
Microsoft DirectX is a collection of application programming interfaces (APIs) for handling tasks related to multimedia, especially game programming and video, on Microsoft platforms. Originally, the names of these APIs all began with "Direct", such as Direct3D, DirectDraw, DirectMusic, DirectPlay, DirectSound, and so forth. The name DirectX was coined as a shorthand term for all of these APIs and soon became the name of the collection. When Microsoft later set out to develop a gaming console, the X was used as the basis of the name Xbox to indicate that the console was based on DirectX technology. The X initial has been carried forward in the naming of APIs designed for the Xbox such as XInput and the Cross-platform Audio Creation Tool (XACT), while the DirectX pattern has been continued for Windows APIs such as Direct2D and DirectWrite.

macOS, originally Mac OS X, previously shortened as OS X, is an operating system developed and marketed by Apple since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac computers. Within the market of desktop and laptop computers, it is the second most widely used desktop OS, after Microsoft Windows and ahead of all Linux distributions, including ChromeOS.
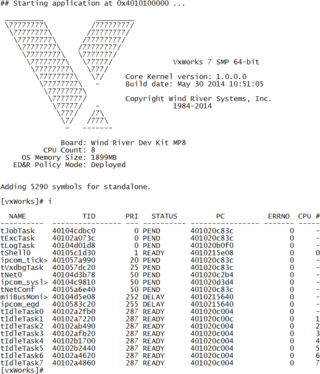
VxWorks is a real-time operating system developed as proprietary software by Wind River Systems, a subsidiary of Aptiv. First released in 1987, VxWorks is designed for use in embedded systems requiring real-time, deterministic performance and in many cases, safety and security certification for industries such as aerospace, defense, medical devices, industrial equipment, robotics, energy, transportation, network infrastructure, automotive, and consumer electronics.

Mega Man 2 is a 1988 action-platform game developed and published by Capcom for the Nintendo Entertainment System. It was released in Japan in 1988 and in North America and PAL regions the following years. Mega Man 2 continues Mega Man's battle against the evil Dr. Wily and his rogue robots. It introduced graphical and gameplay changes, many of which became series staples.

Unreal Engine (UE) is a 3D computer graphics game engine developed by Epic Games, first showcased in the 1998 first-person shooter video game Unreal. Initially developed for PC first-person shooters, it has since been used in a variety of genres of games and has been adopted by other industries, most notably the film and television industry. Unreal Engine is written in C++ and features a high degree of portability, supporting a wide range of desktop, mobiles, console, and virtual reality platforms.
A video game genre is an informal classification of a video game based on how it is played rather than visual or narrative elements. This is independent of setting, unlike works of fiction that are expressed through other media, such as films or books. For example, a shooter game is still a shooter game, regardless of where or when it takes place. A specific game's genre is open to subjective interpretation. An individual game may belong to several genres at once.

Epic Games, Inc. is an American video game and software developer and publisher based in Cary, North Carolina. The company was founded by Tim Sweeney as Potomac Computer Systems in 1991, originally located in his parents' house in Potomac, Maryland. Following its first commercial video game release, ZZT (1991), the company became Epic MegaGames, Inc. in early 1992 and brought on Mark Rein, who has been its vice president since. After moving the headquarters to Cary in 1999, the studio changed its name to Epic Games.
Christian video games are a video game genre and a form of Christian media that focus on the narrative and themes of Christian morals and Christianity. The term can also refer to Christian symbolism, mythology, media franchises, and Christian media organizations within video game culture and industry.

Frictional Games AB is a Swedish independent video game developer based in Malmö, founded in January 2007 by Thomas Grip and Jens Nilsson. The company specialises in the development of survival horror games with very little or no combat gameplay mechanics. It is best known for its games Amnesia: The Dark Descent and Soma.

OpenFeint was a social platform for mobile games for devices running on Android or iOS. It was developed by Aurora Feint, a company named after a video game by the same developers. The platform consisted of an SDK for use by games, allowing its various social networking features to be integrated into the game's functionality. OpenFeint was discontinued at the end of 2012.
Cloud gaming, sometimes called gaming on demand or game streaming, is a type of online gaming that runs video games on remote servers and streams the game's output directly to a user's device, or more colloquially, playing a game remotely from a cloud. It contrasts with traditional means of gaming, wherein a game is run locally on a user's video game console, personal computer, or mobile device.

Tommy Refenes is an American video game designer and programmer, best known for his work on the game Super Meat Boy, a platformer he co-created with designer Edmund McMillen.
Moovit is an Israel-based mobility as a service provider and journey planner app. It is owned by Mobileye and was acquired by Intel in 2020 until Mobileye's IPO in 2022. Moovit uses both crowdsourced and official public transit data to provide route planning to users as well as transit data APIs to transit companies, cities, and transit agencies. Because Moovit integrates crowdsourced data, it can provide transit information for areas where no data is officially available.

Tango was an augmented reality computing platform, developed and authored by the Advanced Technology and Projects (ATAP), a skunkworks division of Google. It used computer vision to enable mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, to detect their position relative to the world around them without using GPS or other external signals. This allowed application developers to create user experiences that include indoor navigation, 3D mapping, physical space measurement, environmental recognition, augmented reality, and windows into a virtual world.

Geometry Dash is a side-scrolling music platforming game series developed by Robert Topala. The game was released on 13 August 2013 on iOS and Android, and the Windows and macOS versions on 22 December 2014. In Geometry Dash, players control the movement of an icon and navigate music-based levels while avoiding obstacles such as spikes.
Ketchapp SARL is a French video game publisher based in Paris, specializing in the mobile games market. Founded in 2014 by brothers Antoine and Michel Morcos, the company first came into the public eye later that year, through its port of the open-source game 2048. Ketchapp has been accused of cloning popular casual games by other developers. When Ketchapp was acquired by Ubisoft in September 2016, the company had more than 700 million downloads across their portfolio of games.

Kill Screen is an online magazine founded in 2009 by Jamin Warren and Chris Dahlen and owned by Kill Screen Media, Inc. It focused on video games and culture, but also included articles based on entertainment. The name is based on the video game term of the same name.

The Lost Legends of Redwall is a series of six episodic indie adventure games for Microsoft Windows, macOS, and Xbox One developed and published by studio Soma Games. They are the first officially licensed video games to be based on the Redwall book series since its introduction in 1986, and began production following a successful Kickstarter campaign for the Minecraft map "AbbeyCraft" in 2013.
The Christian Game Developers Conference (CGDC) is an annual conference for video game developers who profess the Christian religion. Attendees of the conference gather together to discuss how to improve their games through discussions, keynote speeches, and workshops.














