
Justinian I, also known as Justinian the Great, was the Eastern Roman emperor from 527 to 565.
Procopius of Caesarea was a prominent late antique Greek scholar and historian from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman general Belisarius in Emperor Justinian's wars, Procopius became the principal Roman historian of the 6th century, writing the History of the Wars, the Buildings, and the Secret History.

The Battle of Ad Decimum took place on September 13, 533 between the armies of the Vandals, commanded by King Gelimer, and the Byzantine Empire, under the command of General Belisarius. This event and events in the following year are sometimes jointly referred to as the Battle of Carthage, one of several battles to bear that name. The Byzantine victory marked the beginning of the end for the Vandals and began the reconquest of the west under the Emperor Justinian I.

Totila, original name Baduila, was the penultimate King of the Ostrogoths, reigning from 541 to 552 AD. A skilled military and political leader, Totila reversed the tide of the Gothic War, recovering by 543 almost all the territories in Italy that the Eastern Roman Empire had captured from his Kingdom in 540.
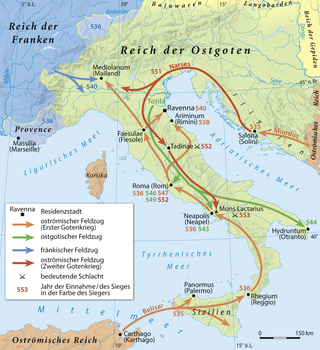
The Gothic War between the Byzantine Empire during the reign of Emperor Justinian I and the Ostrogothic Kingdom of Italy took place from 535 to 554 in the Italian Peninsula, Dalmatia, Sardinia, Sicily and Corsica. It was one of the last of the many Gothic Wars against the Roman Empire. The war had its roots in the ambition of the Byzantine emperor Justinian I to recover the provinces of the former Western Roman Empire, which the Romans had lost to invading barbarian tribes in the previous century, during the Migration Period.

The Iberian War was fought from 526 to 532 between the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire over the eastern Georgian kingdom of Iberia—a Sasanian client state that defected to the Byzantines. Conflict erupted among tensions over tribute and the spice trade.

The Anastasian War was fought from 502 to 506 between the Byzantine Empire and the Sasanian Empire. It was the first major conflict between the two powers since 440, and would be the prelude to a long series of destructive conflicts between the two empires over the next century.

The sack of Rome in 546 was carried out by the Gothic king Totila during the Gothic War of 535–554 between the Ostrogoths and the Eastern Roman Empire. Totila was based at Tivoli and, in pursuit of his quest to reconquer the region of Latium, he moved against Rome. The city endured a siege lasting almost a year before falling to the Goths.

Belisarius was a military commander of the Byzantine Empire under the emperor Justinian I. He was instrumental in the reconquest of much of the Mediterranean territory belonging to the former Western Roman Empire, which had been lost less than a century prior.
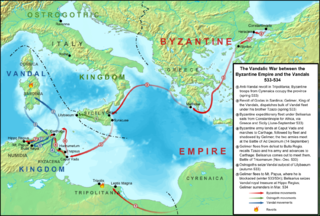
John the Armenian was a Byzantine official and military leader. There is no written account of his physical appearance or confirmation of the year he was born. John served as financial manager of the campaign and was a close friend of Belisarius. He was killed during the Vandalic War in 533. John the Armenian was the linchpin general of the Byzantine army during the Vandalic war.
(Anicius) Maximus was a Roman senator and patrician during the Ostrogothic kingdom, who celebrated the last games in the Flavian Amphitheater.

The Battle of Satala was fought between the forces of the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire and the Sassanid (Persian) Empire in summer 530, near Satala in Byzantine Armenia. The Persian army approached the city to lay siege, when it was attacked in the rear by a small Byzantine force. The Persians turned back to meet them, but were then attacked by the main army from inside the city. A determined attack by a Byzantine unit led to the loss of the Persian general's flag, causing the panicking Persians to retreat.
The siege of Naples in 536 was a successful siege of Naples by the Eastern Roman Empire under Belisarius during the Gothic War.

Petra was a fortified town on the eastern Black Sea coast, in Lazica in what is now western Georgia. In the 6th century, under the Byzantine emperor Justinian I, it served as an important Eastern Roman outpost in the Caucasus and, due to its strategic location, became a battleground of the 541–562 Lazic War between Rome and Sasanian Persia (Iran). Mainstream scholarly opinion identifies Petra with a ruined settlement of Late Antiquity at the village of Tsikhisdziri in Adjara, southwestern Georgia.
The Battle of the River Bagradas or Battle of Membresa was an engagement in 536 AD between Byzantine forces under Belisarius and rebel forces under Stotzas. Stotzas had besieged Carthage shortly before with a force of 8,000 rebels, 1,000 Vandal soldiers, and many slaves. Belisarius had only 2,000 men under his command. Upon Belisarius’ arrival the rebels had lifted the siege. Before battle commenced Stotzas wanted to reposition his troops so the high wind would not aid the Byzantines in the fighting. Stotzas neglected to move any troops to cover this movement. Belisarius, seeing that much of the rebel force was disorganised and exposed, decided to charge the rebels, who almost immediately fled in disorder. Rebel casualties remained relatively light as the Byzantine force was too small to safely chase the fleeing rebels. Instead Belisarius allowed his men to plunder the abandoned rebel camp.
The siege of Auximus was a siege during Justinian’s Gothic War which took place in the year 539. It ended with Belisarius’ Byzantine force victorious. The Gothic garrison surrendered the town and joined the Byzantines after negotiations. The siege lasted 7 months.
The Siege of Ariminum also referred to as the siege of Rimini was fought between Byzantine forces under Belisarius and John and an Ostrogothic force. The Goths lifted the siege after Belisarius approached with multiple forces from multiple angles. He also had his men light extra camp fires, this way it seemed to the besieging Goths like a large force was approaching them.
The siege of Urbinus also called siege of Urbino or siege of Urbinum took place in the year 538 during Justinian's Gothic War. Earlier, when John took Ariminum, he had bypassed Auximus and Urbinus which would have to be taken now to secure the road to Ravenna. The Gothic king, Witigis, had sent a man called Moras with 2.000 troops to defend the city. In the year 538, the Byzantine commander, Belisarius went to besiege the town while another strong Byzantine contingents besieged Urviventus. The forces of Narses and John, other Byzantine commanders, who were undermining Belisarius' authority, joined him in this venture. Thinking the defenders would be terrified on seeing the Byzantine army, Belisarius sent envoys offering the garrison a chance to surrender. Narses and John set up camp separately form Belisarius, on the other side of the town, and, after negotiations with the garrison failed, totally abandoned the siege. They declared taking the town impossible and moved to capture Aemilia but while Belisarius was preparing to assault the town surrendered due to the failure of its spring. Astonished by such success, Narses sent John to capture Caesena but this assault failed. John then moved to and managed to capture Forocornelius. After this siege Belisarius moved to support in the siege of Urviventus, also capturing that city shortly after.
The siege of Ravenna of 539-540 took place during Justinian’s Gothic War.
The Battle of Mammes or Battle of Mamma was an engagement between troops of the Byzantine Empire and an army of Moors in 534. The Byzantines were led by Solomon. The Moors used a tactic that had worked well with Vandals, they made a circle of camels which scared Byzantine horses to such an extent that horse archery became impractical. The Moors also hid some of their own cavalry in some nearby mountains. Solomon anticipated the trap and sent men to the side of the circle not facing the mountains. Due to the Moor formation these were not able to do much damage and when the Moors charged the fighting turned against them. Solomon then decided to attack the other side of the circle, predicting it to be weakened to such an extent that the hidden cavalry could not spring into action in time. Solomon’s prediction was correct, the Byzantines quickly broke through. They killed hundreds of camels, enslaved the Moor women and children and according to Procopius slew 10,000 men. The situation was not yet stabilized and the Moors soon returned but were decisively defeated at Mount Burgaon.








