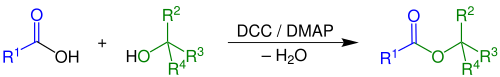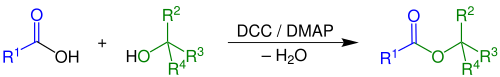In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula R−C(=O)−NR′R″, where R, R', and R″ represent any group, typically organyl groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is part of the main chain of a protein, and an isopeptide bond when it occurs in a side chain, as in asparagine and glutamine. It can be viewed as a derivative of a carboxylic acid with the hydroxyl group replaced by an amine group ; or, equivalently, an acyl (alkanoyl) group joined to an amine group.

In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is often written as R−COOH or R−CO2H, sometimes as R−C(O)OH with R referring to an organyl group, or hydrogen, or other groups. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

In chemistry, an ester is a functional group derived from an acid in which the hydrogen atom (H) of at least one acidic hydroxyl group of that acid is replaced by an organyl group. Analogues derived from oxygen replaced by other chalcogens belong to the ester category as well. According to some authors, organyl derivatives of acidic hydrogen of other acids are esters as well, but not according to the IUPAC.

In organic chemistry, a ketene is an organic compound of the form RR'C=C=O, where R and R' are two arbitrary monovalent chemical groups. The name may also refer to the specific compound ethenone H2C=C=O, the simplest ketene.
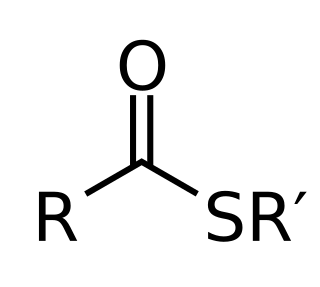
In organic chemistry, thioesters are organosulfur compounds with the molecular structure R−C(=O)−S−R’. They are analogous to carboxylate esters with the sulfur in the thioester replacing oxygen in the carboxylate ester, as implied by the thio- prefix. They are the product of esterification of a carboxylic acid with a thiol. In biochemistry, the best-known thioesters are derivatives of coenzyme A, e.g., acetyl-CoA. The R and R' represent organyl groups, or H in the case of R.

Fischer esterification or Fischer–Speier esterification is a special type of esterification by refluxing a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst. The reaction was first described by Emil Fischer and Arthur Speier in 1895. Most carboxylic acids are suitable for the reaction, but the alcohol should generally be primary or secondary. Tertiary alcohols are prone to elimination. Contrary to common misconception found in organic chemistry textbooks, phenols can also be esterified to give good to near quantitative yield of products. Commonly used catalysts for a Fischer esterification include sulfuric acid, p-toluenesulfonic acid, and Lewis acids such as scandium(III) triflate. For more valuable or sensitive substrates other, milder procedures such as Steglich esterification are used. The reaction is often carried out without a solvent or in a non-polar solvent that can facilitate Dean–Stark distillation to remove the water byproduct. Typical reaction times vary from 1–10 hours at temperatures of 60–110 °C.
In organic chemistry, an acyl chloride is an organic compound with the functional group −C(=O)Cl. Their formula is usually written R−COCl, where R is a side chain. They are reactive derivatives of carboxylic acids. A specific example of an acyl chloride is acetyl chloride, CH3COCl. Acyl chlorides are the most important subset of acyl halides.

The Claisen rearrangement is a powerful carbon–carbon bond-forming chemical reaction discovered by Rainer Ludwig Claisen. The heating of an allyl vinyl ether will initiate a [3,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement to give a γ,δ-unsaturated carbonyl, driven by exergonically favored carbonyl CO bond formation (Δ = −327 kcal/mol.

N,N′-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC or DCCD) is an organic compound with the chemical formula (C6H11N)2C. It is a waxy white solid with a sweet odor. Its primary use is to couple amino acids during artificial peptide synthesis. The low melting point of this material allows it to be melted for easy handling. It is highly soluble in dichloromethane, tetrahydrofuran, acetonitrile and dimethylformamide, but insoluble in water.

In organic chemistry, a carbodiimide is a functional group with the formula RN=C=NR. On Earth they are exclusively synthetic, but in interstellar space the parent compound HN=C=NH has been detected by its maser emissions.
4-Dimethylaminopyridine (DMAP) is a derivative of pyridine with the chemical formula (CH3)2NC5H4N. This white solid is of interest because it is more basic than pyridine, owing to the resonance stabilisation from the NMe2 substituent.

The Curtius rearrangement, first defined by Theodor Curtius in 1885, is the thermal decomposition of an acyl azide to an isocyanate with loss of nitrogen gas. The isocyanate then undergoes attack by a variety of nucleophiles such as water, alcohols and amines, to yield a primary amine, carbamate or urea derivative respectively. Several reviews have been published.

1,1'-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) is an organic compound with the molecular formula (C3H3N2)2CO. It is a white crystalline solid. It is often used for the coupling of amino acids for peptide synthesis and as a reagent in organic synthesis.
In organic chemistry, the Arndt–Eistert reaction is the conversion of a carboxylic acid to its homologue. It is named for the German chemists Fritz Arndt (1885–1969) and Bernd Eistert (1902–1978). The method entails treating an acid chlorides with diazomethane. It is a popular method of producing β-amino acids from α-amino acids.
The Kulinkovich reaction describes the organic synthesis of substituted cyclopropanols through reaction of esters with dialkyldialkoxytitanium reagents, which are generated in situ from Grignard reagents containing a hydrogen in beta-position and titanium(IV) alkoxides such as titanium isopropoxide. This reaction was first reported by Oleg Kulinkovich and coworkers in 1989.

N-Hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) is an organic compound with the formula (CH2CO)2NOH. It is a white solid that is used as a reagent for preparing active esters in peptide synthesis. It can be synthesized by heating succinic anhydride with hydroxylamine or hydroxylamine hydrochloride.
Fluorination by sulfur tetrafluoride produces organofluorine compounds from oxygen-containing organic functional groups using sulfur tetrafluoride. The reaction has broad scope, and SF4 is an inexpensive reagent. It is however hazardous gas whose handling requires specialized apparatus. Thus, for many laboratory scale fluorinations diethylaminosulfur trifluoride ("DAST") is used instead.
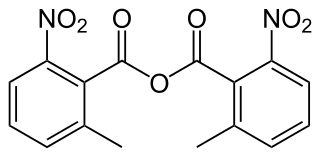
2-Methyl-6-nitrobenzoic anhydride is an organic acid anhydride also known as the Shiina reagent, having a structure wherein carboxylic acids undergo intermolecular dehydration condensation. It was developed in 2002 by Prof. Isamu Shiina. The compound is often abbreviated MNBA.
Shiina macrolactonization is an organic chemical reaction that synthesizes cyclic compounds by using aromatic carboxylic acid anhydrides as dehydration condensation agents. In 1994, Prof. Isamu Shiina reported an acidic cyclization method using Lewis acid catalyst, and, in 2002, a basic cyclization using nucleophilic catalyst.
Shiina esterification is an organic chemical reaction that synthesizes carboxylic esters from nearly equal amounts of carboxylic acids and alcohols by using aromatic carboxylic acid anhydrides as dehydration condensation agents. In 1994, Prof. Isamu Shiina reported an acidic coupling method using Lewis acid, and, in 2002, a basic esterification using nucleophilic catalyst.