Craig, both shipbuilders, their first ship was built in 1864 at Craig Shipbuilding Toledo. John F. Craig opened his shipbuilding company in Port of Long Beach on the south side of Channel 3, the current location of Pier 41 in the inner harbor, becoming the port's first shipyard. In 1908 Craig Shipbuilding was given the contract to finishing dredging of the Port of Long Beach inner harbor and to dredge the channel connecting it to the Pacific ocean. In 1917 Craig sold the shipyard to the short-lived California Shipbuilding Company. but then opened a new shipyard next to the one he just sold and called it the Long Beach Shipbuilding Company. The Long Beach Shipbuilding Company built cargo ships in 1918, 1919, and 1920 for the United States Shipping Board.













