Related Research Articles

Cardiac arrest, also known as sudden cardiac arrest, is when the heart suddenly and unexpectedly stops beating. As a result, blood cannot properly circulate around the body and there is diminished blood flow to the brain and other organs. When the brain does not receive enough blood, this can cause a person to pass out and become unresponsive. Cardiac arrest is also identified by a lack of central pulses and abnormal or absent breathing.

Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation, or mouth to mouth in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest. It is recommended for those who are unresponsive with no breathing or abnormal breathing, for example, agonal respirations.

Advanced cardiac life support, advanced cardiovascular life support (ACLS) refers to a set of clinical guidelines for the urgent and emergent treatment of life-threatening cardiovascular conditions that will cause or have caused cardiac arrest, using advanced medical procedures, medications, and techniques. ACLS expands on Basic Life Support (BLS) by adding recommendations on additional medication and advanced procedure use to the CPR guidelines that are fundamental and efficacious in BLS. ACLS is practiced by advanced medical providers including physicians, some nurses and paramedics; these providers are usually required to hold certifications in ACLS care.
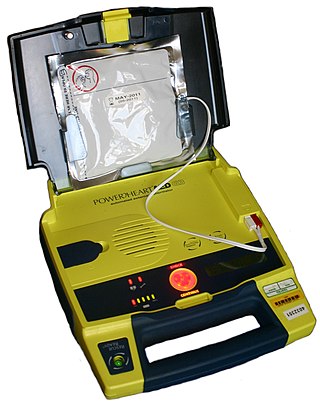
An automated external defibrillator or automatic electronic defibrillator (AED) is a portable electronic device that automatically diagnoses the life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias of ventricular fibrillation (VF) and pulseless ventricular tachycardia, and is able to treat them through defibrillation, the application of electricity which stops the arrhythmia, allowing the heart to re-establish an effective rhythm.

The National University of Singapore (NUS) is a national public collegiate and research university in Singapore. It was officially established in 1980 by the merger of the University of Singapore and Nanyang University.

The American Heart Association (AHA) is a nonprofit organization in the United States that funds cardiovascular medical research, educates consumers on healthy living and fosters appropriate cardiac care in an effort to reduce disability and deaths caused by cardiovascular disease and stroke. They are known for publishing guidelines on cardiovascular disease and prevention, standards on basic life support, advanced cardiac life support (ACLS), pediatric advanced life support (PALS), and in 2014 issued the first guidelines for preventing strokes in women. The American Heart Association is also known for operating a number of highly visible public service campaigns starting in the 1970s, and also operates several fundraising events.
Basic life support (BLS) is a level of medical care which is used for patients with life-threatening illnesses or injuries until they can be given full medical care by advanced life support providers. It can be provided by trained medical personnel, such as emergency medical technicians, and by qualified bystanders.

Laerdal is a multinational company that develops products and programs for healthcare providers, voluntary organizations, educational institutions, hospitals, and the military worldwide. Laerdal has almost 2,000 employees in 26 countries. The headquarters is located in Stavanger, Norway.

The British Heart Foundation (BHF) is a cardiovascular research charity in the United Kingdom. It funds medical research related to heart and circulatory diseases and their risk factors, and runs influencing work aimed at shaping public policy and raising awareness.

Singapore General Hospital (SGH) is an academic health science centre and tertiary referral hospital in Singapore. It is located next to the Bukit Merah and Chinatown districts of the Central Region, close to the Outram Community Hospital (OCH), which functions as a supplementary community and rehabilitation hospital to SGH for newly-discharged patients. There is also the Outram Polyclinic to complement outpatient care. All of these institutions are operated by SingHealth, which comes under the purview of the Ministry of Health (MOH).

The National University Hospital (NUH) is a tertiary referral hospital and academic medical centre in Singapore, located in Kent Ridge. It is a 1,160-bed tertiary hospital serving more than 670,000 outpatients and 49,000 inpatients and serves as a clinical training centre and research centre for the medical and dental faculties of the National University of Singapore (NUS).

Singapore Health Services, commonly known as SingHealth, is Singapore's largest group of healthcare institutions. The group was formed in 2000 and consists of four public hospitals, three community hospitals, five national specialty centres and a network of eight polyclinics. The Singapore General Hospital is the largest hospital in the group and serves as the flagship hospital for the cluster.

Nanyang Academy of Fine Arts is a publicly-funded post-secondary arts institution in Singapore, and a constituent college of the University of the Arts Singapore (UAS) from 2024.
The chain of survival refers to a series of actions that, properly executed, reduce the mortality associated with sudden cardiac arrest. Like any chain, the chain of survival is only as strong as its weakest link. The six interdependent links in the chain of survival are early recognition of sudden cardiac arrest and access to emergency medical care, early CPR, early defibrillation, early advanced cardiac life support, and physical and emotional recovery. The first three links in the chain can be performed by lay bystanders, while the second three links are designated to medical professionals. Currently, between 70 and 90% of cardiac arrest patients die before they reach the hospital. However, a cardiac arrest does not have to be lethal if bystanders can take the right steps immediately.
Pediatric advanced life support (PALS) is a course offered by the American Heart Association (AHA) for health care providers who take care of children and infants in the emergency room, critical care and intensive care units in the hospital, and out of hospital. The course teaches healthcare providers how to assess injured and sick children and recognize and treat respiratory distress/failure, shock, cardiac arrest, and arrhythmias.

Jose Chacko Periappuram is an Indian cardiac surgeon and medical writer who performed the first successful heart transplant in the state of Kerala, India, as well as the first successful heart retransplant in the country. His other achievements include the first beating heart, awake bypass and total arterial revascularization surgeries in the state. Periappuram is a fellow of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh, the Royal College of Surgeons of Glasgow and the Royal College of Surgeons of London. He is the founder and chairman of "Heart Care Foundation", a charitable trust that financially assists poor heart patients. The Government of India awarded him the Padma Shri, the fourth highest civilian award, in 2011.
Freddy Boey is a Singaporean academic currently serving as the president of the City University of Hong Kong. Boey was previously the deputy president of the National University of Singapore (NUS), overseeing the university's initiatives and activities in the areas of innovation, entrepreneurship and research translation, as well as graduate studies. He was previously the senior vice president of NUS. Before joining NUS in 2018, Boey was deputy president and provost of Nanyang Technological University (NTU) from July 2011 to September 2017. Prior to these appointments, he was the chair of NTU's School of Materials Science and Engineering from 2005 to 2010.
Temasek Foundation International is a Singapore-based non-profit organisation under the philanthropic arm of the Singapore state sovereign fund Temasek Holdings. Temasek has established 17 endowments since 1974, focused on promoting social and cultural interaction, education, and aid for the disadvantaged in Asia.

The Cyber Security Agency (CSA) is a government agency under the Prime Minister's Office, but is managed by the Ministry of Communications and Information of the Government of Singapore. It provides centralised oversight of national cyber security functions and works with sector leads to protect Singapore's Critical Information Infrastructure (CII), such as the energy and banking sectors. Formed on 1 April 2015, the agency also engages with various industries and stakeholders to heighten cyber security awareness as well as to ensure the development of Singapore's cyber security. It is headed by the Commissioner of Cybersecurity, David Koh.

The COVID-19 vaccination in Singapore is an ongoing immunisation campaign against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the virus that causes coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), in response to the ongoing pandemic in the country. Singapore has a very high vaccination rate, with more than 92% of its total population having completed their vaccination regimen.
References
- 1 2 3 "About Us". Singapore Heart Foundation. 2 December 2014. Retrieved 2 August 2015.
- 1 2 3 "Organisation Profile Details". Ministry of Culture, Community and Youth . 2 December 2014. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- 1 2 "Annual Report 2019/2020" (PDF). Singapore Heart Foundation. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ↑ "Forum: Make eye goggles part of publicly accessible emergency equipment". The Straits Times. 26 October 2020. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- 1 2 "Asia Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS) Public Education Forum". National University of Singapore. 9 September 2017. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ↑ "Programmes". Singapore Heart Foundation. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ↑ "Take a course | Singapore Heart Foundation". www.myheart.org.sg. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ↑ "Singapore Heart Foundation launches Asia's first ever CPR Kiosk". BioSpectrum Asia. 28 September 2018. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ↑ "Asia's first kiosks for learning hands-only CPR launched in Singapore". The Straits Times. 29 September 2018. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ↑ "Register an AED | Singapore Heart Foundation". www.myheart.org.sg. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ↑ "Singapore Heart Foundation launches new heart-wellness centre". The Straits Times. 14 April 2014. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ↑ "Cardiovascular disease the leading cause of death for women in Singapore last year". The Straits Times. 4 October 2020. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ↑ "Covid-19 and hypertension: What are the links and risks?". The Straits Times. 31 May 2020. Retrieved 8 November 2020.
- ↑ "National Heart Week/World Heart Day 2020 Virtual | Singapore Heart Foundation". www.myheart.org.sg. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ↑ "National Heart Week/World Heart Day 2021 Virtual | Singapore Heart Foundation". www.myheart.org.sg. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ↑ Auto, Hermes (17 September 2022). "National Heart Week intensifies fight against high blood cholesterol | The Straits Times". www.straitstimes.com. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ↑ toneads. "Largest Mass CPR + AED Certification Workshop | Singapore Book Of Records" . Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ↑ "Knowledge, Attitudes & Practices (KAP) of CPR+AED Survey 2020 | Singapore Heart Foundation". www.myheart.org.sg. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- 1 2 3 Auto, Hermes (17 January 2021). "New female manikin vest to help train rescuers on proper CPR technique for women | The Straits Times". www.straitstimes.com. Retrieved 11 October 2022.