Related Research Articles

Hornchurch is a suburban town in East London the London Borough of Havering. It is located 15.2 miles (24.5 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross. It comprises a number of shopping streets and a large residential area. It historically formed a large ancient parish in the county of Essex that became the manor and liberty of Havering. The economic history of Hornchurch is underpinned by a shift away from agriculture to other industries with the growing significance of nearby Romford as a market town and centre of administration. As part of the suburban growth of London in the 20th century, Hornchurch significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming an urban district in 1926 and has formed part of Greater London since 1965. It is the location of Queen's Theatre, Havering Sixth Form College and Havering College of Further and Higher Education.

Romford is a large town in East London and the administrative centre of the London Borough of Havering. It is located 14 miles northeast of Charing Cross and is one of the major metropolitan centres identified in the London Plan. Historically, Romford was a market town in the county of Essex, and formed the administrative centre of the liberty of Havering before that liberty was dissolved in 1892. Good road links to London and the opening of the railway station in 1839 were key to the development of the town. The economic history of Romford is characterised by a shift from agriculture to light industry and then to retail and commerce. As part of the suburban growth of London throughout the 20th century, Romford significantly expanded and increased in population, becoming a municipal borough in 1937 and was incorporated into Greater London in 1965. Today, it is one of the largest commercial, retail, entertainment and leisure districts in London and has a well-developed night-time economy. Its population, as of 2011, was 122,854.

Upminster is a suburban town in East London, England, within the London Borough of Havering. Located 16.5 miles (26.6 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross, it is one of the district centres identified for development in the London Plan.
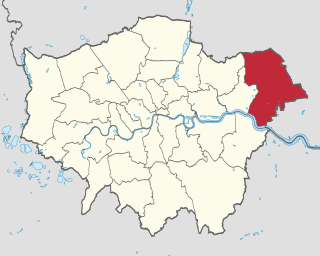
The London Borough of Havering in East London, England, forms part of Outer London. It has a population of 259,552 inhabitants; the principal town is Romford, while other communities are Hornchurch, Upminster, Collier Row and Rainham. The borough is mainly suburban, with large areas of protected open space. Romford is a major retail and night time entertainment centre, and to the south the borough extends into the London Riverside redevelopment area of the Thames Gateway. The name Havering is a reference to the Royal Liberty of Havering which occupied the area for several centuries. The local authority is Havering London Borough Council. It is the easternmost London borough.

Elm Park is a suburban planned community in East London and part of the London Borough of Havering. Located 14.3 miles (23.0 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross, it is identified as a district centre in the London Plan with several streets of shops and a priority for regeneration. Prior to the construction of the extensive Elm Park Garden City development in the 1930s it was a scattered settlement of farms in the south of the parish of Hornchurch. Elm Park has been connected to central London by the electrified District line service since 1935 and the planned development of the area formed part of the interwar private housing boom that was interrupted by World War II. After the war Elm Park expanded with social housing and it has formed part of Greater London since 1965.

Collier Row is an area of Romford in East London, England, within the London Borough of Havering. It is a suburban development north of Romford town centre, around 14 miles (22.5 km) north-east of Charing Cross.

Romford Market is a large outdoor retail market located in Romford in the London Borough of Havering, England. The market right was established by royal order in 1247. Rival markets are prohibited within 6.66 miles (10.72 km). Governance of the market was strengthened by the 1465 charter of the Liberty of Havering, which was administered from a court house at the western end of the market. Formerly a livestock and agricultural market, cattle was last sold in 1958. The market has been in local authority ownership since it was purchased by the Romford Local Board in 1892 and is now owned by Havering Council. The marketplace was located on the main east–west road through the town until traffic was diverted away from the market in 1969. The market is promoted as a filming location. It is open on Wednesday, Friday, Saturday and Sunday. As of July 2020 it has 60 licensed traders, down from a peak of over 300.

Rush Green is a suburban area in Romford in East London, England. It straddles the boundary of the London Borough of Barking and Dagenham and the London Borough of Havering, and is located 13.5 miles (22 km) east-northeast of Charing Cross.

Hornchurch was a local government district in southwest Essex from 1926 to 1965, formed as an urban district for the civil parish of Hornchurch. It was greatly expanded in 1934 with the addition of Cranham, Great Warley, Rainham, Upminster and Wennington; and in 1935 by gaining North Ockendon. Hornchurch Urban District Council was based at Langtons House in Hornchurch from 1929. The district formed a suburb of London and with a population peaking at 131,014 in 1961, it was one of the largest districts of its type in England. It now forms the greater part of the London Borough of Havering in Greater London.

Romford was a local government district in southwest Essex from 1851 to 1965. It was significantly expanded in 1934 and gained the status of municipal borough in 1937. The population density of the district consistently increased during its existence and its former area now corresponds to the northern part of the London Borough of Havering in Greater London.

Bedfords Park is public open space of 215 acres or approximately 87½ hectares near Havering-atte-Bower in the London Borough of Havering in England. It is one of three large parklands around Havering-atte-Bower; the others are Havering Country Park and Pyrgo Park.
Rush Green Hospital was a hospital located at Rush Green in the London Borough of Barking and Dagenham in London from 1900 to 1995.

Harold Wood Hospital was a hospital in east London, United Kingdom. It was located in Gubbins Lane, Harold Wood in Romford, in the London Borough of Havering. It was managed by Barking, Havering and Redbridge Hospitals NHS Trust. The Havering Campus of London South Bank University, an NHS polyclinic and a long term conditions unit continue to operate at the hospital site, and a residential development by Countryside Properties known as Kings Park is in development.
Allied Breweries was the result of a 1961 merger between Ind Coope, Ansells, and Tetley Walker.

Beam Park is a new neighbourhood in the south of the London Borough of Barking and Dagenham and the London Borough of Havering. It is named after the River Beam which forms the boundary between the boroughs. It is part of the London Riverside opportunity area and is designated with neighbouring Rainham as a housing zone by the Greater London Authority. It covers an area of 29 hectares. It will include a town centre in the Havering part of the development and will be served by Beam Park railway station. Much of the land previously part of the Ford Dagenham site is being redeveloped as a joint venture between London and Quadrant and Countryside Properties. Planning consent for 3,000 homes was issued in February 2019 and construction began in May 2019. The first residents moved into Beam Park in December 2020. Planning permission was given for 947 additional homes in December 2022

The Mercury Mall is an enclosed shopping centre in Romford town centre, in the London Borough of Havering, Greater London. It opened in June 1990 as Liberty 2. From 2006 to August 2010 it was owned by The Mall Fund and was known as The Mall Romford. It is—along with The Liberty and The Brewery—one of the three main shopping centres in Romford.

Benskins was the pre-eminent brewery in Watford, and Hertfordshire's biggest brewer until its acquisition by Ind Coope in 1957.

Havering Museum is a local museum located in the town of Romford, in the London Borough of Havering. It is primarily focused on the studies and artifacts from the five towns that encompass the borough of Havering. Located in what remains of the old Ind Coope Romford Brewery, it is one of the last reminders of Romford's brewing history. Completely volunteer run, the museum is self-funded through various Events, Groups and Sponsors. Relating to the history of the London Borough of Havering, providing a home for exhibits of Havering's past defining what makes Havering Havering, celebrating the achievements of local people past and present.

The Brewery is a shopping and leisure centre in Romford town centre, in the London Borough of Havering, England. It is located on the site of the former Star Brewery, and it opened in 2001. It is—along with The Liberty and The Mercury—one of the three main shopping centres in Romford.

The Dolphin Centre was a swimming and leisure facility in Romford, in the London Borough of Havering, England.
References
- 1 2 3 British History Online - Romford Economic History, (1978)
- ↑ Havering London Borough Council Archived 2007-06-30 at the Wayback Machine - Romford Area Action Plan. March 2006. (PDF)
- ↑ Havering London Borough Council Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine - A history of Romford
- ↑ Havering London Borough Council Archived 2007-09-27 at the Wayback Machine - Romford Town Centre
- ↑ beer-pages - John Bull Bounces Back
- ↑ Brewery History Society, East London Brewery History , (2000)
- ↑ Fryer, John (2004). Romford. A pocket album. Salisbury: Frith book company. p. 76. ISBN 1-85937-888-9.