
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent islands such as the Mentawai Islands, Enggano Island, Nias Island, Simeulue Island, Riau Islands, Bangka Belitung Islands and Krakatoa archipelago.

Southeast Asia or Southeastern Asia is the southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are geographically south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent and north-west of Australia. Southeast Asia is bordered to the north by East Asia, to the west by South Asia and the Bay of Bengal, to the east by Oceania and the Pacific Ocean, and to the south by Australia and the Indian Ocean. The region is the only part of Asia that lies partly within the Southern Hemisphere, although the majority of it is in the Northern Hemisphere. In contemporary definition, Southeast Asia consists of two geographic regions:
- Mainland Southeast Asia, also known historically as Indochina, comprising Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar, Peninsular Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam.
- Maritime Southeast Asia, also known historically as Nusantara, the East Indies, or the Malay Archipelago, comprising the Andaman and Nicobar Islands (India), Ashmore and Cartier Islands (Australia), Brunei, Christmas Island (Australia), the Cocos (Keeling) Islands (Australia), East Malaysia, East Timor, Indonesia, the Philippines and Singapore.

The Strait of Malacca or Straits of Malacca is a narrow, 890 km (550 mi) stretch of water between the Malay Peninsula and the Indonesian island of Sumatra. As the main shipping channel between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean, it is one of the most important shipping lanes in the world. It is named after the Malacca Sultanate that ruled over the archipelago between 1400 and 1511, the center of administration of which was located in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia.

The Riau Islands is a province of Indonesia. It comprises a total of 1,796 islands scattered between the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, and Borneo. Situated on one of the world's busiest shipping lanes along the Malacca Strait and the South China Sea, the province shares water borders with neighboring countries such as Singapore, Malaysia, and Vietnam. The Riau Islands also has a relatively large potential of mineral resources, energy, as well as marine resources. The capital of the province is Tanjung Pinang and the largest city is Batam.
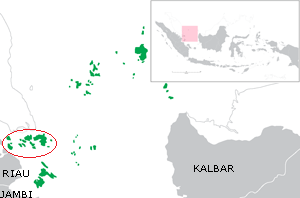
The Riau Archipelago is a geographic term for the core group of islands within the Riau Islands Province in Indonesia, and located south of Singapore. Before the province of Riau Islands was formed, there was no ambiguity in term; however, in Indonesian language, both the archipelago and administrative province are referred to as simply "Kepulauan Riau". The province may have the word "Provinsi" preceding it for clarity. Additionally the term BBK for Batam Bintan Karimun may refer to the archipelago.

Batam is the largest city in the province of Riau Islands, Indonesia. The city administrative area covers three main islands of Batam, Rempang, and Galang, as well as several small islands. Batam Island is the core urban and industrial zone, while both Rempang Island and Galang Island maintain their rural character and are connected to Batam Island by short bridges. Batam is an industrial boomtown, an emerging transport hub, and part of a free trade zone in the Indonesia–Malaysia–Singapore Growth Triangle, located 20 km (12 mi) off Singapore's south coast and also part of the Indonesia–Malaysia–Thailand Growth Triangle.

Maritime Southeast Asia comprises the countries of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore and East Timor. Maritime Southeast Asia is sometimes also referred to as Island Southeast Asia, Insular Southeast Asia or Oceanic Southeast Asia. The 16th-century term "East Indies" and the later 19th-century term "Malay Archipelago" are also used to refer to maritime Southeast Asia.

Pekanbaru is the capital of Indonesian province of Riau, and a major economic center on the eastern part of Sumatra Island. Its name is derived from the Malay words for 'new market'. It has an area of 32.26 km2 (12.46 sq mi) with a population of 1,035,834 at the 2010 Census, and 1,121,562 according to the latest official estimate for mid 2019. Located on the banks of the Siak River, which flows into the Strait of Malacca, Pekanbaru has direct access to the busy strait and long known as a trading port. Pekanbaru was originally built as a market by Minangkabau merchants during the 18th century.

Bintan Island or Negeri Segantang Lada is an island in the Riau archipelago of Indonesia. It is part of the Riau Islands province, the capital of which, Tanjung Pinang, lies in the island's south and is the island's main community.

Anambas Islands Regency is a small archipelago of Indonesia, located 150 nautical miles northeast of Batam Island in the North Natuna Sea between the Malaysian mainland to the west and the island of Borneo to the east. Geographically part of the Tudjuh Archipelago, it is administratively a regency within the Riau Islands Province. It covers a land area of 590.2 km2 and had a population of 37,411 at the 2010 Census. The administrative centre is at Tarempa on Siantan Island.

The Orang Laut are several seafaring ethnic groups and tribes living around Singapore, peninsular Malaysia and the Indonesian Riau Islands. The Orang Laut are commonly identified as the Orang Seletar from the Straits of Johor, but the term may also refer to any Malay origin people living on coastal islands, including those of Andaman Sea islands of India and those in Thailand and Burma, commonly known as Moken.
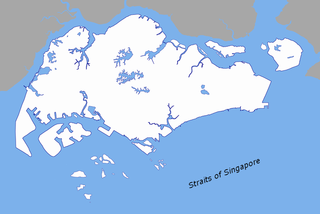
The Singapore Strait is a 105-kilometre-long (65 mi), 16-kilometre-wide (9.9 mi) strait between the Strait of Malacca in the west and the Karimata Strait in the east. Singapore is on the north of the channel, and the Riau Islands are on the south. The Indonesia-Singapore border lies along the length of the strait.
Galang is an island of 80 km2 located 25 mi (40 km) southeast of Batam, belonging to a group of three islands called Barelang. Part of the Riau Archipelago, Indonesia, Galang is located just south of Batam and Rempang which themselves are just south of Singapore and Johor. The nearest city to Galang is Tanjung Pinang on Bintan, about a 30-minute boat ride away. The island is connected by the Barelang Bridge to Rempang and Batam.
The Sijori was established in 1994 between three countries, Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore, to strengthen economic links in the region and optimise the complementarity between the three countries. It started off as the SIJORI Growth Triangle in 1989, which includes Singapore, Johor, and a part of Riau Islands Province, specifically the Riau Archipelago.
A fixed link or fixed crossing is a persistent, unbroken road or rail connection across water that uses some combination of bridges, tunnels, and causeways and does not involve intermittent connections such as drawbridges or ferries. A bridge–tunnel combination is commonly used for major fixed links.
The Indonesia–Singapore border is a maritime boundary in the Straits of Singapore between Indonesia's Riau Islands which lie to the south of the border, and the islands of Singapore which lie to the north. The Straits of Singapore is one of the region's busiest waterways as it is the main channel for Singapore's ports.

Kundur Island is an island within the Riau Archipelago, part of the Riau Islands Province of Indonesia. It lies at about 80 kilometres southwest of Singapore, 76 kilometres (47 mi) southwest of Batam, 32 kilometres (20 mi) south of Great Karimun, 172 kilometres (107 mi) northwest of Lingga Islands and 120 kilometres (75 mi) west of Tanjung Pinang. It has an area of about 304 square kilometres (117 sq mi), not including district Buru. According to the 2010 Census population, the population of Kundur Island is 67,090. As Kundur does not have an airport, all visitors arrive by ferry.

Indonesia–Singapore relations are foreign bilateral relations between Republic of Indonesia and Republic of Singapore. The two countries established formal diplomatic relations on 7 September 1967, a month after the formation of the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN) on 8 August 1967. Indonesia and Singapore are two of the five founding members of ASEAN. Both nations are also members of the Non-Aligned Movement and APEC.

Riau-Lingga Sultanate, also known as the Lingga-Riau Sultanate, Riau Sultanate or Lingga Sultanate was a Malay sultanate that existed from 1824 to 1911, before being dissolved following Dutch intervention.

Riau Strait is a strait in Riau Archipelago. The Riau Strait separates islands of Batam and Bintan. It is an important commercial waterway to the port of Singapore.
















