
Immunosuppressive drugs, also known as immunosuppressive agents, immunosuppressants and antirejection medications, are drugs that inhibit or prevent the activity of the immune system.

A monoclonal antibody is an antibody produced from a cell lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell.
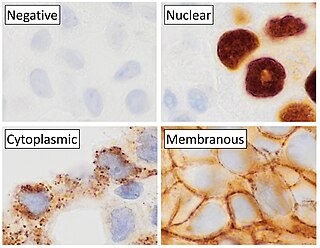
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) is the most common application of immunostaining. It involves the process of selectively identifying antigens (proteins) in cells of a tissue section by exploiting the principle of antibodies binding specifically to antigens in biological tissues. IHC takes its name from the roots "immuno", in reference to antibodies used in the procedure, and "histo", meaning tissue. Albert Coons conceptualized and first implemented the procedure in 1941.

Cetuximab, sold under the brand name Erbitux, is an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor medication used for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer and head and neck cancer. Cetuximab is a chimeric (mouse/human) monoclonal antibody given by intravenous infusion.

The epidermal growth factor receptor is a transmembrane protein that is a receptor for members of the epidermal growth factor family of extracellular protein ligands.

Targeted therapy or molecularly targeted therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment (pharmacotherapy) for cancer, others being hormonal therapy and cytotoxic chemotherapy. As a form of molecular medicine, targeted therapy blocks the growth of cancer cells by interfering with specific targeted molecules needed for carcinogenesis and tumor growth, rather than by simply interfering with all rapidly dividing cells. Because most agents for targeted therapy are biopharmaceuticals, the term biologic therapy is sometimes synonymous with targeted therapy when used in the context of cancer therapy. However, the modalities can be combined; antibody-drug conjugates combine biologic and cytotoxic mechanisms into one targeted therapy.
Panitumumab, sold under the brand name Vectibix, is a fully human monoclonal antibody specific to the epidermal growth factor receptor.

Pertuzumab, sold under the brand name Perjeta, is a monoclonal antibody used in combination with trastuzumab and docetaxel for the treatment of metastatic HER2-positive breast cancer; it also used in the same combination as a neoadjuvant in early HER2-positive breast cancer.
Matuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody for the treatment of cancer. It binds to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) with high affinity. The mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb425) from which matuzumab was developed at the Wistar Institute in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Nimotuzumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that as of 2014 had orphan status in the US and EU for glioma, and marketing approval in India, China, and other countries for squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck, and was undergoing several clinical trials.
Zalutumumab is a fully human IgG1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) directed towards the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR). It is a product developed by Genmab in Utrecht, the Netherlands. Specifically, zalutumumab is designed for the treatment of squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (SCCHN), a type of cancer.
The ErbB family of proteins contains four receptor tyrosine kinases, structurally related to the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), its first discovered member. In humans, the family includes Her1, Her2 (ErbB2), Her3 (ErbB3), and Her4 (ErbB4). The gene symbol, ErbB, is derived from the name of a viral oncogene to which these receptors are homologous: erythroblastic leukemia viral oncogene. Insufficient ErbB signaling in humans is associated with the development of neurodegenerative diseases, such as multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease, while excessive ErbB signaling is associated with the development of a wide variety of types of solid tumor.

Ira Pastan is an American scientist at the National Cancer Institute. He is a member of the National Academy of Sciences, a Fellow of the AAAS and the American Society of Microbiology. In 2009, he was awarded the prestigious International Antonio Feltrinelli Prize for Medicine. His wife, Linda Pastan, was an American poet.
A bispecific monoclonal antibody is an artificial protein that can simultaneously bind to two different types of antigen or two different epitopes on the same antigen. Naturally occurring antibodies typically only target one antigen. BsAbs can be manufactured in several structural formats. BsAbs can be designed to recruit and activate immune cells, to interfere with receptor signaling and inactivate signaling ligands, and to force association of protein complexes. BsAbs have been explored for cancer immunotherapy, drug delivery, and Alzeimer's disease.

John Mendelsohn was a president of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston. He was an internationally recognized leader in cancer research.
A rabbit hybridoma is a hybrid cell line formed by the fusion of an antibody producing rabbit B cell with a cancerous B-cell (myeloma).
Dalotuzumab is an anti-IGF1 receptor (IGF1R) humanized monoclonal antibody designed for the potential treatment of various cancers. Common adverse effects include hyperglycemia, nausea, vomiting, and fatigue. Dalotuzumab was developed by Merck and Co., Inc.
Amivantamab, sold under the brand name Rybrevant, is a bispecific monoclonal antibody used to treat non-small cell lung cancer. Amivantamab is a bispecific epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-directed and mesenchymal–epithelial transition (MET) receptor-directed antibody. It is the first treatment for adults with non-small cell lung cancer whose tumors have specific types of genetic mutations: epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations.
Passive antibody therapy, also called serum therapy, is a subtype of passive immunotherapy that administers antibodies to target and kill pathogens or cancer cells. It is designed to draw support from foreign antibodies that are donated from a person, extracted from animals, or made in the laboratory to elicit an immune response instead of relying on the innate immune system to fight disease. It has a long history from the 18th century for treating infectious diseases and is now a common cancer treatment. The mechanism of actions include: antagonistic and agonistic reaction, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).
Oligoclonal antibodies are an emerging immunological treatment relying on the combinatory use of several monoclonal antibodies (mAb) in one single drug. The composition can be made of mAb targeting different epitopes of a same protein (homo-combination) or mAb targeting different proteins (hetero-combination). It mimicks the natural polyclonal humoral immunological response to get better efficiency of the treatment. This strategy is most efficient in infections and in cancer treatment as it allow to overcome acquired resistance by pathogens and the plasticity of cancers.









