
The London Borough of Islington is a London borough which forms part of Inner London. Islington has an estimated population of 215,667. It was formed in 1965 under the London Government Act 1963, which simultaneously abolished the metropolitan boroughs of Islington and Finsbury.

Clerkenwell is an area of central London, England.

The Royal Mile is a succession of streets forming the main thoroughfare of the Old Town of the city of Edinburgh in Scotland. The term was first used descriptively in W. M. Gilbert's Edinburgh in the Nineteenth Century (1901), describing the city "with its Castle and Palace and the royal mile between", and was further popularised as the title of a guidebook by R. T. Skinner published in 1920, "The Royal Mile (Edinburgh) Castle to Holyrood(house)".
The A1 is the longest numbered road in the United Kingdom, at 410 miles (660 km). It connects London, the capital of England, with Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. It passes through or near North London, Hatfield, Welwyn Garden City, Stevenage, Baldock, Letchworth Garden City, Biggleswade, St Neots, Huntingdon, Peterborough, Stamford, Grantham, Newark-on-Trent, Retford, Doncaster, York, Pontefract, Wetherby, Ripon, Darlington, Durham, Sunderland, Gateshead, Newcastle upon Tyne, Morpeth, Alnwick and Berwick-upon-Tweed.

Old Street is a 1-mile (1.6 km) street in inner north-east Central London that runs west to east from Goswell Road in Clerkenwell, in the London Borough of Islington, via St Luke's and Old Street Roundabout, to the crossroads where it meets Shoreditch High Street (south), Kingsland Road (north) and Hackney Road (east) in Shoreditch in the London Borough of Hackney.

The Metropolitan Borough of Finsbury was a Metropolitan borough within the County of London from 1900 to 1965, when it was amalgamated with the Metropolitan Borough of Islington to form the London Borough of Islington.
Princes Street is one of the major thoroughfares in central Edinburgh, Scotland and the main shopping street in the capital. It is the southernmost street of Edinburgh's New Town, stretching around 1.2 km from Lothian Road in the west, to Leith Street in the east. The street has few buildings on the south side and looks over Princes Street Gardens allowing panoramic views of the Old Town, Edinburgh Castle, as well as the valley between. Most of the street is limited to trams, buses and taxis with only the east end open to all traffic.

The Angel, Islington, is a historic landmark and a series of buildings that have stood on the corner of Islington High Street and Pentonville Road in Islington, London, England. The land originally belonged to the Clerkenwell Priory and has had various properties built on it since the 16th century. An inn on the site was called the "Angel Inn" by 1614, and the crossing became generally known as "the Angel". The site was bisected by the New Road, which opened in 1756, and properties on the site have been rebuilt several times up to the 20th century. The corner site gave its name to Angel tube station, opened in 1901, and the surrounding Angel area of London.
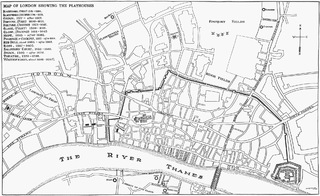
The Red Bull was an inn-yard conversion erected in Clerkenwell, London, operating in the 17th century. For more than four decades, it entertained audiences drawn primarily from the City and its suburbs, developing a reputation over the years for rowdiness. After Parliament closed the theatres in 1642, it continued to host illegal performances intermittently, and when the theatres reopened after the Restoration, it became a legitimate venue again. There is a myth that it burned down in the Great Fire of London but the direct reason for its end is unclear.

Goswell Road, in Central London, is an end part of the A1. The southern part ends with one block, on the east side, in City of London; the rest is in the London Borough of Islington, the north end being Angel. It crosses Old Street/Clerkenwell Road. In the north it splits Clerkenwell from Finsbury; the south was sometimes used as a demarcator but all but the southern corporate/legal/financial end in the modern era forms the heart of the highly developed mixed-use district Barbican.

Hicks Hall, or Hickes' Hall, was a courthouse at the southern end of St John Street, Clerkenwell, London. It opened in 1612, and was closed and demolished in 1782. It was the first purpose-built sessions house for justices of the peace of the county of Middlesex, and became the main court of petty sessions and arraignment for more serious offences, including cases involving plots, attacks and minor transgressions against the state.

The Great North Road was the main highway between England and Scotland from medieval times until the 20th century. It became a coaching route used by mail coaches travelling between London, York and Edinburgh. The modern A1 mainly parallels the route of the Great North Road. Coaching inns, many of which survive, were staging posts providing accommodation, stabling for horses and replacement mounts. Nowadays virtually no surviving coaching inns can be seen while driving on the A1, because the modern route bypasses the towns in which the inns are found.

St Sepulchre was an ancient parish which had its southern part within the boundaries of the City of London and its northern part outside. Its former area is now within the contemporary neighbourhoods of Smithfield, Farringdon and Clerkenwell.

Coade stone or Lithodipyra or Lithodipra is stoneware that was often described as an artificial stone in the late 18th and early 19th centuries. It was used for moulding neoclassical statues, architectural decorations and garden ornaments of the highest quality that remain virtually weatherproof today.

Princes Street Station was a mainline railway station which stood at the west end of Princes Street, in Edinburgh, Scotland, for almost 100 years. Temporary stations were opened in 1848 and 1870, with construction of the main station commencing in the 1890s. The station was closed completely in 1965 and largely demolished in 1969–70. Only its hotel remains, but it is no longer in railway ownership.

The Cockpit-in-Court was an early theatre in London, located at the Palace of Whitehall, next to St. James's Park, now the site of 70 Whitehall, in Westminster.
Hockley-in-the-Hole was an area of Clerkenwell Green in central London where bull-baiting, bear-baiting and similar activities occurred in the 17th and 18th centuries. The Beargarden was located at Hockley-in-the-Hole where the Coach & Horses pub at Back Hill and Ray Street meet today, north of the junction of Clerkenwell Road and Farringdon Road.

St Mary-at-Hill is an Anglican parish church in the Ward of Billingsgate, City of London. It is situated on Lovat Lane, a cobbled street off Eastcheap.

Angel is an area on the northern fringes of Central London within the London Borough of Islington. It is 2 miles (3.2 km) north-northeast of Charing Cross on the Inner Ring Road at a busy transport intersection. The area is identified in the London Plan as one of 35 major centres in London. It is a significant commercial and retail centre, and a business improvement district. Angel straddles the ancient boundary of the parishes of Clerkenwell and Islington that later became the metropolitan boroughs of Finsbury and Islington. It is named from the former Angel Inn which stood on the corner of Islington High Street and Pentonville Road. Since 1965 the whole area has formed part of the London Borough of Islington in Greater London.

The Bull and Mouth Inn was a coaching inn in the City of London that dated from before the Great Fire of London in 1666. It was located between Bull and Mouth Street in the north and Angel Street in the south. It was once an important arrival and departure point for coaches from all over Britain, but particularly for the north of England and Scotland. It became the Queen's Hotel in 1830 but was demolished in 1887 or 1888 when new post office buildings were built in St Martin's Le Grand.

















