Related Research Articles

The Balkans, corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the whole of Bulgaria. The Balkan Peninsula is bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the northwest, the Ionian Sea in the southwest, the Aegean Sea in the south, the Turkish straits in the east, and the Black Sea in the northeast. The northern border of the peninsula is variously defined. The highest point of the Balkans is Musala, 2,925 metres (9,596 ft), in the Rila mountain range, Bulgaria.

The League of the Balkans was a quadruple alliance formed by a series of bilateral treaties concluded in 1912 between the Eastern Orthodox kingdoms of Greece, Bulgaria, Serbia and Montenegro, and directed against the Ottoman Empire, which at the time still controlled much of Southeastern Europe.

The Aromanians are an ethnic group native to the southern Balkans who speak Aromanian, an Eastern Romance language. They traditionally live in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, northern and central Greece and North Macedonia, and can currently be found in central and southern Albania, south-western Bulgaria, south-western and eastern North Macedonia, northern and central Greece, southern Serbia and south-eastern Romania. An Aromanian diaspora living outside these places also exists. The Aromanians are known by several other names, such as "Vlachs" or "Macedo-Romanians".

Southern Europe is the southern region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of southern Europe include some or all of these countries and regions: Albania, Andorra, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, Cyprus, Gibraltar, Greece, Italy,, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, North Macedonia, Portugal, San Marino, Serbia, Slovenia, southern France, Spain, Turkey, and Vatican City.
Rakija, rakia, rachiu, rakı or rakiya, is the collective term for fruit spirits popular in the Balkans. The alcohol content of rakia is normally 40% ABV, but home-produced rakia can be stronger.
Europe, the westernmost portion of Eurasia, is often divided into regions and subregions based on geographical, cultural or historical factors. Since there is no universal agreement on Europe's regional composition, the placement of individual countries may vary based on criteria being used. For instance, the Balkans is a distinct geographical region within Europe, but individual countries may alternatively be grouped into South-eastern Europe or Southern Europe.
This is a list of languages spoken in regions ruled by Balkan countries. With the exception of several Turkic languages, all of them belong to the Indo-European family. A subset of these languages is notable for forming a well-studied sprachbund, a group of languages that have developed some striking structural similarities over time.

Southeast Europe or Southeastern Europe (SEE) is a geographical sub-region of Europe, consisting primarily of the cultural region of the Balkans, as well as adjacent regions and archipelagos. There are overlapping and conflicting definitions of the region, due to political, economic, historical, cultural, and geographical considerations.
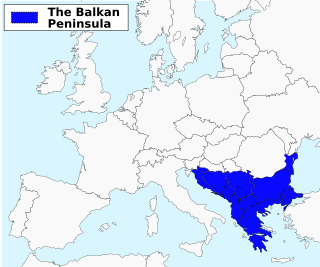
The Balkans and parts of this area may also be placed in Southeastern, Southern, Eastern Europe and Central Europe. The distinct identity and fragmentation of the Balkans owes much to its common and often turbulent history regarding centuries of Ottoman conquest and to its very mountainous geography.
The Balkans Cup was an international football competition for clubs from Albania, Bulgaria, Greece, Romania, Turkey, and Yugoslavia. It was introduced in 1961 and was very popular in the 1960s, being the second most important international club competition for clubs from the region. The competition has been dominated by Bulgaria-based teams. The Bulgarian teams have won together a total number of 9 titles.

The South-East European Cooperation Process (SEECP) was launched on Bulgaria's initiative in 1996. At the Bulgaria-chaired meeting in Sofia, the Southeast Europe (SEE) countries laid the foundations for regional co-operation for the purposes of creating an atmosphere of trust, good neighbourly relations and stability.

The official language of North Macedonia is Macedonian, while Albanian has co-official status. Macedonian is spoken by roughly two-thirds of the population natively, and as a second language by much of the rest of the population. Albanian is the largest minority language. There are a further five national minority languages: Turkish, Romani, Serbian, Bosnian, and Aromanian. The Macedonian Sign Language is the country's official sign language.
East-Central Europe is the region between German-, Hungarian-, and West Slavic-speaking Europe and the East Slavic countries of Belarus, Russia, and Ukraine. Those lands are described as situated "between two": "between two worlds, between two stages, between two futures".

The 29th and final SPAR European Cup took place in June 2008. Track and field events were held on 21 and 22 June 2008 at the Parc des Sports Stadium in Annecy, France. Other event venues included Estádio Dr. Magalhães Pessoa in Portugal and facilities in Istanbul, Turkey, Kadriorg Stadium in Estonia and SNP Stadium in Slovakia, and facilities in Eindhoven, Netherlands. The Parc des Sports Annecy Stadium was also stadium for 1998 World Junior Championships in Athletics. It was the last edition of the European Cup which from 2009 has been replaced by European Team Championships combining the men and women competitions.
Victor A. Friedman is an American linguist, Slavist. He is the Andrew W. Mellon Distinguished Service Professor in Humanities at the University of Chicago. He holds an appointment in the Department of Linguistics and an associate appointment in the Department of Anthropology. He has published numerous articles in English, Macedonian, and Albanian.
The Association of the Balkan Athletics Federations, commonly known as Balkan Athletics is the organisation which organises the annual senior Balkan Athletics Championships and Balkan Athletics Indoor Championships, as well as other competitions at junior and youth level on track and field and other surfaces.
This page describes the qualification procedure for FIBA Women's EuroBasket 2021. 14 teams joined the co-hosts France and Spain.
The Balkan Masters Athletics Championships is an annual international athletics competition between masters athletes aged 35 and over from nations in the Balkans. It is typically held over two or three days in September. It features a full programme of track and field events, plus a half marathon. Organised by Balkan Masters Athletics, it was first held in 1991 and has been held every year since. The competition was the organisation's first regular championships, and was followed by a Balkan Masters Cross Country Championships in 2007 and a Balkan Masters Indoor Athletics Championships in 2015.