
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology. Related terms include aquitard, which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, and aquiclude, which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer, the pressure of which could lead to the formation of a confined aquifer. The classification of aquifers is as follows: Saturated versus unsaturated; aquifers versus aquitards; confined versus unconfined; isotropic versus anisotropic; porous, karst, or fractured; transboundary aquifer.

Fly fishing is an angling technique that uses an ultra-lightweight lure called an artificial fly, which typically mimics small invertebrates such as flying and aquatic insects to attract and catch fish. Because the mass of the fly lure is insufficient to overcome air resistance, it cannot be launched far using conventional gears and techniques, so specialized tackles are used instead and the casting techniques are significantly different from other forms of angling. It is also very common for the angler to wear waders, carry a hand net, and stand in the water when fishing.

A spring is a natural exit point at which groundwater emerges out of the aquifer and flows onto the top of the Earth's crust (pedosphere) to become surface water. It is a component of the hydrosphere, as well as a part of the water cycle. Springs have long been important for humans as a source of fresh water, especially in arid regions which have relatively little annual rainfall.

The Deschutes River in central Oregon is a major tributary of the Columbia River. The river provides much of the drainage on the eastern side of the Cascade Range in Oregon, gathering many of the tributaries that descend from the drier, eastern flank of the mountains. The Deschutes provided an important route to and from the Columbia for Native Americans for thousands of years, and then in the 19th century for pioneers on the Oregon Trail. The river flows mostly through rugged and arid country, and its valley provides a cultural heart for central Oregon. Today the river supplies water for irrigation and is popular in the summer for whitewater rafting and fishing.

The Lamar River is a tributary of the Yellowstone River, approximately 40 miles (64 km) long, in northwestern Wyoming in the United States. The river is located entirely within Yellowstone National Park.

Chalk streams are rivers that rise from springs in landscapes with chalk bedrock. Since chalk is permeable, water percolates easily through the ground to the water table and chalk streams therefore receive little surface runoff. As a result, the water in the streams contains little organic matter and sediment and is generally very clear.

The Firehole River is located in northwestern Wyoming, and is one of the two major tributaries of the Madison River. It flows north approximately 21 miles (34 km) from its source in Madison Lake on the Continental Divide to join the Gibbon River at Madison Junction in Yellowstone National Park. It is part of the Missouri River system.

The Jarbidge River is a 51.8-mile-long (83.4 km), high elevation river in Elko County, Nevada, and Owyhee County, Idaho, in the United States. The Jarbidge originates as two main forks in the Jarbidge Mountains of northeastern Nevada and then flows through basalt and rhyolite canyons on the high plateau of the Owyhee Desert before joining the Bruneau River.

The Pheasant Tail nymph or PT Nymph or Sawyer's Pheasant Tail is a popular all purpose nymph imitation used by fly anglers. It imitates a large variety of olive, olive-brown colored aquatic insect larvae that many fish including trout and grayling feed upon.

Intermittent, temporary or seasonal rivers or streams cease to flow every year or at least twice every five years. Such rivers drain large arid and semi-arid areas, covering approximately a third of the Earth's surface. The extent of temporary rivers is increasing, as many formerly perennial rivers are becoming temporary because of increasing water demand, particularly for irrigation. Despite inconsistent water flow, intermittent rivers are considered land-forming agents in arid regions, as they are agents of significant deposition and erosion during flood events. The combination of dry crusted soils and the highly erosive energy of the rain cause sediment resuspension and transport to the coastal areas. They are among the aquatic habitats most altered by human activities. During the summer even under no flow conditions the point sources are still active such as the wastewater effluents, resulting in nutrients and organic pollutants accumulating in the sediment. Sediment operates as a pollution inventory and pollutants are moved to the next basin with the first flush. Their vulnerability is intensified by the conflict between water use demand and aquatic ecosystem conservation. Advanced modelling tools have been developed to better describe intermittent flow dynamic changes such as the tempQsim model.

The Gibbon River flows east of the Continental Divide in Yellowstone National Park, in northwestern Wyoming, the Northwestern United States. Along with the Firehole River, it is a major tributary of the Madison River, which itself is a tributary of the Missouri River.

Giant Springs is a large first magnitude spring located near Great Falls, Montana and is the central feature of Giant Springs State Park. Its water has a constant temperature of 54 °F (12 °C) and originates from snowmelt in the Little Belt Mountains, 60 miles (97 km) away. According to chlorofluorocarbon dating, the water takes about 3,000 years to travel underground before returning to the surface at the springs.

A seep or flush is a moist or wet place where water, usually groundwater, reaches the Earth's surface from an underground aquifer.

A stream is a continuous body of surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream may be referred to by a variety of local or regional names. Long, large streams are usually called rivers, while smaller, less voluminous and more intermittent streams are known as streamlets, brooks or creeks.

A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually a freshwater stream, flowing on the Earth's land surface or inside caves towards another waterbody at a lower elevation, such as an ocean, sea, bay, lake, wetland, or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground or becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to by names such as creek, brook, and rivulet. There are no official definitions for these various generic terms for a watercourse as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities, a stream is customarily referred to by one of these names as determined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and Northeast England, and "beck" in Northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always; in English the language is vague compared to some languages like French, where a fleuve flows into the sea and a rivière is a tributary of another rivière or fleuve.

Freshwater biology is the scientific biological study of freshwater ecosystems and is a branch of limnology. This field seeks to understand the relationships between living organisms in their physical environment. These physical environments may include rivers, lakes, streams, ponds, lakes, reservoirs, or wetlands. Knowledge from this discipline is also widely used in industrial processes to make use of biological processes involved with sewage treatment and water purification. Water presence and flow is an essential aspect to species distribution and influences when and where species interact in freshwater environments.
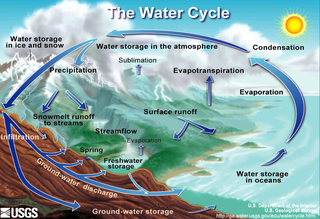
Freshwater environmental quality parameters are those chemical, physical or biological parameters that can be used to characterise a freshwater body. Because almost all water bodies are dynamic in their composition, the relevant quality parameters are typically expressed as a range of expected concentrations.

Salmon Falls Creek is a tributary of the Snake River, flowing from northern Nevada into Idaho in the United States. Formed in high mountains at the northern edge of the Great Basin, Salmon Falls Creek flows northwards 121 miles (195 km), draining an arid and mountainous basin of 2,103 square miles (5,450 km2). The Salmon Falls Creek valley served as a trade route between the Native American groups of the Snake River Plain and Great Basin. Today, most of its water is used for irrigation.
The Snake River Aquifer is a large reservoir of groundwater underlying the Snake River Plain in the southern part of the U.S. state of Idaho. Most of the water in the aquifer comes from irrigation recharge. Measuring about 400 miles (640 km) from east to west, it is an important water source for agricultural irrigation in the Plain. The Snake River Aquifer is commonly defined as two separate parts, separated by Salmon Falls Creek: the Eastern Snake River Plain Aquifer and Western Snake River Plain Aquifer.
Kissingen Spring was a natural spring formerly flowing in Polk County, Southwest Florida. It was also a venue for recreation until it dried up in 1950. Hundreds of wells drilled into the Floridan Aquifer may have caused the demise of the springs. Its site is located near the northern end of Peace River, approximately 3/4 mile east of U.S. Highway 17 and 4 miles south of Florida SR 60 / south of Bartow.


















