
Alectryon is a genus of about 30 species of trees and shrubs from the family Sapindaceae. They grow naturally across Australasia, Papuasia, Melanesia, western Polynesia, east Malesia and Southeast Asia, including across mainland Australia, especially diverse in eastern Queensland and New South Wales, the Torres Strait Islands, New Guinea, the Solomon Islands, New Caledonia, New Zealand, Vanuatu, Fiji, Samoa, Hawaii, Indonesia and the Philippines. They grow in a wide variety of natural habitats, from rainforests, gallery forests and coastal forests to arid savannas and heaths.

Flindersia is a genus of 17 species of small to large trees in the family Rutaceae. They have simple or pinnate leaves, flowers arranged in panicles at or near the ends of branchlets and fruit that is a woody capsule containing winged seeds. They grow naturally in Australia, the Moluccas, New Guinea and New Caledonia.

Xylomelum is a genus of six species of flowering plants, often commonly known as woody pears, in the family Proteaceae and are endemic to Australia. Plants in this genus are tall shrubs or small trees with leaves arranged in opposite pairs, relatively small flowers arranged in spike-like groups, and the fruit a woody, more or less pear-shaped follicle.

Cupaniopsis is a genus of about 45 species of flowering plants in the family, Sapindaceae and are native to Fiji, Indonesia, New Caledonia, New Guinea, the Solomon Islands Vanuatu, Samoa, Torres Strait Islands, Micronesia and Australia. Plants in the genus Cupaniopsis are trees with paripinnate with small, regular flowers with 5 sepals and petals with 6 to 10 stamens and the fruit a capsule.

Tristaniopsis is a genus of shrubs and trees in the myrtle family Myrtaceae described as a genus in 1863. They have a wide distribution in Southeast Asia, New Guinea, New Caledonia and Australia.

Triunia is a genus of medium to tall shrubs or small trees found as understorey plants in rainforests of eastern Australia. Members of the plant family Proteaceae, they are notable for their poisonous fleshy fruits or drupes. Only one species, T. youngiana, is commonly seen in cultivation.

Medicosma is a genus of shrubs and trees in the family Rutaceae, all native to New Guinea, Australia or New Caledonia. They usually have simple leaves arranged in opposite pairs, flowers arranged in cymes with four sepals, four petals and eight stamens. The fruit is a follicle fused at the base in groups of up to four, each containing one or two brown or black seeds.

Gmelina is a genus of plants in the family Lamiaceae. It consists of about 35 species, native to Australia, Southeast Asia, India, New Guinea and New Caledonia. Some species such as G. arborea have been planted and/or become naturalised in India, Africa and Australia. It was named by Carl Linnaeus in honour of botanist Johann Georg Gmelin.
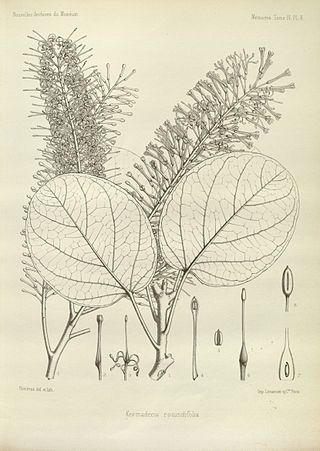
Kermadecia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. The genus comprises eight species of rainforest trees from New Caledonia, Fiji, and Vanuatu. Its closest relative is Euplassa from South America.

Xanthostemon is a genus of plants in the myrtle family Myrtaceae, first described in 1857 by the German–born Australian botanist Ferdinand von Mueller. The genus is distributed across Malesia, Papuasia and northern Australia. The genera Pleurocalyptus and Purpureostemon from New Caledonia are morphologically close to Xanthostemon.

Lepidosperma is a genus of flowering plant of the family Cyperaceae. Most of the species are endemic to Australia, with others native to southern China, southeast Asia, New Guinea, New Caledonia and New Zealand.

Parsonsia is a genus of woody vines in the family Apocynaceae. Species occur throughout Indomalaya, Australasia and Melanesia.

Styphelia is a genus of shrubs in the family Ericaceae, native from Indo-China through the Pacific to Australia. Most have minute or small leaves with a sharp tip, single, tube-shaped flowers arranged in leaf axils and with the ends of the petals rolled back with hairs in the inside of the tube.

Stenocarpus sinuatus, known as the firewheel tree, is an Australian rainforest tree in the family Proteaceae. The range of natural distribution is in various rainforest types from the Nambucca River in New South Wales to the Atherton Tableland in tropical Queensland. Stenocarpus sinuatus is widely planted as an ornamental tree in other parts of Australia and in different parts of the world.

Stenocarpus cryptocarpus, commonly known as the giant-leaved stenocarpus, is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to north Queensland. It is a tree with buttress roots at the base, simple, mostly elliptical adult leaves, groups of cream-coloured flowers and narrow oblong follicles.

Stenocarpus umbelliferus is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae. It is endemic to New Caledonia. It has a prostrate or upright habit, growing up to 5 metres in height. Stems are flattened when young, later becoming rounded. The leaves are thick and leathery with a slightly wavy margin. These may be ovate, elliptic, lanceolate or spathulate in shape with petioles that are 3 to 12 mm long. White, cream or pale yellow flowers occur in groups of 3 to 8 per umbel. These are followed by dark-coloured glabrous follicles that are 25 to 80 mm long and 3 to 5 mm wide.

Virotia is a genus of six species of flowering plants in the family Proteaceae. The genus is endemic to New Caledonia with six species that were once placed in Macadamia. Its closest relatives are the Australian Athertonia and the Asian Heliciopsis. The genus is named after Robert Virot, pioneer of ecological studies in New Caledonia and author of a monograph of New Caledonian Proteaceae.

Stenocarpus davallioides, commonly known as the fern-leaved stenocarpus, is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to north Queensland. It is a tree with simple or pinnate adult leaves, groups of creamy-green flowers and narrow oblong follicles.
Donald Bruce Foreman was an Australian botanist who worked on the Monimiaceae and Proteaceae of Australia. He also helped with the editing of selected Flora of Victoria and Flora of Australia Volumes.






















