Lock picking is the practice of unlocking a lock by manipulating the components of the lock device without the original key.

A warded lock is a type of lock that uses a set of obstructions, or wards, to prevent the lock from opening unless the correct key is inserted. The correct key has notches or slots corresponding to the obstructions in the lock, allowing it to rotate freely inside the lock.

Linus Yale Jr. was a mechanical engineer, manufacturer, and co-founder with millionaire Henry R. Towne of the Yale Lock Company, which became the premier manufacturer of locks in the United States. He was the country's leading expert on bank locks and its most important maker. By the early 20th century, about three-quarter of all banks in America used his bank locks. He is best remembered for his inventions of locks, especially the cylinder lock, and his basic lock design is still widely distributed today, and constitutes a majority of personal locks and safes.

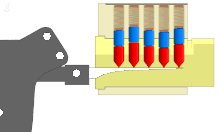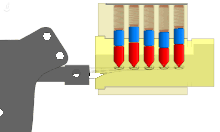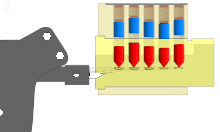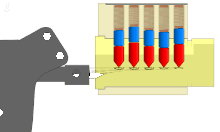
The pin tumbler lock is a lock mechanism that uses pins of varying lengths to prevent the lock from opening without the correct key. Pin tumblers are most commonly employed in cylinder locks, but may also be found in tubular pin tumbler locks.

A disc tumbler or disc detainer lock is a lock composed of slotted rotating detainer discs. The lock was invented by Finnish founder of Abloy, Emil Henriksson (1886–1959) in 1907 and first manufactured under the Abloy brand in 1918.

A combination lock is a type of locking device in which a sequence of symbols, usually numbers, is used to open the lock. The sequence may be entered using a single rotating dial which interacts with several discs or cams, by using a set of several rotating discs with inscribed symbols which directly interact with the locking mechanism, or through an electronic or mechanical keypad. Types range from inexpensive three-digit luggage locks to high-security safes. Unlike ordinary padlocks, combination locks do not use keys.

A tubular pin tumbler lock, also known as a circle pin tumbler lock, radial lock, or the trademark Ace lock popularized by manufacturer Chicago Lock Company since 1933, is a variety of pin tumbler lock in which a number of pins are arranged in a circular pattern, and the corresponding key is tubular or cylindrical in shape. Most locks use between six and eight pins, although some use as few as four or as many as ten. The devices have been widely used on vending machines, elevators, public computers, and bicycle locks.

A lock is a mechanical or electronic fastening device that is released by a physical object, by supplying secret information, by a combination thereof, or it may only be able to be opened from one side, such as a door chain.

A lever tumbler lock is a type of lock that uses a set of levers to prevent the bolt from moving in the lock. In the simplest form of these, lifting the tumbler above a certain height will allow the bolt to slide past.

A mortise lock is a lock that requires a pocket—the mortise—to be cut into the edge of the door or piece of furniture into which the lock is to be fitted. In most parts of the world, mortise locks are found on older buildings constructed before the advent of bored cylindrical locks, but they have recently become more common in commercial and upmarket residential construction in the United States. The design is widely used in domestic properties of all vintages in Europe.

Padlocks are portable locks usually with a shackle that may be passed through an opening to prevent use, theft, vandalism or harm.
Rekeying a lock is replacing the old lock pins with new lock pins.

An impact wrench is a socket wrench power tool designed to deliver high torque output with minimal exertion by the user, by storing energy in a rotating mass, then delivering it suddenly to the output shaft. It was invented by Robert H. Pott of Evansville, Indiana.

Lock bumping is a lock picking technique for opening a pin tumbler lock using a specially crafted bump key, rapping key or 999 key. A bump key must correspond to the target lock in order to function correctly.

A wafer tumbler lock is a type of lock that uses a set of flat wafers to prevent the lock from opening unless the correct key is inserted. This type of lock is similar to the pin tumbler lock and works on a similar principle. However, unlike the pin tumbler lock, where each pin consists of two or more pieces, each wafer in the lock is a single piece. The wafer tumbler lock is often incorrectly referred to as a disc tumbler lock, which uses an entirely different mechanism.

Bilock is a high-security keying system designed and manufactured by Australian Lock Company. It is advertised to be bump-proof, pick-resistant, and drill-resistant. The Bilock cylinder uses a patented locking system with two sidebars, 12 pins, and 12 springs. In the New Generation Bilock, a trigger pin has been added to increase security and extend the registered design of the product. The key design is a U-shape profile with six cuts on each side of the key, along with a central roller to activate the trigger pin in the front and center of the cylinder.
The term protector lock has referred to two unrelated lock designs, one invented in the 1850s by Alfred Hobbs, the other in 1874 by Theodor Kromer.

A magnetic keyed lock or magnetic-coded lock is a locking mechanism whereby the key utilizes magnets as part of the locking and unlocking mechanism. Magnetic-coded locks encompass knob locks, cylinder locks, lever locks, and deadbolt locks as well as applications in other security devices.

The Bramah lock was created by Joseph Bramah in 1784. The lock employed the first known high-security design.
This is a glossary of locksmithing terms.