
A door is a hinged or otherwise movable barrier that allows ingress (entry) into and egress (exit) from an enclosure. The created opening in the wall is a doorway or portal. A door's essential and primary purpose is to provide security by controlling access to the doorway (portal). Conventionally, it is a panel that fits into the doorway of a building, room, or vehicle. Doors are generally made of a material suited to the door's task. They are commonly attached by hinges, but can move by other means, such as slides or counterbalancing.
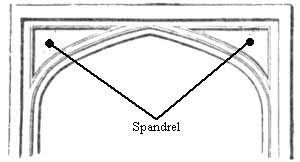
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements.

A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent material, a sash set in a frame in the opening; the sash and frame are also referred to as a window. Many glazed windows may be opened, to allow ventilation, or closed, to exclude inclement weather. Windows may have a latch or similar mechanism to lock the window shut or to hold it open by various amounts.

A barn is an agricultural building usually on farms and used for various purposes. In North America, a barn refers to structures that house livestock, including cattle and horses, as well as equipment and fodder, and often grain. As a result, the term barn is often qualified e.g. tobacco barn, dairy barn, cow house, sheep barn, potato barn. In the British Isles, the term barn is restricted mainly to storage structures for unthreshed cereals and fodder, the terms byre or shippon being applied to cow shelters, whereas horses are kept in buildings known as stables. In mainland Europe, however, barns were often part of integrated structures known as byre-dwellings. In addition, barns may be used for equipment storage, as a covered workplace, and for activities such as threshing.
Scantling is a measurement of prescribed size, dimensions, or cross sectional areas.

A framer is someone who frames, or someone who constructs.

Framing, in construction, is the fitting together of pieces to give a structure support and shape. Framing materials are usually wood, engineered wood, or structural steel. The alternative to framed construction is generally called mass wall construction, where horizontal layers of stacked materials such as log building, masonry, rammed earth, adobe, etc. are used without framing.
This page is a glossary of architecture.

Hamilton railway station is a heritage-listed railway station on the Newcastle line in the inner Newcastle suburb of Hamilton in New South Wales, Australia. It was added to the New South Wales State Heritage Register on 2 April 1999.

A bressummer, breastsummer, summer beam is a load-bearing beam in a timber-framed building. The word summer derived from sumpter or French sommier, "a pack horse", meaning "bearing great burden or weight". "To support a superincumbent wall", "any beast of burden", and in this way is similar to a wall plate.

A wall stud is a vertical repetitive framing member in a building's wall of smaller cross section than a post. It is a fundamental element in frame building.
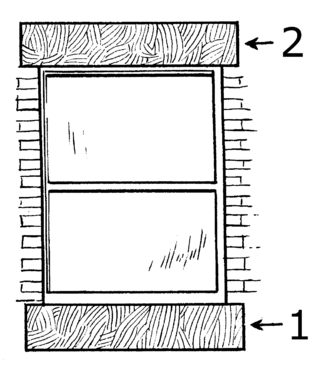
A windowsill is the horizontal structure or surface at the bottom of a window. Window sills serve to structurally support and hold the window in place.

A sill plate or sole plate in construction and architecture is the bottom horizontal member of a wall or building to which vertical members are attached. The word "plate" is typically omitted in America and carpenters speak simply of the "sill". Other names are rat sill, ground plate, ground sill, groundsel, night plate, and midnight sill.

Pole framing or post-frame construction is a simplified building technique that is an alternative to the labor-intensive traditional timber framing technique. It uses large poles or posts buried in the ground or on a foundation to provide the vertical structural support, along with girts to provide horizontal support. The method was developed and matured during the 1930s as agricultural practices changed, including the shift toward engine-powered farm equipment and the demand for cheaper, larger barns and storage areas.

The Longmire Buildings in Mount Rainier National Park comprise the park's former administrative headquarters, and are among the most prominent examples of the National Park Service Rustic style in the national park system. They comprise the Longmire Community Building of 1927, the Administration Building of 1928, and the Longmire Service Station of 1929. Together, these structures were designated National Historic Landmarks on May 28, 1987. The administration and community buildings were designed by National Park Service staff under the direction of Thomas Chalmers Vint.

The Church of the New Jerusalem, now known as The Fryeburg New Church, is a congregation of The New Church (Swedenborgianism) at 12 Oxford Street in Fryeburg, Maine. The historic church building is a Stick style structure designed by Portland architect, Charles H. Kimball, and built in 1878. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1986.
A post is a main vertical or leaning support in a structure similar to a column or pillar, the term post generally refers to a timber but may be metal or stone. A stud in wooden or metal building construction is similar but lighter duty than a post and a strut may be similar to a stud or act as a brace. In the U.K. a strut may be very similar to a post but not carry a beam. In wood construction posts normally land on a sill, but in rare types of buildings the post may continue through to the foundation called an interrupted sill or into the ground called earthfast, post in ground, or posthole construction. A post is also a fundamental element in a fence. The terms "jack" and "cripple" are used with shortened studs and rafters but not posts, except in the specialized vocabulary of shoring.
Havelock Mills in central Manchester were built between 1820 and 1840. It was probably the largest surviving silk mill in the north-west region in the 1970s and had a unique combination of silk and cotton mills on one site. It was a landmark on the Rochdale Canal, overlooking Tib Lock, one of the Rochdale Nine.

Temora Post Office is a heritage-listed post office at 173 Hoskins Street, Temora, New South Wales, Australia. It was added to the Australian Commonwealth Heritage List on 8 November 2011.















