Amplitude modulation (AM) is a modulation technique used in electronic communication, most commonly for transmitting messages with a radio wave. In amplitude modulation, the amplitude of the wave is varied in proportion to that of the message signal, such as an audio signal. This technique contrasts with angle modulation, in which either the frequency of the carrier wave is varied, as in frequency modulation, or its phase, as in phase modulation.

Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries.
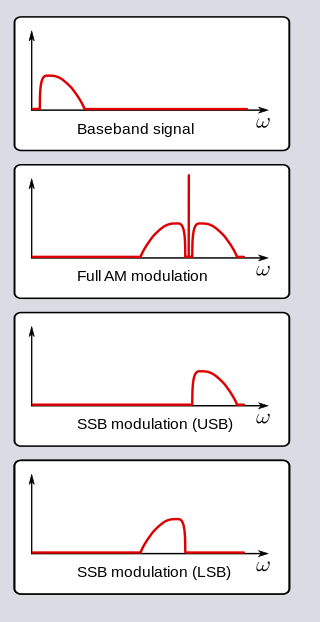
In radio communications, single-sideband modulation (SSB) or single-sideband suppressed-carrier modulation (SSB-SC) is a type of modulation used to transmit information, such as an audio signal, by radio waves. A refinement of amplitude modulation, it uses transmitter power and bandwidth more efficiently. Amplitude modulation produces an output signal the bandwidth of which is twice the maximum frequency of the original baseband signal. Single-sideband modulation avoids this bandwidth increase, and the power wasted on a carrier, at the cost of increased device complexity and more difficult tuning at the receiver.
Linear predictive coding (LPC) is a method used mostly in audio signal processing and speech processing for representing the spectral envelope of a digital signal of speech in compressed form, using the information of a linear predictive model.
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal representing sound or a video signal representing images, in an electronic device or communication channel.
A signal generator is one of a class of electronic devices that generates electrical signals with set properties of amplitude, frequency, and wave shape. These generated signals are used as a stimulus for electronic measurements, typically used in designing, testing, troubleshooting, and repairing electronic or electroacoustic devices, though it often has artistic uses as well.

A microphone, colloquially called a mic, or mike, is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and public events, motion picture production, live and recorded audio engineering, sound recording, two-way radios, megaphones, and radio and television broadcasting. They are also used in computers and other electronic devices, such as mobile phones, for recording sounds, speech recognition, VoIP, and other purposes, such as ultrasonic sensors or knock sensors.
Reverberation, in acoustics, is a persistence of sound after it is produced. Reverberation is created when a sound or signal is reflected. This causes numerous reflections to build up and then decay as the sound is absorbed by the surfaces of objects in the space – which could include furniture, people, and air. This is most noticeable when the sound source stops but the reflections continue, their amplitude decreasing, until zero is reached.
Audio power is the electrical power transferred from an audio amplifier to a loudspeaker, measured in watts. The electrical power delivered to the loudspeaker, together with its efficiency, determines the sound power generated.

Acoustical engineering is the branch of engineering dealing with sound and vibration. It includes the application of acoustics, the science of sound and vibration, in technology. Acoustical engineers are typically concerned with the design, analysis and control of sound.
A weighting curve is a graph of a set of factors, that are used to 'weight' measured values of a variable according to their importance in relation to some outcome. An important example is frequency weighting in sound level measurement where a specific set of weighting curves known as A-, B-, C-, and D-weighting as defined in IEC 61672 are used. Unweighted measurements of sound pressure do not correspond to perceived loudness because the human ear is less sensitive at low and high frequencies, with the effect more pronounced at lower sound levels. The four curves are applied to the measured sound level, for example by the use of a weighting filter in a sound level meter, to arrive at readings of loudness in phons or in decibels (dB) above the threshold of hearing.
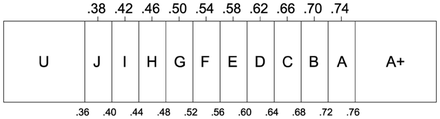
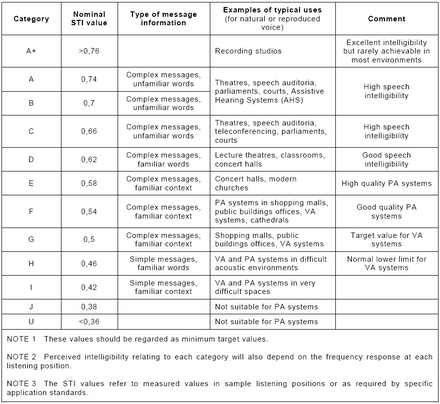
In speech communication, intelligibility is a measure of how comprehensible speech is in given conditions. Intelligibility is affected by the level and quality of the speech signal, the type and level of background noise, reverberation, and, for speech over communication devices, the properties of the communication system. A common standard measurement for the quality of the intelligibility of speech is the Speech Transmission Index (STI). The concept of speech intelligibility is relevant to several fields, including phonetics, human factors, acoustical engineering, and audiometry.

A sound level meter is used for acoustic measurements. It is commonly a hand-held instrument with a microphone. The best type of microphone for sound level meters is the condenser microphone, which combines precision with stability and reliability. The diaphragm of the microphone responds to changes in air pressure caused by sound waves. That is why the instrument is sometimes referred to as a sound pressure level meter (SPL). This movement of the diaphragm, i.e. the sound pressure, is converted into an electrical signal. While describing sound in terms of sound pressure, a logarithmic conversion is usually applied and the sound pressure level is stated instead, in decibels (dB), with 0 dB SPL equal to 20 micropascals.

Loudspeaker measurement is the practice of determining the behaviour of loudspeakers by measuring various aspects of performance. This measurement is especially important because loudspeakers, being transducers, have a higher level of distortion than other audio system components used in playback or sound reinforcement.

Underwater acoustic communication is a technique of sending and receiving messages in water. There are several ways of employing such communication but the most common is by using hydrophones. Underwater communication is difficult due to factors such as multi-path propagation, time variations of the channel, small available bandwidth and strong signal attenuation, especially over long ranges. Compared to terrestrial communication, underwater communication has low data rates because it uses acoustic waves instead of electromagnetic waves.

Smaart is a suite of audio and acoustical measurements and instrumentation software tools introduced in 1996 by JBL's professional audio division. It is designed to help the live sound engineer optimize sound reinforcement systems before public performance and actively monitor acoustical parameters in real time while an audio system is in use. Most earlier analysis systems required specific test signals sent through the sound system, ones that would be unpleasant for the audience to hear. Smaart is a source-independent analyzer and therefore will work effectively with a variety of test signals including speech or music.
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the amplitude of the analog signal is sampled at uniform intervals, and each sample is quantized to the nearest value within a range of digital steps.

NTi Audio AG is a manufacturer of test and measurement instruments for acoustics, audio and vibration applications. With headquarters in Schaan, Liechtenstein, the company specializes in end-of-line audio testing for manufacturing quality control purposes, provides instruments for testing public address systems in safety-critical environments and also produces handheld Audio Analyzers and generators aimed at the professional audio industry.
Temporal envelope (ENV) and temporal fine structure (TFS) are changes in the amplitude and frequency of sound perceived by humans over time. These temporal changes are responsible for several aspects of auditory perception, including loudness, pitch and timbre perception and spatial hearing.
Jacob, K., McManus, S., Verhave, J.A., and Steeneken, H., (2002) "Development of an Accurate, Handheld, Simple-to-use Meter for the Prediction of Speech Intelligibility", Past, Present, and Future of the Speech Transmission Index, International Symposium on STI