Cameco Corporation is the world's largest publicly traded uranium company, based in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada. In 2015, it was the world's second largest uranium producer, accounting for 18% of world production.
The McArthur River Uranium Mine, in northern Saskatchewan, Canada, is the world's largest high-grade uranium deposit.
The Key Lake mine is a former uranium mine in Saskatchewan, Canada. It is 570 kilometres (350 mi) north of Saskatoon by air on the southern rim of the uranium-rich Athabasca Basin. Key Lake was initially developed to open-pit mine two nearby uranium ore deposits: the Gaertner deposit and the Deilmann deposit. Mining of this ore ceased in the late 1990s; the Key Lake mill now processes uranium ore from the McArthur River mine and from existing stockpiles on site. High-grade ore from McArthur river is blended with lower grade local rock before being passed through the mill. The mill has a permitted annual production capacity of 25 million pounds of U3O8. In addition, ammonium sulfate fertilizer is produced as a byproduct from used reagents. The pits of the mined out local deposits are being used as mill tailings management facilities.
Rabbit Lake is the second largest uranium milling facility in the western world, and is the longest operating uranium production facility in Saskatchewan. The facility is located approximately 800 km north of Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, on the northeast edge of the uranium rich Athabasca Basin. The closest community is Wollaston Lake, about 40 kilometers by lake or air. Rabbit Lake was the first Canadian mine to offer a seven-days-in/seven-days-out commuter system of staffing. Access is provided by Highway 905. Production at Rabbit Lake was suspended in April 2016.

National Atomic Company Kazatomprom Joint Stock Company (Kazatomprom) is the world’s largest producer and seller of natural uranium, providing over 40% of global primary uranium supply in 2019 from its operations in Kazakhstan. Kazatomprom's uranium is used for the generation of nuclear power around the world.
Paladin Energy Ltd is a Western Australian based uranium production company.
Uranium mining in the United States produced 173,875 pounds (78.9 tonnes) of U3O8 in 2019, 88% lower than the 2018 production of 1,447,945 pounds (656.8 tonnes) of U3O8 and the lowest US annual production since 1948. The 2019 production represents 0.3% of the anticipated uranium fuel requirements of the US's nuclear power reactors for the year.

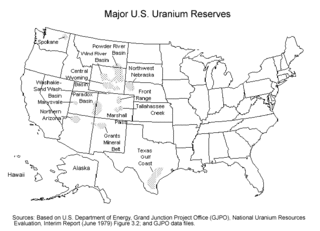
Uranium mining in Colorado, United States, goes back to 1872, when pitchblende ore was taken from gold mines near Central City, Colorado. The Colorado uranium industry has seen booms and busts, but continues to this day. Not counting byproduct uranium from phosphate, Colorado is considered to have the third largest uranium reserves of any US state, behind Wyoming and New Mexico.

Uranium mining in Wyoming was formerly a much larger industry than it is today. Wyoming once had many operating uranium mines, and still has the largest known uranium ore reserves of any state in the U.S. At the end of 2008, the state had estimated reserves dependent on price: 539 million pounds of uranium oxide at $50 per pound, and 1,227 million pounds at $100 per pound.

In-situ leaching (ISL), also called in-situ recovery (ISR) or solution mining, is a mining process used to recover minerals such as copper and uranium through boreholes drilled into a deposit, in situ. In situ leach works by artificially dissolving minerals occurring naturally in a solid state. For recovery of material occurring naturally in solution, see: Brine mining.

The Cigar Lake Mine is a large high-grade underground uranium mine, located in the uranium-rich Athabasca Basin of northern Saskatchewan, Canada, at the south-west corner of Waterbury Lake. The deposit, discovered in 1981, is second in size of high-grade deposits only to the nearby McArthur River mine. Other deposits, such as Olympic Dam in Australia, contain more uranium but at lower grades.

Crow Butte is a uranium mining operation located four miles (6 km) southeast of the city of Crawford in Dawes County, Nebraska, United States. Cameco Corporation owns and operates Crow Butte through its wholly owned subsidiary, Crow Butte Resources, Inc.

Radioactive ores were first extracted in South Australia at Radium Hill in 1906 and Mount Painter in 1911. 2,000 tons of ore were treated to recover radium for medical use. Several hundred kilograms of uranium were also produced for use in ceramic glazes.
Inkai is a uranium mine located in Kazakhstan. Commercial production commenced in 2009, with the main processing plant being commissioned in 2010.
The Kintyre uranium project is located 60 km south of the Telfer gold mine and 260 km northeast of Newman at the western edge of the Great Sandy Desert in the East Pilbara region of Western Australia.

Hathor Exploration Limited is a uranium exploration company based in Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada. Its exploration office is located in Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada. Hathor's exploration projects concentrate on properties within the Athabasca Basin of Northern Saskatchewan, Canada.
The Yeelirrie uranium project is a uranium deposit located approximately 70 km southwest of Wiluna, in the Mid West region of Western Australia. The name Yeelirrie is taken from the local sheep station.
The world's largest producer of uranium is Kazakhstan, which in 2019 produced 43% of the world's mining output. Canada was the next largest producer with a 13% share, followed by Australia with 12%. Uranium has been mined in every continent except Antarctica.
The Willow Creek mine is an in-situ leach (ISL) uranium mining project located in Powder River Basin in the state of Wyoming, United States. It comprises the Irigaray central processing plant and wellfields, and the Christensen Ranch ion exchange plant and wellfields.