Related Research Articles

A chordate is a deuterostomic animal belonging to the phylum Chordata. All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five distinctive physical characteristics (synapomorphies) that distinguish them from other taxa. These five synapomorphies are a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, an endostyle or thyroid, pharyngeal slits, and a post-anal tail. The name "chordate" comes from the first of these synapomorphies, the notochord, which plays a significant role in chordate body plan structuring and movements. Chordates are also bilaterally symmetric, have a coelom, possess a closed circulatory system, and exhibit metameric segmentation.

The Echiura, or spoon worms, are a small group of marine animals. Once treated as a separate phylum, they are now considered to belong to Annelida. Annelids typically have their bodies divided into segments, but echiurans have secondarily lost their segmentation. The majority of echiurans live in burrows in soft sediment in shallow water, but some live in rock crevices or under boulders, and there are also deep sea forms. More than 230 species have been described. Spoon worms are cylindrical, soft-bodied animals usually possessing a non-retractable proboscis which can be rolled into a scoop-shape to feed. In some species the proboscis is ribbon-like, longer than the trunk and may have a forked tip. Spoon worms vary in size from less than a centimetre in length to more than a metre.

Hemichordata is a phylum which consists of triploblastic, enterocoelomate, and bilaterally symmetrical marine deuterostome animals, generally considered the sister group of the echinoderms. They appear in the Lower or Middle Cambrian and include two main classes: Enteropneusta, and Pterobranchia. A third class, Planctosphaeroidea, is known only from the larva of a single species, Planctosphaera pelagica. The class Graptolithina, formerly considered extinct, is now placed within the pterobranchs, represented by a single living genus Rhabdopleura.

Lobopodians are members of the informal group Lobopodia, or the formally erected phylum Lobopoda Cavalier-Smith (1998). They are panarthropods with stubby legs called lobopods, a term which may also be used as a common name of this group as well. While the definition of lobopodians may differ between literatures, it usually refers to a group of soft-bodied, marine worm-like fossil panarthropods such as Aysheaia and Hallucigenia.

Priapulida, sometimes referred to as penis worms, is a phylum of unsegmented marine worms. The name of the phylum relates to the Greek god of fertility, because their general shape and their extensible spiny introvert (eversible) proboscis may resemble the shape of a human penis. They live in the mud and in comparatively shallow waters up to 90 metres (300 ft) deep. Some species show a remarkable tolerance for hydrogen sulfide, anoxia and low salinity. Halicryptus spinulosus appears to prefer brackish shallow waters. They can be quite abundant in some areas. In an Alaskan bay as many as 85 adult individuals of Priapulus caudatus per square meter has been recorded, while the density of its larvae can be as high as 58,000 per square meter.

Hallucigenia is a genus of lobopodian, known from Cambrian aged fossils in Burgess Shale-type deposits in Canada and China, and from isolated spines around the world. The generic name reflects the type species' unusual appearance and eccentric history of study; when it was erected as a genus, H. sparsa was reconstructed as an enigmatic animal upside down and back to front. Lobopodians are a grade of Paleozoic panarthropods from which the velvet worms, water bears, and arthropods arose.

Opabinia regalis is an extinct, stem group arthropod found in the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale Lagerstätte of British Columbia. Opabinia was a soft-bodied animal, measuring up to 7 cm in body length, and its segmented trunk had flaps along the sides and a fan-shaped tail. The head shows unusual features: five eyes, a mouth under the head and facing backwards, and a clawed proboscis that probably passed food to the mouth. Opabinia probably lived on the seafloor, using the proboscis to seek out small, soft food. Fewer than twenty good specimens have been described; 3 specimens of Opabinia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they constitute less than 0.1% of the community.

Tullimonstrum, colloquially known as the Tully monster or sometimes Tully's monster, is an extinct genus of soft-bodied bilaterian animal that lived in shallow tropical coastal waters of muddy estuaries during the Pennsylvanian geological period, about 300 million years ago. A single species, T. gregarium, is known. Examples of Tullimonstrum have been found only in the Essex biota, a smaller section of the Mazon Creek fossil beds of Illinois, United States. Its classification has been the subject of controversy, and interpretations of the fossil have likened it to molluscs, arthropods, conodonts, worms, tunicates, and vertebrates. This creature had a mostly cigar shaped body, with a triangular tail fin, two long stalked eyes, and a proboscis tipped with a mouth-like appendage. Based on the fossils, it seems this creature was a nektonic carnivore that hunted in the ocean’s water column. When Tullimonstrum was alive, Illinois was a mixture of ecosystems like muddy estuaries, marine environments, and rivers and lakes. Fossils of other organisms like crustacean Belotelson, the cnidarian Essexella, and the elasmobranch fish Bandringa have been found alongside Tullimonstrum.

Pikaia gracilens is an extinct species of primitive chordate animal known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale of British Columbia. Described in 1911 by Charles Doolittle Walcott as an annelid, and in 1979 by Harry B. Whittington and Simon Conway Morris as a chordate, it became "one of the most famous early chordate fossils," or "famously known as the earliest described Cambrian chordate". It is estimated to have lived during the latter period of the Cambrian explosion. Since its initial discovery, more than a hundred specimens have been recovered.

Pterobranchia is a class of small worm-shaped animals. They belong to the Hemichordata, and live in secreted tubes on the ocean floor. Pterobranchia feed by filtering plankton out of the water with the help of cilia attached to tentacles. There are about 25 known living pterobranch species in three genera, which are Rhabdopleura, Cephalodiscus, and Atubaria. On the other hand, there are several hundred extinct genera, some of which date from the Cambrian Period.
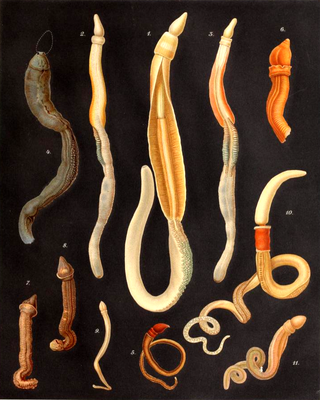
The acorn worms or Enteropneusta are a hemichordate class of invertebrates consisting of one order of the same name. The closest non-hemichordate relatives of the Enteropneusta are the echinoderms. There are 111 known species of acorn worm in the world, the main species for research being Saccoglossus kowalevskii. Two families—Harrimaniidae and Ptychoderidae—separated at least 370 million years ago.
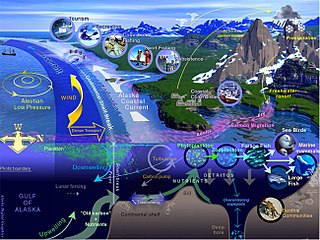
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals, and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. Marine organisms, mostly microorganisms, produce oxygen and sequester carbon. Marine life in part shape and protect shorelines, and some marine organisms even help create new land.

Marine invertebrates are the invertebrates that live in marine habitats. Invertebrate is a blanket term that includes all animals apart from the vertebrate members of the chordate phylum. Invertebrates lack a vertebral column, and some have evolved a shell or a hard exoskeleton. As on land and in the air, marine invertebrates have a large variety of body plans, and have been categorised into over 30 phyla. They make up most of the macroscopic life in the oceans.
A number of assemblages bear fossil assemblages similar in character to that of the Burgess Shale. While many are also preserved in a similar fashion to the Burgess Shale, the term "Burgess Shale-type fauna" covers assemblages based on taxonomic criteria only.

Deuterostomes are bilaterian animals of the superphylum Deuterostomia, typically characterized by their anus forming before the mouth during embryonic development. The three major clades of extant deuterostomes include chordates, echinoderms and hemichordates.

Diania is an extinct genus of lobopodian panarthropod found in the Lower Cambrian Maotianshan shale of China, represented by a single species - D. cactiformis. Known during its investigation by the nickname "walking cactus", this organism belongs to a group known as the armoured lobopodians, and has a simple worm-like body with robust, spiny legs. Initially, the legs were thought to have a jointed exoskeleton and Diania was suggested to be evolutionarily close to early arthropods, but many later studies have rejected this interpretation.

Ooedigera peeli is an extinct vetulicolian from the Early Cambrian of North Greenland. The front body was flattened horizontally, oval-shaped, likely bearing a reticulated or anastomosing pattern, and had 5 evenly-spaced gill pouches along the midline. The tail was also bulbous and flattened horizontally, but was divided into 7 plates connected by flexible membranes, allowing movement. Ooedigera likely swam by moving side-to-side like a fish. It may have lived in an oxygen minimum zone alongside several predators in an ecosystem based on chemosynthetic microbial mats, and was possibly a deposit or filter feeder living near the seafloor.
Torquaratoridae is a family of acorn worms (Hemichordata) that lives in deep waters between 350 and 4000 meters. They can grow up to three feet in length and have semitransparent gelatinous bodies, often brightly colored.

Hallucigeniidae is a family of extinct worms belonging to the group Lobopodia that originated during the Cambrian explosion. It is based on the species Hallucigenia sparsa, the fossil of which was discovered by Charles Doolittle Walcott in 1911 from the Burgess Shale of British Columbia. The name Hallucigenia was created by Simon Conway Morris in 1977, from which the family was erected after discoveries of other hallucigeniid worms from other parts of the world. Classification of these lobopods and their relatives are still controversial, and the family consists of at least four genera.

Lenisambulatrix is a genus of extinct worm belonging to the group Lobopodia and known from the Lower Cambrian Maotianshan shale of China. It is represented by a single species L. humboldti. The incomplete fossil was discovered and described by Qiang Ou and Georg Mayer in 2018. Due to its missing parts, its relationship with other lobopodians is not clear. It shares many structural features with another Cambrian lobopodian Diania cactiformis, a fossil of which was found alongside it.
References
- ↑ Halanych, Kenneth M.; Cannon, Johanna T.; Mahon, Andrew R.; Swalla, Billie J.; Smith, Craig R. (7 November 2013). "Modern Antarctic acorn worms form tubes". Nature Communications. 4 (1): 2738. Bibcode:2013NatCo...4.2738H. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3738 . PMID 24201563. S2CID 205320979.