
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR.

A Trombe wall is a massive equator-facing wall that is painted a dark color in order to absorb thermal energy from incident sunlight and covered with a glass on the outside with an insulating air-gap between the wall and the glaze. A Trombe wall is a passive solar building design strategy that adopts the concept of indirect-gain, where sunlight first strikes a solar energy collection surface which covers thermal mass located between the Sun and the space. The sunlight absorbed by the mass is converted to thermal energy (heat) and then transferred into the living space.

In passive solar building design, windows, walls, and floors are made to collect, store, reflect, and distribute solar energy, in the form of heat in the winter and reject solar heat in the summer. This is called passive solar design because, unlike active solar heating systems, it does not involve the use of mechanical and electrical devices.

Radiators are heat exchangers used to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of cooling and heating. The majority of radiators are constructed to function in cars, buildings, and electronics.

Solar thermal energy (STE) is a form of energy and a technology for harnessing solar energy to generate thermal energy for use in industry, and in the residential and commercial sectors.

Solar water heating (SWH) is heating water by sunlight, using a solar thermal collector. A variety of configurations is available at varying cost to provide solutions in different climates and latitudes. SWHs are widely used for residential and some industrial applications.

A radiant barrier is a type of building material that reflects thermal radiation and reduces heat transfer. Because thermal energy is also transferred by conduction and convection, in addition radiation, radiant barriers are often supplemented with thermal insulation that slows down heat transfer by conduction or convection.

A solar thermal collector collects heat by absorbing sunlight. The term "solar collector" commonly refers to a device for solar hot water heating, but may refer to large power generating installations such as solar parabolic troughs and solar towers or non water heating devices such as solar air heaters.

A central heating system provides warmth to a number of spaces within a building and optionally also able to heat domestic hot water from one main source of heat. It is a component of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, which can both cool and warm interior spaces.
Renewable heat is an application of renewable energy referring to the generation of heat from renewable sources; for example, feeding radiators with water warmed by focused solar radiation rather than by a fossil fuel boiler. Renewable heat technologies include renewable biofuels, solar heating, geothermal heating, heat pumps and heat exchangers. Insulation is almost always an important factor in how renewable heating is implemented.
Seasonal thermal energy storage (STES), also known as inter-seasonal thermal energy storage, is the storage of heat or cold for periods of up to several months. The thermal energy can be collected whenever it is available and be used whenever needed, such as in the opposing season. For example, heat from solar collectors or waste heat from air conditioning equipment can be gathered in hot months for space heating use when needed, including during winter months. Waste heat from industrial process can similarly be stored and be used much later or the natural cold of winter air can be stored for summertime air conditioning.
Solar air conditioning refers to any air conditioning (cooling) system that uses solar power.
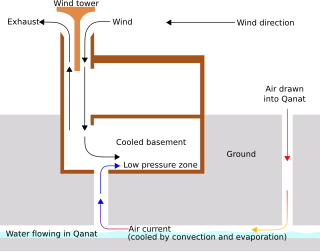
Passive cooling is a building design approach that focuses on heat gain control and heat dissipation in a building in order to improve the indoor thermal comfort with low or no energy consumption. This approach works either by preventing heat from entering the interior or by removing heat from the building.
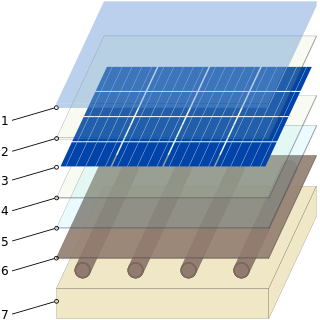
Photovoltaic thermal collectors, typically abbreviated as PVT collectors and also known as hybrid solar collectors, photovoltaic thermal solar collectors, PV/T collectors or solar cogeneration systems, are power generation technologies that convert solar radiation into usable thermal and electrical energy. PVT collectors combine photovoltaic solar cells, which convert sunlight into electricity, with a solar thermal collector, which transfers the otherwise unused waste heat from the PV module to a heat transfer fluid. By combining electricity and heat generation within the same component, these technologies can reach a higher overall efficiency than solar photovoltaic (PV) or solar thermal (T) alone.

Radiators and convectors are heat exchangers designed to transfer thermal energy from one medium to another for the purpose of space heating.

Solar air heating is a solar thermal technology in which the energy from the sun, insolation, is captured by an absorbing medium and used to heat air. Solar air heating is a renewable energy heating technology used to heat or condition air for buildings or process heat applications. It is typically the most cost-effective out of all the solar technologies, especially in commercial and industrial applications, and it addresses the largest usage of building energy in heating climates, which is space heating and industrial process heating.

Leonard "Lynn" L. Northrup Jr. was an American engineer who was a pioneer of the commercialization of solar thermal energy. Influenced by the work of John Yellott, Maria Telkes, and Harry Tabor, Northrup's company designed, patented, developed and manufactured some of the first commercial solar water heaters, solar concentrators, solar-powered air conditioning systems, solar power towers and photovoltaic thermal hybrid systems in the United States. The company he founded became part of ARCO Solar, which in turn became BP Solar, which became the largest solar energy company in the world. Northrup was a prolific inventor with 14 US patents.
Solar energy – radiant light and heat from the sun. It has been harnessed by humans since ancient times using a range of ever-evolving technologies. Solar energy technologies include solar heating, solar photovoltaics, solar thermal electricity and solar architecture, which can make considerable contributions to solving some of the most urgent problems that the world now faces.
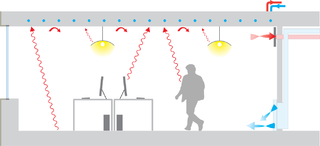
Radiant heating and cooling is a category of HVAC technologies that exchange heat by both convection and radiation with the environments they are designed to heat or cool. There are many subcategories of radiant heating and cooling, including: "radiant ceiling panels", "embedded surface systems", "thermally active building systems", and infrared heaters. According to some definitions, a technology is only included in this category if radiation comprises more than 50% of its heat exchange with the environment; therefore technologies such as radiators and chilled beams are usually not considered radiant heating or cooling. Within this category, it is practical to distinguish between high temperature radiant heating, and radiant heating or cooling with more moderate source temperatures. This article mainly addresses radiant heating and cooling with moderate source temperatures, used to heat or cool indoor environments. Moderate temperature radiant heating and cooling is usually composed of relatively large surfaces that are internally heated or cooled using hydronic or electrical sources. For high temperature indoor or outdoor radiant heating, see: Infrared heater. For snow melt applications see: Snowmelt system.
The liquid droplet radiator (LDR) or previously termed liquid droplet stream radiator is a proposed lightweight radiator for the dissipation of waste heat generated by power plants, propulsion or spacecraft systems in space.















