
In digital imaging, a pixel, pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software.

Video is an electronic medium for the recording, copying, playback, broadcasting, and display of moving visual media. Video was first developed for mechanical television systems, which were quickly replaced by cathode-ray tube (CRT) systems, which, in turn, were replaced by flat-panel displays of several types.

Video Graphics Array (VGA) is a video display controller and accompanying de facto graphics standard, first introduced with the IBM PS/2 line of computers in 1987, which became ubiquitous in the IBM PC compatible industry within three years. The term can now refer to the computer display standard, the 15-pin D-subminiature VGA connector, or the 640 × 480 resolution characteristic of the VGA hardware.

A plasma display panel is a type of flat-panel display that uses small cells containing plasma: ionized gas that responds to electric fields. Plasma televisions were the first large flat-panel displays to be released to the public.

Anamorphic widescreen is a process by which a widescreen image is horizontally compressed to fit into a storage medium with a narrower aspect ratio, reducing the horizontal resolution of the image while keeping its full original vertical resolution. Compatible play-back equipment can then expand the horizontal dimension to show the original widescreen image. This is typically used to allow one to store widescreen images on a medium that was originally intended for a narrower ratio, while using as much of the frame – and therefore recording as much detail – as possible.

The display resolution or display modes of a digital television, computer monitor, or other display device is the number of distinct pixels in each dimension that can be displayed. It can be an ambiguous term especially as the displayed resolution is controlled by different factors in cathode-ray tube (CRT) displays, flat-panel displays and projection displays using fixed picture-element (pixel) arrays.
Pixels per inch (ppi) and pixels per centimetre are measurements of the pixel density of an electronic image device, such as a computer monitor or television display, or image digitizing device such as a camera or image scanner. Horizontal and vertical density are usually the same, as most devices have square pixels, but differ on devices that have non-square pixels. Pixel density is not the same as resolution — where the former describes the amount of detail on a physical surface or device, the latter describes the amount of pixel information regardless of its scale. Considered in another way, a pixel has no inherent size or unit, but when it is printed, displayed, or scanned, then the pixel has both a physical size (dimension) and a pixel density (ppi).

A jumbotron, sometimes referred to as jumbovision, is a video display using large-screen television technology.
Image resolution is the level of detail of an image. The term applies to digital images, film images, and other types of images. "Higher resolution" means more image detail. Image resolution can be measured in various ways. Resolution quantifies how close lines can be to each other and still be visibly resolved. Resolution units can be tied to physical sizes, to the overall size of a picture, or to angular subtense. Instead of single lines, line pairs are often used, composed of a dark line and an adjacent light line; for example, a resolution of 10 lines per millimeter means 5 dark lines alternating with 5 light lines, or 5 line pairs per millimeter. Photographic lens are most often quoted in line pairs per millimeter.
576p is the shorthand name for a video display resolution. The p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced, the 576 for a vertical resolution of 576 pixels. Usually it corresponds to a digital video mode with a 4:3 anamorphic resolution of 720x576 and a frame rate of 25 frames per second (576p25), and thus using the same bandwidth and carrying the same amount of pixel data as 576i, but other resolutions and frame rates are possible.
High-definition video is video of higher resolution and quality than standard-definition. While there is no standardized meaning for high-definition, generally any video image with considerably more than 480 vertical scan lines or 576 vertical lines (Europe) is considered high-definition. 480 scan lines is generally the minimum even though the majority of systems greatly exceed that. Images of standard resolution captured at rates faster than normal, by a high-speed camera may be considered high-definition in some contexts. Some television series shot on high-definition video are made to look as if they have been shot on film, a technique which is often known as filmizing.

1080p is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the p stands for progressive scan, i.e. non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes referred to as 2K resolution, other sources differentiate between 1080p and (true) 2K resolution.
The Gigabeat was a line of digital media players by Toshiba.

The display aspect ratio (DAR) is the aspect ratio of a display device and so the proportional relationship between the physical width and the height of the display. It is expressed as two numbers separated by a colon (x:y), where x corresponds to the width and y to the height. Common aspect ratios for displays, past and present, include 5:4, 4:3, 16:10, and 16:9.
"21:9" is a consumer electronics (CE) marketing term to describe the ultrawide aspect ratio of 64:27, designed to show films recorded in CinemaScope and equivalent modern anamorphic formats. The main benefit of this screen aspect ratio is a constant display height when displaying other content with a lesser aspect ratio.

4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 3840 × 2160 with a 16:9 aspect ratio is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the movie projection industry uses 4096 × 2160.
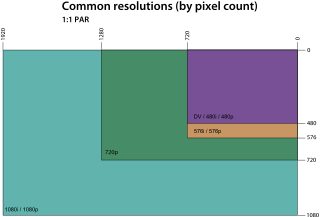
A display resolution standard is a commonly used width and height dimension of an electronic visual display device, measured in pixels. This information is used for electronic devices such as a computer monitor. Certain combinations of width and height are standardized and typically given a name and an initialism which is descriptive of its dimensions.

5K resolution refers to display formats with a horizontal resolution of around 5,000 pixels. The most common 5K resolution is 5120 × 2880, which has an aspect ratio of 16∶9 with around 14.7 million pixels, with exactly twice the linear resolution of 1440p and four times that of 720p. This resolution is typically used in computer monitors to achieve a higher pixel density, and is not a standard format in digital television and digital cinematography, which feature 4K resolutions and 8K resolutions.










