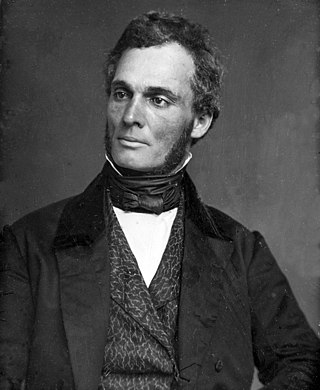The Underground Railroad was a network of secret routes and safe houses established in the United States during the early to mid-19th century. It was used by enslaved African Americans primarily to escape into free states and from there to Canada. The network, primarily the work of free African Americans, was assisted by abolitionists and others sympathetic to the cause of the escapees. The slaves who risked capture and those who aided them are also collectively referred to as the passengers and conductors of the "Underground Railroad". Various other routes led to Mexico, where slavery had been abolished, and to islands in the Caribbean that were not part of the slave trade. An earlier escape route running south toward Florida, then a Spanish possession, existed from the late 17th century until approximately 1790. However, the network now generally known as the Underground Railroad began in the late 18th century. It ran north and grew steadily until the Emancipation Proclamation was signed by President Abraham Lincoln. One estimate suggests that, by 1850, approximately 100,000 slaves had escaped to freedom via the network.
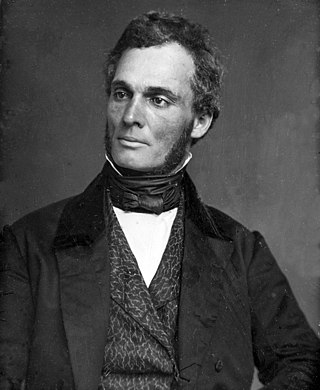
Robert Purvis was an American abolitionist in the United States. He was born in Charleston, South Carolina, and was likely educated at Amherst Academy, a secondary school in Amherst, Massachusetts. He spent most of his life in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. In 1833 he helped found the American Anti-Slavery Society and the Library Company of Colored People. From 1845 to 1850 he served as president of the Pennsylvania Anti-Slavery Society and also traveled to Britain to gain support for the movement.

William Still was an African-American abolitionist based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. He was a conductor of the Underground Railroad and was responsible for aiding and assisting at least 649 slaves to freedom towards North. Still was also a businessman, writer, historian and civil rights activist. Before the American Civil War, Still was chairman of the Vigilance Committee of the Pennsylvania Anti-Slavery Society, named the Vigilant Association of Philadelphia. He directly aided fugitive slaves and also kept records of the people served in order to help families reunite.

In the United States, fugitive slaves or runaway slaves were terms used in the 18th and 19th centuries to describe people who fled slavery. The term also refers to the federal Fugitive Slave Acts of 1793 and 1850. Such people are also called freedom seekers to avoid implying that the enslaved person had committed a crime and that the slaveholder was the injured party.
A vigilance committee is a group of private citizens who take it upon themselves to administer law and order or exercise power in places where they considered the governmental structures or actions inadequate. Some vigilance committees engaged in forms of vigilantism such as aiding fugitive slaves in violation of the laws on the books at the time. Beginning in the 1830s committees of abolitionists worked to free enslaved people and transport them to freedom.

Thomas Garrett was an American abolitionist and leader in the Underground Railroad movement before the American Civil War. He helped more than 2,500 African Americans escape slavery.

Rev. Jermain Wesley Loguen, born Jarm Logue, in slavery, was an African-American abolitionist and bishop of the African Methodist Episcopal Zion Church, and an author of a slave narrative.

Erastus Hussey (1800–1889) was a leading abolitionist, a stationmaster on the Underground Railroad, and one of the founders of the Republican Party. He supported himself and his family as a farmer, teacher, businessman, legislator, and editor.

Lewis Hayden escaped slavery in Kentucky with his family and escaped to Canada. He established a school for African Americans before moving to Boston, Massachusetts to aid in the abolition movement. There he became an abolitionist, lecturer, businessman, and politician. Before the American Civil War, he and his wife Harriet Hayden aided numerous fugitive slaves on the Underground Railroad, often sheltering them at their house.

David Ruggles was an African-American abolitionist in New York who resisted slavery by his participation in a Committee of Vigilance and the Underground Railroad to help fugitive slaves reach free states. He was a printer in New York City during the 1830s, who also wrote numerous articles, and "was the prototype for black activist journalists of his time." He claimed to have led more than 600 fugitive slaves to freedom in the North, including Frederick Douglass, who became a friend and fellow activist. Ruggles opened the first African-American bookstore in 1834.

The Boston Vigilance Committee (1841–1861) was an abolitionist organization formed in Boston, Massachusetts, to protect escaped slaves from being kidnapped and returned to slavery in the South. The Committee aided hundreds of escapees, most of whom arrived as stowaways on coastal trading vessels and stayed a short time before moving on to Canada or England. Notably, members of the Committee provided legal and other aid to George Latimer, Ellen and William Craft, Shadrach Minkins, Thomas Sims, and Anthony Burns.

William Cooper Nell was an American abolitionist, journalist, publisher, author, and civil servant of Boston, Massachusetts, who worked for the integration of schools and public facilities in the state. Writing for abolitionist newspapers The Liberator and The North Star, he helped publicize the anti-slavery cause. He published the North Star from 1847 to 18xx, moving temporarily to Rochester, New York.

The William C. Nell House, now a private residence, was a boarding home located in 3 Smith Court in the Beacon Hill neighbourhood of Boston, Massachusetts, opposite the former African Meeting House, now the Museum of African American History.

The Underground Railroad in Indiana was part of a larger, unofficial, and loosely-connected network of groups and individuals who aided and facilitated the escape of runaway slaves from the southern United States. The network in Indiana gradually evolved in the 1830s and 1840s, reached its peak during the 1850s, and continued until slavery was abolished throughout the United States at the end of the American Civil War in 1865. It is not known how many fugitive slaves escaped through Indiana on their journey to Michigan and Canada. An unknown number of Indiana's abolitionists, anti-slavery advocates, and people of color, as well as Quakers and other religious groups illegally operated stations along the network. Some of the network's operatives have been identified, including Levi Coffin, the best-known of Indiana's Underground Railroad leaders. In addition to shelter, network agents provided food, guidance, and, in some cases, transportation to aid the runaways.

The William Ingersoll Bowditch House is a historic house at 9 Toxteth Street in Brookline, Massachusetts. It is a good example of vernacular Gothic and Greek Revival architecture, built c. 1844-45 as part of one of Brookline's earliest formal residential subdivisions. William Bowditch, the first owner, was an active abolitionist who sheltered fugitive slaves as part of the Underground Railroad, and was a member of the Boston Vigilance Committee. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places on October 17, 1985.

Lewis and Harriet Hayden House was the home of African-American abolitionists who had escaped from slavery in Kentucky; it is located in Beacon Hill, Boston. They maintained the home as a stop on the Underground Railroad, and the Haydens were visited by Harriet Beecher Stowe as research for her book, Uncle Tom's Cabin (1852). Lewis Hayden was an important leader in the African-American community of Boston; in addition, he lectured as an abolitionist and was a member of the Boston Vigilance Committee, which resisted the Fugitive Slave Act of 1850.

William Lawrence Chaplin was a prominent abolitionist in the years before the American Civil War. Known by the title of "General," he was an agent for the American Anti-Slavery Society and a general agent for the Underground Railroad. He was imprisoned for the attempted escape of two individuals, which required $25,000 to get out of jail and safely out of Maryland. He was an editor at two anti-slavery newspapers and he was a Harvard-educated lawyer for a couple of years. He and his wife operated the Glen Haven Water Cure spa in his later years.

Stephen Myers was an abolitionist and agent of the Underground Railroad through the 1830s–1850s. He was also the editor of multiple abolitionist newspapers such as The Elevator, The Northern Star, and Freeman's Advocate, and The Telegraph and Temperance Journal.

Thomas Elkins was an African-American dentist, abolitionist, surgeon, pharmacist, and inventor. He lived in Albany, New York, for most of his life, but travelled during his service as the medical examiner of the 54th and 55th Massachusetts infantries and visited Liberia. Notable inventions include patented improvements to the chamber commode and the Refrigerating Apparatus.