Related Research Articles

Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) is a viral respiratory disease of zoonotic origin caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, the first identified strain of the SARS coronavirus species severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV). The syndrome caused the 2002–2004 SARS outbreak. Around late 2017, Chinese scientists traced the virus through the intermediary of Asian palm civets to cave-dwelling horseshoe bats in Xiyang Yi Ethnic Township, Yunnan.
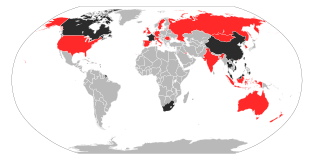
The 2002–2004 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, infected over 8,000 people from 29 different countries and territories, and resulted in at least 774 deaths worldwide.
Singapore has taken a series of measures against avian influenza and the potential threat of a pandemic.

Human coronavirus NL63 (HCoV-NL63) is a species of coronavirus, specifically a Setracovirus from among the Alphacoronavirus genus. It was identified in late 2004 in a seven-month-old child with bronchiolitis in the Netherlands. The virus is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to ACE2. Infection with the virus has been confirmed worldwide, and has an association with many common symptoms and diseases. Associated diseases include mild to moderate upper respiratory tract infections, severe lower respiratory tract infection, croup and bronchiolitis.
An emergent virus is a virus that is either newly appeared, notably increasing in incidence/geographic range or has the potential to increase in the near future. Emergent viruses are a leading cause of emerging infectious diseases and raise public health challenges globally, given their potential to cause outbreaks of disease which can lead to epidemics and pandemics. As well as causing disease, emergent viruses can also have severe economic implications. Recent examples include the SARS-related coronaviruses, which have caused the 2002-2004 outbreak of SARS (SARS-CoV-1) and the 2019–21 pandemic of COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2). Other examples include the human immunodeficiency virus which causes HIV/AIDS; the viruses responsible for Ebola; the H5N1 influenza virus responsible for avian flu; and H1N1/09, which caused the 2009 swine flu pandemic. Viral emergence in humans is often a consequence of zoonosis, which involves a cross-species jump of a viral disease into humans from other animals. As zoonotic viruses exist in animal reservoirs, they are much more difficult to eradicate and can therefore establish persistent infections in human populations.
Professor Malik Peiris FRS, d'Honneur, is a Sri Lankan pathologist and virologist. He has been long based in Hong Kong. His research interests include ecology, evolution, pathogenesis, epidemiology of animal-human influenza and other human respiratory viral infections, authoring over 320 research publications. Peiris is most notable for being the first person to isolate SARS virus.

The 2009 flu pandemic in Hong Kong was part of the worldwide pandemic that started with the city's first reported case of influenza A virus subtype H1N1 infection, commonly called swine flu, on 1 May 2009, in a Mexican national who had travelled to Hong Kong via Shanghai. It was also the first reported case of in Asia. As of 25 November 2009, there have been 32,301 confirmed cases of swine flu in the city.

Influenza-like illness (ILI), also known as flu-like syndrome or flu-like symptoms, is a medical diagnosis of possible influenza or other illness causing a set of common symptoms. These include fever, shivering, chills, malaise, dry cough, loss of appetite, body aches, and nausea, typically in connection with a sudden onset of illness. In most cases, the symptoms are caused by cytokines released by immune system activation, and are thus relatively non-specific.

The 2009 swine flu pandemic in Canada was part of an epidemic in 2009 of a new strain of influenza A virus subtype H1N1 causing what has been commonly called swine flu. In Canada, roughly 10% of the populace has been infected with the virus, with 428 confirmed deaths ; non-fatal individual cases are for the most part no longer being recorded. About 40% of Canadians have been immunized against H1N1 since a national vaccination campaign began in October 2009, with Canada among the countries in the world leading in the percentage of the population that has been vaccinated. The widespread effect of H1N1 in Canada raised concerns during the months leading to the XXI Olympic Winter Games, which took place in Vancouver in February 2010.

Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (MERS-CoV), or EMC/2012 (HCoV-EMC/2012), is the virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS). It is a species of coronavirus which infects humans, bats, and camels. The infecting virus is an enveloped, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA virus which enters its host cell by binding to the DPP4 receptor. The species is a member of the genus Betacoronavirus and subgenus Merbecovirus.

Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), also known as camel flu, is a viral respiratory infection caused by Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (MERS-CoV). Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. Typical symptoms include fever, cough, diarrhea, and shortness of breath. The disease is typically more severe in those with other health problems.
MERS coronavirus EMC/2012 is a strain of coronavirus isolated from the sputum of the first person to become infected with what was later named Middle East respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (MERS-CoV), a virus that causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS).

Since 2012, an outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus has affected several countries, primarily in its namesake, the Middle East. The virus, which causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), is a novel coronavirus that was first identified in a patient from Jeddah, Saudi Arabia on June 6, 2012.

An outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus occurred in South Korea from May 2015 to July 2015. The virus, which causes Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), was a newly emerged betacoronavirus that was first identified in a patient from Saudi Arabia in April 2012. From the outbreak, a total of 186 cases have been infected, with a death toll of 38.
The 2018 Middle East respiratory syndrome outbreak was a set of infections of Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS-CoV). The cases were most numerous in, and are believed to have originated from, Saudi Arabia.
Maria DeJoseph Van Kerkhove is an American infectious disease epidemiologist. With a background in high-threat pathogens, Van Kerkhove specializes in emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases and is based in the Health Emergencies Program at the World Health Organization (WHO). She is the technical lead of COVID-19 response and the head of emerging diseases and zoonosis unit at WHO.
The New and Emerging Respiratory Virus Threats Advisory Group (NERVTAG) is an advisory body that advises the United Kingdom Government's Chief Medical Advisor / Chief Medical Officer for England, who in turn advises the UK Department of Health and Social Care and relevant ministers regarding threats from viral respiratory tract infections. The body replaced the UK Scientific Pandemic Influenza Advisory Committee (SPI) as part of a move to expand the scope to cover the threat of other respiratory viruses, besides pandemic influenza. The inaugural meeting was held on 19 December 2014 where the terms of reference were agreed. The group has been advising the Department of Health for some years and minutes of meetings are now regularly published, backdated to 2014. As of 2020, the group has been advising specifically on the COVID-19 pandemic.
Allison McGeer is a Canadian infectious disease specialist in the Sinai Health System, a Professor at the Dalla Lana School of Public Health and a Senior Clinician Scientist at the Lunenfeld-Tanenbaum Research Institute. McGeer has led investigations into the severe acute respiratory syndrome outbreak in Toronto and worked alongside Donald Low. During the COVID-19 pandemic, McGeer has studied how SARS-CoV-2 survives in the air.

The COVID-19 pandemic has had many impacts on global health beyond those caused by the COVID-19 disease itself. It has led to a reduction in hospital visits for other reasons. There have been 38 per cent fewer hospital visits for heart attack symptoms in the United States and 40 per cent fewer in Spain. The head of cardiology at the University of Arizona said, "My worry is some of these people are dying at home because they're too scared to go to the hospital." There is also concern that people with strokes and appendicitis are not seeking timely treatment. Shortages of medical supplies have impacted people with various conditions.

Yee-Sin Leo is a Singaporean physician. Leo is the executive director of the National Centre for Infectious Diseases and researches emerging infectious diseases. She has been in charge of Singapore's response to several outbreaks, including Nipah, SARS and COVID-19. In 2020, she was selected as one of the BBC's top 100 Women.
References
- ↑ "62 suspected MERS cases investigated, all negative: MOH" . Retrieved 14 July 2015.
- ↑ "Health Advisory (July 2015)" . Retrieved 14 July 2015.
- ↑ "Pandemic Prepardness" . Retrieved 14 July 2015.