
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.

Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock containing 25% to 75% ash is described as tuffaceous. Tuff composed of sandy volcanic material can be referred to as volcanic sandstone.

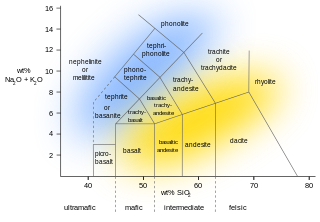
Rhyolite is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals (phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The mineral assemblage is predominantly quartz, sanidine, and plagioclase. It is the extrusive equivalent to granite.

Andesite is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende.
Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as their creating process, shape, elevation, slope, orientation, rock exposure, and soil type.

Misti, also known as Putina or Guagua Putina, is a stratovolcano of andesite, dacite, and rhyolite located in southern Peru near the city of Arequipa. With its seasonally snow-capped, symmetrical cone, Misti stands at 5,822 metres (19,101 ft) above sea level and lies between the Chachani massif and Pichu Pichu volcano. Its last eruption was in 1985, 198 years after its previous documented eruption.
Extrusive rock refers to the mode of igneous volcanic rock formation in which hot magma from inside the Earth flows out (extrudes) onto the surface as lava or explodes violently into the atmosphere to fall back as pyroclastics or tuff. In contrast, intrusive rock refers to rocks formed by magma which cools below the surface.

Scoria is a pyroclastic, highly vesicular, dark-colored volcanic rock that was ejected from a volcano as a molten blob and cooled in the air to form discrete grains or clasts. It is typically dark in color, and basaltic or andesitic in composition. Scoria is relatively low in density as a result of its numerous macroscopic ellipsoidal vesicles, but in contrast to pumice, all scoria has a specific gravity greater than 1 and sinks in water.

Medicine Lake Volcano is a large shield volcano in northeastern California about 30 mi (50 km) northeast of Mount Shasta. The volcano is located in a zone of east-west crustal extension east of the main axis of the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the Cascade Range. The 0.6 mi (1 km) thick shield is 22 mi (35 km) from east to west and 28 to 31 mi from north to south, and covers more than 770 sq mi (2,000 km2). The underlying rock has downwarped by 0.3 mi (0.5 km) under the center of the volcano. The volcano is primarily composed of basalt and basaltic andesite lava flows, and has a 4.3 by 7.5 mi caldera at the center.
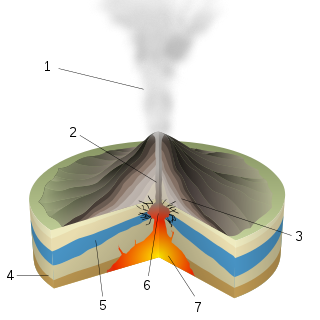
A phreatic eruption, also called a phreatic explosion, ultravulcanian eruption or steam-blast eruption, occurs when magma heats ground water or surface water. The extreme temperature of the magma causes near-instantaneous evaporation of water to steam, resulting in an explosion of steam, water, ash, rock, and volcanic bombs. At Mount St. Helens in Washington state, hundreds of steam explosions preceded the 1980 Plinian eruption of the volcano. A less intense geothermal event may result in a mud volcano.

Goat Rocks is an extinct stratovolcano in the Cascade Range, located between Mount Rainier and Mount Adams in southern Washington, in the United States. Part of the Cascade Volcanoes, it was formed by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca Plate under the western edge of the North American Plate. The volcano was active from 3.2 million years ago until eruptions ceased between 1 and 0.5 million years ago. Throughout its complex eruptive history, volcanism shifted from silicic explosive eruptions to voluminous, mafic activity.

La Garita Caldera is a large caldera in the San Juan volcanic field in the San Juan Mountains around the town of Creede in southwestern Colorado, United States. It is west of La Garita, Colorado. The eruption that created the La Garita Caldera is among the largest known volcanic eruptions in Earth's history, as well as being one of the most powerful known supervolcanic events.

Fiamme are lens-shapes, usually millimetres to centimetres in size, seen on surfaces of some volcaniclastic rocks. They can occur in welded pyroclastic fall deposits and in ignimbrites, which are the deposits of pumiceous pyroclastic density currents. The name fiamme comes from the Italian word for flames, describing their shape. The term is descriptive and non-genetic.
The Mount Pleasant Caldera is a large eroded Late Devonian volcanic caldera complex, located in the northern Appalachian Mountains of southwestern New Brunswick, Canada. It is one of few noticeable pre-Cenozoic calderas, and its formation is associated to a period of crustal thinning that followed the Acadian orogeny in the northern Appalachian Mountains. It sits relatively near to the coastline.

Igneous rock, or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava.

The Canadian Cascade Arc, also called the Canadian Cascades, is the Canadian segment of the North American Cascade Volcanic Arc. Located entirely within the Canadian province of British Columbia, it extends from the Cascade Mountains in the south to the Coast Mountains in the north. Specifically, the southern end of the Canadian Cascades begin at the Canada–United States border. However, the specific boundaries of the northern end are not precisely known and the geology in this part of the volcanic arc is poorly understood. It is widely accepted by geologists that the Canadian Cascade Arc extends through the Pacific Ranges of the Coast Mountains. However, others have expressed concern that the volcanic arc possibly extends further north into the Kitimat Ranges, another subdivision of the Coast Mountains, and even as far north as Haida Gwaii.
Calabozos is a Holocene caldera in central Chile's Maule Region. Part of the Chilean Andes' volcanic segment, it is considered a member of the Southern Volcanic Zone (SVZ), one of the three distinct volcanic belts of South America. This most active section of the Andes runs along central Chile's western edge, and includes more than 70 of Chile's stratovolcanoes and volcanic fields. Calabozos lies in an extremely remote area of poorly glaciated mountains.
Cerro Morado is a monogenetic volcanic field, in Argentina. It is part of a group of mafic volcanic centres in the Altiplano-Puna region, which is dominated by silicic rocks such as dacitic - rhyolitic rocks.

Chachani is a volcanic group in southern Peru, 22 kilometres (14 mi) northwest of the city of Arequipa. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, it is 6,057 metres (19,872 ft) above sea level. It consists of several lava domes and individual volcanoes such as Nocarane, along with lava shields such as the Airport Domes. Underneath Chachani lies a caldera.















