Related Research Articles

Pseudoephedrine (PSE) is a sympathomimetic drug of the phenethylamine and amphetamine chemical classes. It may be used as a nasal/sinus decongestant, as a stimulant, or as a wakefulness-promoting agent in higher doses.

Over-the-counter (OTC) drugs are medicines sold directly to a consumer without a requirement for a prescription from a healthcare professional, as opposed to prescription drugs, which may be supplied only to consumers possessing a valid prescription. In many countries, OTC drugs are selected by a regulatory agency to ensure that they contain ingredients that are safe and effective when used without a physician's care. OTC drugs are usually regulated according to their active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) rather than final products. By regulating APIs instead of specific drug formulations, governments allow manufacturers the freedom to formulate ingredients, or combinations of ingredients, into proprietary mixtures.

A pharmacist, also known as a chemist or a druggist, is a health professional who specializes in the preparation, properties, effects and use of medicines. The pharmacist provides pharmaceutical care to patients, as well as basic primary health care services. Using knowledge of the mechanism of action of drugs, the pharmacist understands how they should be used to achieve maximum benefit, minimal side effects and to avoid drug interactions. Pharmacists undergo university or graduate-level education to understand the biochemical mechanisms and actions of drugs, drug uses, therapeutic roles, side effects, potential drug interactions, and monitoring parameters. This is mated to anatomy, physiology, and pathophysiology. Pharmacists interpret and communicate this specialized knowledge to patients, physicians, and other health care providers.

Pharmacy is the clinical health science that links medical science with chemistry and it is charged with the discovery, production, disposal, safe and effective use, and control of medications and drugs. The practice of pharmacy requires excellent knowledge of drugs, their mechanism of action, side effects, interactions, mobility and toxicity. At the same time, it requires knowledge of treatment and understanding of the pathological process. Some specialties of pharmacists, such as that of clinical pharmacists, require other skills, e.g. knowledge about the acquisition and evaluation of physical and laboratory data.

A prescription, often abbreviated ℞ or Rx, is a formal communication from a physician or other registered health-care professional to a pharmacist, authorizing them to dispense a specific prescription drug for a specific patient. Historically, it was a physician's instruction to an apothecary listing the materials to be compounded into a treatment—the symbol ℞ comes from the first word of a medieval prescription, Latin: Recipere, that gave the list of the materials to be compounded.

A prescription drug is a pharmaceutical drug that legally requires a medical prescription to be dispensed. In contrast, over-the-counter drugs can be obtained without a prescription. The reason for this difference in substance control is the potential scope of misuse, from drug abuse to practicing medicine without a license and without sufficient education. Different jurisdictions have different definitions of what constitutes a prescription drug.

CVS Pharmacy, Inc. is an American retail corporation. A subsidiary of CVS Health, it is headquartered in Woonsocket, Rhode Island. It was also known as, and originally named, the Consumer Value Store and was founded in Lowell, Massachusetts, in 1963. The chain was owned by its original holding company Melville Corporation from its inception until its current parent company was spun off into its own company in 1996. CVS Pharmacy is currently the largest pharmacy chain in the United States by number of locations and total prescription revenue. Its parent company ranks as the fifth largest U.S. corporation by FY2020 revenues in the Fortune 500. The parent company of CVS Pharmacy's leading competitor (Walgreens) ranked 19th for the same time period. CVS sells prescription drugs and a wide assortment of general merchandise, including over-the-counter drugs, beauty products and cosmetics, film and photo finishing services, seasonal merchandise, greeting cards, and convenience foods through their CVS Pharmacy and Longs Drugs retail stores and online through CVS.com. It also provides healthcare services through its more than 1,100 MinuteClinic medical clinics as well as their Diabetes Care Centers. Most of these clinics are located within or outside CVS stores.

The regulation of therapeutic goods, defined as drugs and therapeutic devices, varies by jurisdiction. In some countries, such as the United States, they are regulated at the national level by a single agency. In other jurisdictions they are regulated at the state level, or at both state and national levels by various bodies, as in Australia.
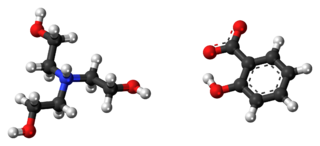
Trolamine salicylate is an organic compound which is the salt formed between triethanolamine and salicylic acid.

Levomethamphetamine is the levorotatory (L-enantiomer) form of methamphetamine. Levomethamphetamine is a sympathomimetic vasoconstrictor that is the active ingredient in some over-the-counter (OTC) nasal decongestant inhalers in the United States.

Southwestern Oklahoma State University (SWOSU) is a public university in Weatherford and Sayre, Oklahoma. It is one of six Regional University System of Oklahoma members.

Pargyline (brand name Eutonyl) is an irreversible selective monoamine oxidase (MAO)-B inhibitor drug (IC50 for MAO-A is 0.01152 μmol/L and for MAO-B is 0.00820 μmol/L) It was brought to market in the US and the UK by Abbott in 1963 as an antihypertensive drug branded "Eutonyl". It was one of several MAO inhibitors introduced in the 1960s including nialamide, isocarboxazid, phenelzine, and tranylcypromine. By 2007 the drug was discontinued and as of 2014 there were no generic versions available in the US. In addition to its actions as an MAOI, pargyline has been found to bind with high affinity to the I2 imidazoline receptor (an allosteric site on the MAO enzyme).
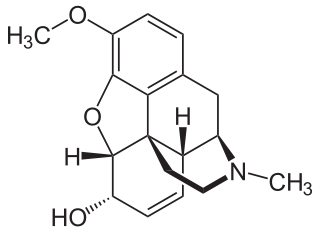
Codeine is an opiate and prodrug of morphine used to treat pain, coughing, and diarrhea. It is found naturally in the sap of the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. It is typically used to treat mild to moderate degrees of pain. Greater benefit may occur when combined with paracetamol (acetaminophen) or a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Evidence does not support its use for acute cough suppression in children or adults. In Europe, it is not recommended as a cough medicine in those under 12 years of age. It is generally taken by mouth. It typically starts working after half an hour, with maximum effect at two hours. Its effects last for about four to six hours. Codeine exhibits similar abuse potential as other opioid medications.
CVS Health Corporation is an American healthcare company that owns CVS Pharmacy, a retail pharmacy chain; CVS Caremark, a pharmacy benefits manager; and Aetna, a health insurance provider, among many other brands. The company's headquarters is in Woonsocket, Rhode Island.
A veterinary pharmacist is a specially trained pharmacist who dispenses veterinary drugs and supplies or products and advice to owners of companion animals and livestock. In addition, they advise the regulatory bodies and are involved in the formulation of veterinary drugs.

A pharmacy is a retail shop which provides pharmaceutical drugs, among other products. At the pharmacy, a pharmacist oversees the fulfillment of medical prescriptions and is available to counsel patients about prescription and over-the-counter drugs or about healthcare and wellness issues. A typical pharmacy would be in the commercial area of a community. Mail-order dispensing is a recent development.
A transdermal analgesic or pain relief patch is a medicated adhesive patch used to relieve minor to severe pain. There are two primary types of analgesic patches: patches containing counterirritants, which are used to treat mild to moderate pain, and patches containing fentanyl, a narcotic used to relieve moderate to severe pain in opioid-tolerant patients.

A tobacco-free pharmacy is a retail pharmacy where the sale of tobacco products is not available. Outside the United States, it is even illegal such as in France or most of Canada for pharmacy stores to sell cigarettes and similar products on the same premises as over-the-counter drugs and prescription medication. Anti-tobacco campaigners advocate the removal of tobacco from pharmacies due to the health risks associated with smoking and the apparent contradiction of selling cigarettes alongside smoking cessation products and asthma medication. Some pharmaceutical retailers counter this argument by reasoning that by selling tobacco, they are more readily able to offer to customers advice and products for quitting smoking.
Carey v. Population Services International, 431 U.S. 678 (1977), was a landmark decision of the U.S. Supreme Court in which the Court held that it was unconstitutional to prohibit anyone other than a licensed pharmacist to distribute nonprescription contraceptives to persons 16 years of age or over, to prohibit the distribution of nonprescription contraceptives by any adult to minors under 16 years of age, and to prohibit anyone, including licensed pharmacists, to advertise or display contraceptives.
Joe Anna Hibler is an American educator. Much of her career was spent teaching business at the university level. Retired from active teaching, she is the former president of Southwestern Oklahoma State University (SWOSU), an inductee into the Oklahoma Women's Hall of Fame, and currently a regent of the Regional University System of Oklahoma.
References
- ↑ "SWOSU Student Secures $2,500 for Local Free Clinic". SWOSU Press Release. January 28, 2009. Retrieved 28 February 2010.
- ↑ Van Hoover, Cheri; Teri Stone-Godena (September–October 2004). "Book review: A history of nonprescription product regulation: By W. Steven Pray, PhD, RPH. Binghamton, NY: Pharmaceutical Products Press, August 2003. 279 pages. $59.95, paperback". Journal of Midwifery & Women's Health. 49 (5): e4–e5. doi:10.1016/j.jmwh.2004.05.014.
- ↑ Pray, W. Steven (2006). Philadelphia (ed.). Nonprescription product therapeutics (2nd ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0-7817-3498-1. OCLC 249140210.
Pharmacists should refer patients to a physician rather than recommending this product.
- ↑ Atoji, Cindy (January 13, 2008). "Humidifiers can ease breathing, minds". Boston Globe. Retrieved 28 February 2010.
- ↑ Nugent, Meg (December 5, 2004). "Over-the-counter cold, flu relief". The Seattle Times. Retrieved 28 February 2010.