Related Research Articles

Eric Eustace Williams was a Trinidad and Tobago politician who is regarded by some as the "Father of the Nation", having led the then British Colony of Trinidad and Tobago to majority rule on 28 October 1956, to independence on 31 August 1962, and republic status on 1 August 1976, leading an unbroken string of general elections victories with his political party, the People's National Movement, until his death in 1981. He was the first Prime Minister of Trinidad and Tobago and also a noted Caribbean historian, especially for his book entitled Capitalism and Slavery.

The West Indies Federation, also known as the West Indies, the Federation of the West Indies or the West Indian Federation, was a short-lived political union that existed from 3 January 1958 to 31 May 1962. Various islands in the Caribbean that were part of the British Empire, including Trinidad and Tobago, Barbados, Jamaica, and those on the Leeward and Windward Islands, came together to form the Federation, with its capital in Port of Spain, Trinidad and Tobago. The expressed intention of the Federation was to create a political unit that would become independent from Britain as a single state — possibly similar to Canada, the Federation of Australia, or the Federation of Rhodesia and Nyasaland. Before that could happen, the Federation collapsed due to internal political conflicts over how it would be governed or function viably. The formation of a West Indian Federation was encouraged by the United Kingdom, but also requested by West Indian nationalists.

The British West Indies (BWI) were colonised British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Guiana and Trinidad and Tobago. Other territories included Bermuda, and the former British Honduras.
Sir Shridath Surendranath Ramphal OM, often known as Sir Sonny Ramphal, is a Guyanese politician who was the second Commonwealth Secretary-General, holding the position from 1975 to 1990. He was also the foreign minister of Guyana from 1972 to 1975, and assistant attorney general of the West Indies Federation from 1958 to 1962.

Patrick George Thomas Buchan-Hepburn, 1st Baron Hailes, was a British Conservative politician and the only Governor-General of the short-lived West Indies Federation from 1958 to 1962.
Sir Samuel William Knaggs was a British colonial administrator.

The University of the West Indies (UWI), originally University College of the West Indies, is a public university system established to serve the higher education needs of the residents of 18 English-speaking countries and territories in the Caribbean: Anguilla, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Belize, Bermuda, British Virgin Islands, Cayman Islands, Dominica, Grenada, Guyana, Jamaica, Montserrat, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, Trinidad and Tobago, and Turks and Caicos Islands. Each country is either a member of the Commonwealth of Nations or a British Overseas Territory.

The term British West Indies refers to the former English and British colonies and the present-day overseas territories of the United Kingdom in the Caribbean.

The British Windward Islands was an administrative grouping of British colonies in the Windward Islands of the West Indies, existing from 1833 until 31 December 1959 and consisting of the islands of Grenada, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent, the Grenadines, Barbados, Tobago, and Dominica, previously included in the British Leeward Islands.

Cricket West Indies (CWI) is the governing body for cricket in the West Indies. It was originally formed in the early 1920s as the West Indies Cricket Board of Control, but changed its name to West Indies Cricket Board (WICB) in 1996. In November 2015, the Board resolved to rename itself as Cricket West Indies as part of a restructuring exercise that would also see the creation of a separate commercial body. This rebranding formally occurred in May 2017.
Sir Gerald Aubrey Goodman KC was a Barbadian barrister and politician. He also served as Attorney-General of the Straits Settlements and as a judge in Malaya. His final appointment was as Chief Justice of the Straits Settlements but he died before he could take up office.
The chief justice of Trinidad and Tobago is the highest judge of the Republic of Trinidad and Tobago and presides over its Supreme Court of Judicature. He is appointed by a common decision of the president, the prime minister and the leader of the main opposition party.

Elizabeth II was Queen of Trinidad and Tobago from the independence of Trinidad and Tobago on 31 August 1962 until the country became a republic on 1 August 1976. Her constitutional role as head of state was delegated to a governor-general, who acted on the advice of government ministers.

Federal elections were held in the West Indies Federation for the first and only time on 25 March 1958. The result was a victory for the West Indies Federal Labour Party, which won 25 of the 45 seats in the House of Representatives.
The attorney general of the Leeward Islands was the chief law officer of the Leeward Islands. The British crown colony of the Leeward Islands, comprising Antigua, Barbuda, the British Virgin Islands, Montserrat, Saint Kitts, Nevis, Anguilla, and Dominica, existed as a political entity, under various names, from 1671 to 1958, when it became part of the West Indies Federation.
The chief justice of Barbados is the head of the Supreme Court of Barbados as defined by the constitution.

Marguerite WykeOBE was an American-born Trinidadian teacher, poet, artist and politician. After growing up in Jersey City, New Jersey, and working as a teacher, she married and moved to Canada for a decade and then relocated to Trinidad. Writing for various journals and newspapers, and cultivating the artistic community in Trinidad, she became active in local politics. Renouncing her U.S. citizenship, Wyke became a Trinidadian citizen in 1953 and became active in the island's governance. With the establishment of the West Indies Federation, she was appointed as one of two senators from Trinidad and Tobago and one of only two women senators to serve in the Federal Parliament of the West Indies Federation. When the Federation dissolved, Wyke returned to her artistic endeavors, publishing poetry and participating in various art media.
Sir Hugh Olliviere Beresford Wooding was a lawyer and politician from Trinidad and Tobago.
Sir Robert Howard Furness (1880–1959) was a British Chief Justice of Barbados, after which he became Chief Justice of Jamaica from April 1936.
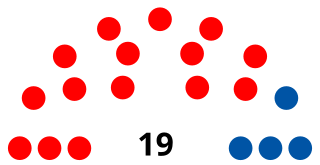
The Federal Parliament of the West Indies Federation was the bicameral legislature in West Indies Federation from 1958 to 1962. It was formally made up of two houses, an appointed Senate and an elected House of Representatives.
References
- ↑ "No. 37238". The London Gazette . 24 August 1945. p. 4298.
- ↑ "No. 41557". The London Gazette . 25 November 1958. p. 7215.
- ↑ "No. 41589". The London Gazette (Supplement). 25 November 1958. p. 2.
- ↑ "Appointment of the Chief Justice of the Federation". The West Indies Gazette. Governor General. 14 August 1961. p. 93. Retrieved 28 February 2016.