Related Research Articles

Albertus Magnus, also known as Saint Albert the Great or Albert of Cologne, was a German Dominican friar, philosopher, scientist, and bishop. Later canonized as a Catholic saint, he was known during his lifetime as Doctor universalis and Doctor expertus and, late in his life, the sobriquet Magnus was appended to his name. Scholars such as James A. Weisheipl and Joachim R. Söder have referred to him as the greatest German philosopher and theologian of the Middle Ages. The Catholic Church distinguishes him as one of the 37 Doctors of the Church.

Francesco Petrarca, commonly anglicized as Petrarch, was a scholar and poet of early Renaissance Italy, and one of the earliest humanists.

The Talmud is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (halakha) and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews.

The Quran, also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters, which consist of verses. In addition to its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic language.
One of the most common ways for chess historians to trace when the board game chess entered a country is to look at the literature of that country. Although due to the names associated with chess sometimes being used for more than one game, the only certain reference to chess is often several hundred years later than uncertain earlier references. The following list contains the earliest references to chess or chess-like games.

Saint Michael Choniates was a Byzantine Greek writer and cleric, born at Chonae. At an early age he studied at Constantinople and was the pupil of Eustathius of Thessalonica. Around 1175 he was appointed archbishop of Athens, a position which he retained until 1204. In 1204, he defended the Acropolis of Athens from attack by Leo Sgouros, holding out until the arrival of the Crusaders in 1205, to whom he surrendered the city. After the establishment of Latin control, he retired to the island of Ceos. Around 1217 he moved again to the monastery of Vodonitsa near Thermopylae, where he died.

Jean-Frédéric Maximilien de Waldeck was a French antiquarian, cartographer, artist and explorer. He was a man of talent and accomplishment, but his love of self-promotion and refusal to let the truth get in the way of a good story leave some aspects of his life in mystery.
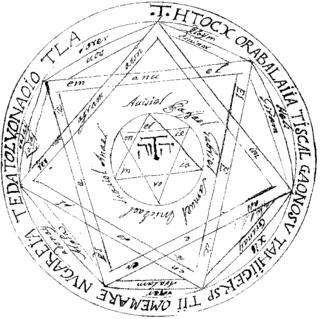
The Key of Solomon is a pseudepigraphical grimoire attributed to King Solomon. It probably dates back to the 14th or 15th century Italian Renaissance. It presents a typical example of Renaissance magic.

The Liezi is a Taoist text attributed to Lie Yukou, a c. 5th century BC Hundred Schools of Thought philosopher. Although there were references to Lie's Liezi from the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC, a number of Chinese and Western scholars believe that the content of the current text was compiled around the 4th century CE by Zhang Zhan.

I Modi, also known as The Sixteen Pleasures or under the Latin title De omnibus Veneris Schematibus, is a famous erotic book of the Italian Renaissance in which a series of sexual positions were explicitly depicted in engravings.
Mirrors for princes or mirrors of princes are an educational literary genre, in a loose sense of the word, of political writings during the Early Middle Ages, the High Middle Ages, the late middle ages and the Renaissance. They are part of the broader speculum or mirror literature genre.

The Liber pantegni is a medieval medical text compiled by Constantinus Africanus prior to 1086. Constantine’s Pantegni has been called “the first fully comprehensive medical text in Latin.” There was, of course, a substantial body of Latin medical writing circulating in western Europe in the early Middle Ages, but the Pantegni was the first text to bring together, in one place, a broad array of learning on anatomy, physiology, and therapeutics. It was dedicated to Abbot Desiderius of Monte Cassino, before he became Pope Victor III in 1086. In 2010, a manuscript at the Hague known to scholars since the early 20th century, but little studied, was recognized as being the earliest copy of the Pantegni, made at Monte Cassino under Constantine's supervision.

The Speculum Humanae Salvationis or Mirror of Human Salvation was a bestselling anonymous illustrated work of popular theology in the late Middle Ages, part of the genre of encyclopedic speculum literature, in this case concentrating on the medieval theory of typology, whereby the events of the Old Testament prefigured, or foretold, the events of the New Testament. The original version is in rhyming Latin verse, and contains a series of New Testament events each with three Old Testament ones that prefigure it. It is one of the most common books found as an illuminated manuscript, and also in early printing in both blockbook and incunabulum forms.

Secundus the Silent was a philosopher who lived in Athens in the early 2nd century, who had taken a vow of silence. An anonymous text entitled Life of Secundus purports to give details of his life as well as answers to philosophical questions posed to him by the emperor Hadrian. The work enjoyed great popularity in the Middle Ages.

During the High Middle Ages, the Islamic world was at its cultural peak, supplying information and ideas to Europe, via Al-Andalus, Sicily and the Crusader kingdoms in the Levant. These included Latin translations of the Greek Classics and of Arabic texts in astronomy, mathematics, science, and medicine. Translation of Arabic philosophical texts into Latin "led to the transformation of almost all philosophical disciplines in the medieval Latin world", with a particularly strong influence of Muslim philosophers being felt in natural philosophy, psychology and metaphysics. Other contributions included technological and scientific innovations via the Silk Road, including Chinese inventions such as paper, compass and gunpowder.

Beelzebub, also spelled Beelzebul or Belzebuth, is a name derived from a Philistine god, formerly worshipped in Ekron, and later adopted by some Abrahamic religions as a major demon. The name Beelzebub is associated with the Canaanite god Baal.

Ecclesiastes 3 is the third chapter of the Book of Ecclesiastes in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book contains philosophical speeches by a character called 'Qoheleth', composed probably between the fifth and second centuries BC. Peshitta, Targum, and Talmud attribute the authorship of the book to King Solomon.

Ecclesiastes 2 is the second chapter of the Book of Ecclesiastes in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book contains philosophical speeches by a character called Qoheleth, composed probably between the 5th and 2nd centuries BCE. Peshitta, Targum, and Talmud attribute the authorship of the book to King Solomon.

Ecclesiastes 9 is the ninth chapter of the Book of Ecclesiastes in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book contains the philosophical and theological reflections of a character known as Qoheleth, a title literally meaning "the assembler" but traditionally translated as "the Teacher" or "The Preacher". The identity of Qoheleth it unknown. In traditional Jewish texts such as the Peshitta, Targum, and Talmud, authorship of Ecclesiastes is attributed to King Solomon, due to the statement in Ecclesiastes 1:1 which identifies Qoheleth as the "son of David, king in Jerusalem". However, it is generally agreed upon by contemporary scholars that the book could not have been written in the 10th century during the time of Solomon. It is now thought to be one of the latest books in the Old Testament to be written, likely sometime between the 5th and 3rd centuries BCE.

Ecclesiastes 12 is the twelfth chapter of the Book of Ecclesiastes in the Hebrew Bible or the Old Testament of the Christian Bible. The book contains philosophical speeches by a character called 'Qoheleth', composed probably between the 5th and 2nd centuries BCE. Peshitta, Targum, and Talmud attribute the authorship of the book to King Solomon. This chapter continues the previous one in the sustained encouragement to make decision and the need to act speedily.
References
- ↑ Michael R. Solomon (ed.) (1986). Text and Concordance of Speculum al foder, Biblioteca Nacional MS. 3356. ISBN 0-942260-60-0
- ↑ Michael R. Solomon (1990). The Mirror of coitus: a translation and edition of the fifteenth-century Speculum al foder. Spanish. ISBN 0-940639-48-3
- ↑ I Modi: The Sixteen Pleasures. An erotic album of the Italian renaissance / Giulio Romano … [et al.] edited, translated from the Italian and with a commentary by Lynne Lawner. Northwestern University Press, 1988. ISBN 0-7206-0724-8